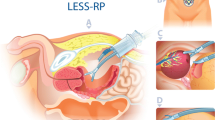
Abstract
To summarize surgical experiences with a new modified technique involving extraperitoneal single-incision robot-assisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy based on Da Vinci SI system by reviewing case data, including follow ups, and to evaluate the safety and clinical efficacy of the surgical procedure. The case data from December 2020 to September 2022 of 321 patients undergoing modified single incision (without dedicated PORT) robotic-assisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy via an extraperitoneal approach were reviewed. All procedures were performed by the same surgeon at our center. Perioperative data and postoperative urinary control, tumor control, and erectile function recovery were assessed. The immediate, 3-months, 6-months, 12-months, 18-months and 24-months complete urinary control rates were 34.3%, 56.6%, 79.7%, 85.7%, 89.6% and 90.7%, respectively; the 3-months, 6-months, 12-months, 18-months and 24-months biochemical recurrence rates were 3.4%, 5.2%, 9.1%, 21.7% and 30.2%, respectively; and for those with normal preoperative erectile function, the 3-months, 6-months, 12-months, 18-months and 24-months postoperative erectile function recovery rates were 52.2%, 60.0%, 70.7%, 72.2% and 73.9%, respectively. The new modified technique involving extraperitoneal single-incision robotic-assisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy is safe and feasible. This technique has satisfactory surgical results, and this new method results in satisfactory urinary control, tumor control and recovery of erectile function. In addition, this new method is not limited to specific dedicated access devices, which facilitates its application.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All the data and material are from patient examination and analysis at Sichuan Academy of Medical Sciences and Sichuan Provincial People’s Hospital, and the information is real, credible and available.
References
Stitzenberg KB, Wong YN, Nielsen ME, Egleston BL, Uzzo RG (2012) Trends in radical prostatectomy: centralization, robotics, and access to urologic cancer care. Cancer 118(1):54–62. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.26274. (Epub 2011/07/01)
Ulmer WD, Prasad SM, Kowalczyk KJ, Gu X, Dodgion C, Lipsitz S et al (2012) Factors associated with the adoption of minimally invasive radical prostatectomy in the United States. J Urol 188(3):775–780. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.juro.2012.05.014. (Epub 2012/07/24)
Kaouk JH, Goel RK, Haber GP, Crouzet S, Stein RJ (2009) Robotic single-port transumbilical surgery in humans: initial report. BJU Int 103(3):366–369. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1464-410X.2008.07949.x. (Epub 2008/09/10)
Kaouk JH, Haber GP, Autorino R, Crouzet S, Ouzzane A, Flamand V et al (2014) A novel robotic system for single-port urologic surgery: first clinical investigation. Eur Urol 66(6):1033–1043. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2014.06.039. (Epub 2014/07/22)
Kallidonis P, Rai BP, Qazi H, Ganzer R, Do M, Dietel A et al (2017) Critical appraisal of literature comparing minimally invasive extraperitoneal and transperitoneal radical prostatectomy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Arab J Urol 15(4):267–279. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aju.2017.07.003. (Epub 2017/12/14)
Zheng CW (2019) The intersection of technological advantages and innovative ideas-professor Ren Shancheng on single-port robotic day surgery for prostate cancer. China Med News 34(17):23. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1000-8039.2019.17.023. (Epub 2019/10/29)
Hinojosa-Gonzalez DE, Roblesgil-Medrano A, Torres-Martinez M, Alanis-Garza C, Estrada-Mendizabal RJ, Gonzalez-Bonilla EA et al (2022) Single-port versus multiport robotic-assisted radical prostatectomy: a systematic review and meta-analysis on the Da Vinci Sp platform. Prostate 82(4):405–414. https://doi.org/10.1002/pros.24296. (Epub 2022/01/06)
Ren SQ, Wei Y, Wang YQ, Ou Y, Wang Q, Feng HL et al (2021) Comparison of single incision robot-assisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy with and without extraperitoneal special channel device. Natl Med J China 101(40):3345–3350. https://doi.org/10.3760/cma.j.cn112137-20210303-00545. (Epub 2021/03/03)
Lo IS, Lee HY, Chou YH, Huang CN, Wu WJ, Yeh HC et al (2018) Robot-assisted extraperitoneal radical prostatectomy, single site plus two model. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech Part A 28(2):140–144. https://doi.org/10.1089/lap.2017.0421. (Epub 2017/11/02)
Khalil MI, Joseph JV (2021) Extraperitoneal single-port robot-assisted radical prostatectomy. J Endourol 35(S2):S100-s1005. https://doi.org/10.1089/end.2021.0440. (Epub 2021/09/10)
Wang LH, Wu ZJ, Zhu QY (2020) Development and prospect of urological laparo-endoscopic single-site surgery in China. Chin J Urol 41(11):807–810. https://doi.org/10.3760/cma.j.cn112330-20200925-00684
Lai A, Dobbs RW, Talamini S, Halgrimson WR, Wilson JO, Vigneswaran HT et al (2020) Single port robotic radical prostatectomy: a systematic review. Transl Androl Urol 9(2):898–905. https://doi.org/10.21037/tau.2019.11.05. (Epub 2020/05/19)
Kaouk J, Aminsharifi A, Wilson CA, Sawczyn G, Garisto J, Francavilla S et al (2020) Extraperitoneal versus transperitoneal single port robotic radical prostatectomy: a comparative analysis of perioperative outcomes. J Urol 203(6):1135–1140. https://doi.org/10.1097/ju.0000000000000700. (Epub 2019/12/18)
Agarwal DK, Sharma V, Toussi A, Viers BR, Tollefson MK, Gettman MT et al (2020) Initial experience with Da Vinci single-port robot-assisted radical prostatectomies. Eur Urol 77(3):373–379. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2019.04.001. (Epub 2019/04/24)
Checcucci E, De Cillis S, Pecoraro A, Peretti D, Volpi G, Amparore D et al (2020) Single-port robot-assisted radical prostatectomy: a systematic review and pooled analysis of the preliminary experiences. BJU Int 126(1):55–64. https://doi.org/10.1111/bju.15069. (Epub 2020/04/06)
Li K, Yu X, Yang X et al (2022) Perioperative and oncologic outcomes of single-port vs multiport robot-assisted radical prostatectomy: a meta-analysis. J Endourol 36(1):83–98. https://doi.org/10.1089/end.2021.0210
Du W, Xu WD, Yang Y, Chang YF, Lu XJ, Xiao YT et al (2020) Single-port robot-assisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy through different approaches: initial experience and outcomes. Chin J Urol 41(11):815–819. https://doi.org/10.3760/cma.j.cn112330-20200909-00657. (Epub 2020/09/09)
Ng CF, Teoh JY, Chiu PK, Yee CH, Chan CK, Hou SS et al (2019) Robot-assisted single-port radical prostatectomy: a phase 1 clinical study. Int J Urol 26(9):878–883. https://doi.org/10.1111/iju.14044. (Epub 2019/07/02)
Thompson JE, Egger S, Böhm M, Siriwardana AR, Haynes AM, Matthews J et al (2018) Superior biochemical recurrence and long-term quality-of-life outcomes are achievable with robotic radical prostatectomy after a long learning curve-updated analysis of a prospective single-surgeon cohort of 2206 consecutive cases. Eur Urol 73(5):664–671. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2017.11.035. (Epub 2017/12/24)
Ren SQ, Lyu Q, Chen ZJ, Fan SD, Zhou F, Nie Y et al (2020) The experience of suprapubic extraperitoneal single-port robot-assisted radical prostatectomy. Chin J Urol 41(10):784–785. https://doi.org/10.3760/cma.j.cn112330-20200204-00063. (Epub 2020/06/30)
Lyu Q, Wei Y, Wang YQ, Ou Y, Wang Q, Feng HL et al (2021) The modified single incision robot-assisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy: initial experience and clinical efficiency. Chin J Urol 42(11):830–833. https://doi.org/10.3760/cma.j.cn112330-20210303-00113. (Epub 2021/03/03)
Shangqing R, Yong O, Yaoqian W, Dong W (2022) Establishment of the operative pathway in single incisional robot-assisted radical prostatectomy without dedicated extraperitoneal access devices. Asian J Surg 45(8):1584–1586. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asjsur.2022.03.031. (Epub 2022/03/26)
Yang CW, Wang HH, Hassouna MF, Chand M, Huang WJS, Chung HJ (2021) Prediction of a positive surgical margin and biochemical recurrence after robot-assisted radical prostatectomy. Sci Rep 11(1):14329. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-93860-y. (Published 2021 Jul 12)
Acknowledgements
I would like to express my gratitude to Shangqing Ren, who provided me with valuable guidance for this article.
Funding
Funding program: Key research and development projects of Sichuan Science and Technology Department (2022YFS0135). Funding program: General program of Medical Engineering Cross of Sichuan Provincial People’s Hospital & University of Electronic Science and Technology of China (ZYGX2021YGLH011). Funding program: Key research and development projects of Sichuan Science and Technology Department (23ZDYF2070). Funding program: Popular application project of Cadre Health Commission of Sichuan Province (SCR2023-210).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Data curation, YW and XL; Investigation, YO and JY; Project administration, SR; Resources, YW and KW; Supervision, DW; writing—original draft, CL and BY; Writing—review and editing, CL, BY, DW and SR.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Institutional review board statement and informed consent statement
This article has been approved by the medical ethics committee of Sichuan Provincial People’s Hospital, and all the included patients signed the informed consent form. We declare that the scientific research of this study did not involve confidential patient information.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Luo, C., Yang, B., Ou, Y. et al. Experience with an innovative surgical approach: 321 cases modified extraperitoneal single-incision robot-assisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy without dedicated PORT based on Da Vinci SI system. J Robotic Surg 17, 1659–1667 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11701-023-01576-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11701-023-01576-0