Abstract
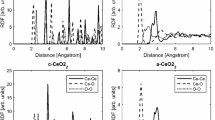
Over the last few decades, despite significant advancements in oxide-based ReRAM (resistive random-access memory) devices, science and technology have faced many obstacles, notably, those relating to data, conducting filament rupture and device uniformity issues. The density functional theory technique based on the first-principles calculations is used to calculate structural, electronic and magnetic properties of pure CeO2, CeO2 + VO, Ce1-xTmxO2 + VO (Tm = Co, Ni). The effect of oxygen vacancy and transition metal doping on the electronic structures is investigated using generalized gradient approximation developed by Perdew, Burke and Ernzerhof. The role of oxygen vacancies has been evaluated in this study as they play an important role in the development as well as rapturing of conducting filaments. Pristine ceria (CeO2) has more structural stability compared to compounds with oxygen vacancies and transition metal doping. It is evident from energy band structures that additional states developed in CeO2 + VO and Ce1-xTmxO2 + VO (Tm = Co, Ni) compared to CeO2. These additional states result in enhanced conductivity of these compounds. From magnetic properties, we can explain that Ce1-xCoxO2 + VO have the highest magnetic moments compared to other compounds. CeO2 can be used effectively in various technological applications like catalysts, medicine, solar reactors, cosmetics, data storage, optics and energy storage applications, but here we are only interested in data storage (memory) applications.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data will be made available on suitable request.
Reference
Abbas Z, Fatima K, Abubakr M, Gorczyca I, Alshahrani T, Muhammad S, Al-Sehemi AG (2022a) A DFT+ U study of the effect of transition metal replacements on optoelectronic and elastic properties of TmCu3S4 (Tm = V, Ta, Nb). Optik 250:168289
Abbas Z, Fatima K, Gorczyca I, Irfan M, Alotaibi N, Alshahrani T, Raza HH, Muhammad S (2022b) Proposition of new stable rare-earth ternary semiconductor sulfides of type LaTlS2 (La = Er, Eu, Tb): Ab-initio study and prospects for optoelectronic, spintronic and thermoelectric applications. Mater Sci Semicond Process 146:106662
Alaydrus M, Sakaue M, Aspera SM, Wungu TD, Linh TP, Kasai H, Ishihara T, Mohri T (2013) A first-principles study on defect association and oxygen ion migration of Sm3+ and Gd3+ co-doped ceria. J Phys Condens Matter 25(22):225401
Alaydrus M, Sakaue M, Kasai H (2016) A DFT+ U study on the contribution of 4f electrons to oxygen vacancy formation and migration in Ln-doped CeO 2. Phys Chem Chem Phys 18(18):12938–12946
Ali A, Raza R, Khalil RA, Ahmad MA, Rafique A, UllahurRehman, Mushtaq, Belova MKAMNLM (2018) A potential electrolyte (Ce1-x CaxO2-δ) for fuel cells: theoretical and experimental study. Ceram Int 44(11):12676–12683
Bach TP-A, Jaffery SHA, Nguyen DC, Ali A, Hussain S, Hussain M, Seo Y, Jung J (2022) Schottky barrier height modulation and photoconductivity in a vertical graphene/ReSe2 vdW pn heterojunction barristor. J Market Res 17:2796–2806
Baek I, Lee M, Seo S, Lee M, Seo D, Suh D-S, Park J, Park S, Kim H, Yoo I (2004) Highly scalable nonvolatile resistive memory using simple binary oxide driven by asymmetric unipolar voltage pulses. In: IEDM technical digest. IEEE International electron devices meeting, IEEE, p 587-590
Bernal S, Calvino JJ, Gatica JM, Cartes CL, Pintado JM (2002) Chemical and nanostructural aspects of the preparation and characterisation of ceria and ceria-based mixed oxide-supported metal catalysts. In: Catalysis by ceria and related materials. World Scientific. p 85-168
Bersuker G, Gilmer D, Veksler D, Kirsch P, Vandelli L, Padovani A, Larcher L, McKenna K, Shluger A, Iglesias V (2011) Metal oxide resistive memory switching mechanism based on conductive filament properties. J Appl Phys 110(12):124518
Borghetti J, Strukov DB, Pickett MD, Yang JJ, Stewart DR, Williams RS (2009) Electrical transport and thermometry of electroformed titanium dioxide memristive switches. J Appl Phys 106(12):124504
Chen Y, Chen B, Gao B, Liu L, Liu X, Kang J (2013) Well controlled multiple resistive switching states in the Al local doped HfO2 resistive random access memory device. J Appl Phys 113(16):164507
Dearnaley G, Stoneham A, Morgan D (1970) Electrical phenomena in amorphous oxide films. Rep Prog Phys 33(3):1129
Esch F, Fabris S, Zhou L, Montini T, Africh C, Fornasiero P, Comelli G, Rosei R (2005) Electron localization determines defect formation on ceria substrates. Science 309(5735):752–755
Fatima K, Abbas Z, Naz A, Alshahrani T, Chaib Y, Jaffery SHA, Muhammad S, Hussain S, Jung J, Algarni H (2022) Shedding light on the structural, optoelectronic, and thermoelectric properties of pyrochlore oxides (La2Q2O7 (Q= Ge, Sn)) for energy applications: a first-principles investigation. J Solid State Chem 313:123305
Gale E (2014) TiO2-based memristors and ReRAM: materials, mechanisms and models (a review). Semicond Sci Technol 29(10):104004
Guo Z, Sa B, Zhou J, Sun Z (2013) Role of oxygen vacancies in the resistive switching of SrZrO3 for resistance random access memory. J Alloy Compd 580:148–151
Guo T, Tan T, Liu Z (2015) Resistive switching behavior of HfO2 film with different Ti doping concentrations. J Phys D Appl Phys 49(4):045103
Hickmott T (1964) Impurity conduction and negative resistance in thin oxide films. J Appl Phys 35(7):2118–2122
Inaba H, Tagawa H (1996) Ceria-based solid electrolytes. Solid State Ionics 83(1–2):1–16
Ismail M, Ahmed E, Rana A, Hussain F, Talib I, Nadeem M, Panda D, Shah N (2016) Improved endurance and resistive switching stability in ceria thin films due to charge transfer ability of Al dopant. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8(9):6127–6136
Kwon D, Kim K, Jang J, Jeon J, Lee M, Kim GH, Li X-S, Park GS, Lee B, Han S, Kim M, Hwang CS (2010) Atomic structure of conducting nanofilaments in TiO2 resistive switching memory. Nat Nanotechnol 5:148–153
Liu Q, Sun J, Lv H, Long S, Yin K, Wan N, Li Y, Sun L, Liu M (2012) Real-time observation on dynamic growth/dissolution of conductive filaments in oxide-electrolyte-based ReRAM. Adv Mater 24(14):1844–1849
Liu Y, Fan L, Cai Y, Zhang W, Wang B, Zhu B (2017) Superionic conductivity of Sm3+, Pr3+, and Nd3+ triple-doped ceria through bulk and surface two-step doping approach. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9(28):23614–23623
Liu X, Lin S, Gao J, Shi H, Kim S-G, Chen Z, Lee H (2021) Enhanced performance of Mo 2 P monolayer as lithium-ion battery anode materials by carbon and nitrogen doping: a first principles study. Phys Chem Chem Phys 23(6):4030–4038
Liu Q, Liu M, Wang Y, Lv H, Long S, Wang W (2011). Doping technology: an effective way to improve the performances of resistive switching memory. In 11th International workshop on junction technology (IWJT). 80–83. IEEE
Luo X, Morrin A, Killard AJ, Smyth MR (2006) Application of nanoparticles in electrochemical sensors and biosensors. Electroanal Int j Devoted Fundam Pract Aspects Electroanal 18(4):319–326
Nolan M, Grigoleit S, Sayle DC, Parker SC, Watson GW (2005) Density functional theory studies of the structure and electronic structure of pure and defective low index surfaces of ceria. Surf Sci 576(1–3):217–229
Nolan M, Fearon JE, Watson GW (2006) Oxygen vacancy formation and migration in ceria. Solid State Ionics 177(35–36):3069–3074
Pan T-M, Lu C-H (2011) Forming-free resistive switching behavior in Nd2O3, Dy2O3, and Er2O3 films fabricated in full room temperature. Appl Phys Lett 99(11):113509
Penn SG, He L, Natan MJ (2003) Nanoparticles for bioanalysis. Curr Opin Chem Biol 7(5):609–615
Perdew JP, Burke K, Ernzerhof M (1997) Generalized gradient approximation made simple [Phys Rev Lett 77, 3865 (1996)]. Phys Rev Lett 78(7):1396–1396
Plata JJ, Márquez AM, Sanz JF (2012) Communication: Improving the density functional theory+ U description of CeO2 by including the contribution of the O 2 p electrons. J Chem Phys 136(4):041101
Qi L, Shibing L, Weihua G, Sen Z, Ming L, Junning C (2009) Unipolar resistive switching of Au+-implanted ZrO2 films. J Semicond 30(4):042001
Rana AM, Akbar T, Ismail M, Ahmad E, Hussain F, Talib I, Imran M, Mehmood K, Iqbal K, Nadeem MY (2017) Endurance and cycle-to-cycle uniformity improvement in tri-layered CeO2/Ti/CeO2 resistive switching devices by changing top electrode material. Sci Rep 7(1):39539
Schmitt R, Spring J, Korobko R, Rupp JL (2017) Design of oxygen vacancy configuration for memristive systems. ACS Nano 11(9):8881–8891
Shang D-S, Sun J-R, Shen B-G, Matthias W (2013) Resistance switching in oxides with inhomogeneous conductivity. Chin Phys B 22(6):067202
Tan T, Guo T, Liu Z (2014) Au doping effects in HfO2-based resistive switching memory. J Alloy Compd 610:388–391
Tran F, Blaha P (2009) Accurate band gaps of semiconductors and insulators with a semilocal exchange-correlation potential. Phys Rev Lett 102(22):226401
Vanpoucke DE, Bultinck P, Cottenier S, Van Speybroeck V, Van Driessche I (2014) Aliovalent doping of CeO2: DFT study of oxidation state and vacancy effects. J Mater Chem A 2(33):13723–13737
Wei X, Pan W, Cheng L, Li B (2009) Atomistic calculation of association energy in doped ceria. Solid State Ionics 180(1):13–17
Wu J, McCreery RL (2008) Solid-state electrochemistry in molecule/TiO2 molecular heterojunctions as the basis of the TiO2 Memristor. J Electrochem Soc 156(1):P29
Xie H, Liu Q, Li Y, Lv H, Wang M, Liu X, Sun H, Yang X, Long S, Liu S (2012) Nitrogen-induced improvement of resistive switching uniformity in a HfO2-based RRAM device. Semicond Sci Technol 27(12):125008
Yahiro H, Eguchi K, Arai H (1989) Electrical properties and reducibilities of ceria-rare earth oxide systems and their application to solid oxide fuel cell. Solid State Ionics 36(1–2):71–75
Yang JJ, Miao F, Pickett MD, Ohlberg DA, Stewart DR, Lau CN, Williams RS (2009) The mechanism of electroforming of metal oxide memristive switches. Nanotechnology 20(21):215201
Yildirim H, Pachter R (2019) Extrinsic dopant effects on oxygen vacancy formation energies in ZrO2 with implication for memristive device performance. ACS Appl Electron Mater 1(4):467–477
Zhang H, Liu L, Gao B, Qiu Y, Liu X, Lu J, Han R, Kang J, Yu B (2011) Gd-doping effect on performance of HfO2 based resistive switching memory devices using implantation approach. Appl Phys Lett 98(4):042105
Zhao H, Tu H, Wei F, Zhang X, Xiong Y, Du J (2013) The enhancement of unipolar resistive switching behavior via an amorphous TiOx layer formation in Dy2O3-based forming-free RRAM. Solid-State Electron 89:12–16
Zhou M, Zhao Q, Zhang W, Liu Q, Dai Y (2012a) The conductive path in HfO2: first principles study. J Semicond 33(7):07200
Zhou M, Zhao Q, Zhang W, Liu Q, Dai Y (2012b) The conductive path in HfO2: first principles study. J Semicond 33(7):072002
Acknowledgements
The authors extend their appreciation to the Research Center for Advanced Materials Science at King Khalid University for funding the work under grant number RCAMS/KKU/027-23.
Funding
Research Center for Advanced Materials Science, King Khalid University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SHM contributed to study design and writing—original draft; SA contributed to acquisition of data and software; ZA contributed to supervision, data interpretation and conception.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Mirza, S.H., Azam, S., Abbas, Z. et al. Enlightening the impact of TM doping on structural, electronic and magnetic properties of ceria for ReRAM applications: a GGA + U study. Chem. Pap. 77, 5481–5494 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-023-02879-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-023-02879-0