Abstract
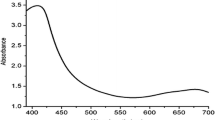
Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles has been studied using a variety of plant extracts for biomedical applications in cancer nanomedicine. Silver nanoparticles were synthesized using Capparis Moonii (CM) fruit extract as reducing agent. Intense surface plasmon resonance (SPR) absorption peaks at 404–420 nm in the UV–visible spectrum appeared to indicate the formation of AgNPs. The function of Capparis Moonii fruit extract as a reducing and capping agent was confirmed by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR). The morphology of the produced nanoparticles was determined using scanning electron microscopy and they exhibit a spherical shape with a size range of 10–20 nm, according to high-resolution transmission electron microscopy. Energy-dispersive X-ray analysis (EDX) demonstrated that silver is present in the silver nanoparticles at a percentage of 56.91% by atom. To determine the surface charge of AgNPs formed during biosynthesis, the zeta potential measurement was carried out. The lack of cytotoxicity to blood erythrocytes and normal human fibroblasts cell lines confirms the blood biocompatibility and cell compatibility of the synthesized AgNPs. The synthesized AgNPs are cytotoxic to breast cancer (MCF-7), lung cancer (A549), pancreatic cancer (PANC-1) and skin cancer (A431) cell lines with IC50 values of 12.06, 24.87, 26.49 and 84.57 µg/mL, respectively. The synthesized silver nanoparticles show excellent photocatalytic activity on the degradation of rose bengal (RB) and methylene blue (MB). By observing the breakdown of RB and MB under direct sunlight radiation, the photocatalytic activity of the synthesized AgNPs was evaluated. At pH-2, 100% photocatalytic degradation of RB was completed in 60 min, whereas at pH-8, 96% photocatalytic degradation of MB was completed in 240 min.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aarthi T, Madras G (2007) Photocatalytic degradation of rhodamine dyes with nano-TiO2. Ind Eng Chem Res 46:7–14. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie060948n
Alahmad FA, Bigall NC, Rusch P, Scheper T, Walter JG (2021) Hypericumperforatum L-mediated green synthesis of silver nanoparticles exhibiting antioxidant and anticancer activities. Nanomaterials 11:487. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11020487
Ali M, Ikram M, Ijaz M, Ul-Hamid A, Avais M, Anjum AA (2020) Green synthesis and evaluation of n-type ZnO nanoparticles doped with plant extract for use as alternative antibacterials. Appl Nanosci 10:3787–3803. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-020-01451-6
Anthony P, Murugan M, Jeyaraj M, Rathinam K, Sangiliyandi G (2014) Synthesis of silver nanoparticles using pine mushroom extract: a potential antimicrobial agent against E. coli and B. subtilis. J Ind Eng Chem 20:2325–2331. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2013.10.008
Arvizo RR, Bhattacharyya S, Kudgus RA, Giri K, Bhattacharya R, Mukherjee P (2012) Intrinsic therapeutic applications of noble metal nanoparticles: past, present and future. Chem Soc Rev 41:2943–2970. https://doi.org/10.1039/C2CS15355F
AshaRani PV, Low KahMun G, Hande MP, Valiyaveettil S (2009) Cytotoxicity and genotoxicity of silver nanoparticles in human cells. ACS Nano 3:279–290. https://doi.org/10.1021/nn800596w
Baker J, Ajani J, Scotté F, Winther D, Martin M, Aapro MS, Minckwitz G (2009) Docetaxel-related side effects and their management. Eur J Oncol Nurs 13:49–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejon.2008.10.003
Balashanmugam P, Kalaichelvan PT (2015) Biosynthesis characterization of silver nanoparticles using Cassia roxburghii DC aqueous extract and coated on cotton cloth for effective antibacterial activity. Int J Nanomed 10:87. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S79984
Bandala ER, Stanisic D, Tasic L (2020) Biogenic nanomaterials for photocatalytic degradation and water disinfection: a review environmentalscience. Water Res Technol 6(12):3195–3213. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0EW00705F
Bapat MS, Singh H, Shukla SK, Singh PP, Vo VN, Yadav A, Kumar D (2022) Evaluating green silver nanoparticles as prospective biopesticides: an environmental standpoint. Chemosphere 286:131761. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.131761
Belteky P, Ronavari A, Zakupszky D, Boka E, Igaz N, Szerencses B, Konya Z (2021) Are smaller nanoparticles always better? Understanding the biological effect of size-dependent silver nanoparticle aggregation under biorelevant conditions. Int J Nanomed 16:3021. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S304138
Bhakya S, Muthukrishnan S, Sukumaran M, Grijalva M, Cumbal L, Benjamin JF, Rao MV (2016) Antimicrobial, antioxidant and anticancer activity of biogenic silver nanoparticles–an experimental report. RSC Adv 6:81436–81446. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6RA17569D
Botto C, Mauro N, Amore E, Martorana E, Giammona G, Bondì ML (2017) Surfactant effect on the physicochemical characteristics of cationic solid lipid nanoparticles. Int J Pharm 516:334–341. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2016.11.052
Cao J, Huang D, Peppas NA (2020) Advanced engineered nanoparticulate platforms to address key biological barriers for delivering chemotherapeutic agents to target sites. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 167:170–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2020.06.030
Chan SS, WuYeong T, Juan JC, Teh CY (2011) Recent developments of metal oxide semiconductors as photocatalysts in advanced oxidation processes (AOPs) for treatment of dye waste-water. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 86:1130–1158. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.2636
Chen D, Qiao X, Qiu X, Chen J (2009) Synthesis and electrical properties of uniform silver nanoparticles for electronic applications. J Mater Sci 44:1076–1081. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-008-3204-y
Chen LQ, Fang L, Ling J, Ding CZ, Kang B, Huang CZ (2015) Nanotoxicity of silver nanoparticles to red blood cells: size dependent adsorption, uptake, and hemolytic activity. Chem Res Toxicol 28:501–509. https://doi.org/10.1021/tx500479m
Creighton JA, Blatchford CG, Albrecht MG (1979) Plasma resonance enhancement of Raman scattering by pyridine adsorbed on silver or gold sol particles of size comparable to the excitation wavelength. J Chem Soc Faraday Transac2 Mol Chem Phys 75:790–798. https://doi.org/10.1039/F29797500790
Deirram N, Zhang C, Kermaniyan S, Johnston AP, Such GK (2019) pH-responsive polymer nanoparticles for drug delivery. Macromol Rapid Commun 40:1800917. https://doi.org/10.1002/marc.201800917
DeLong RK, Reynolds CM, Malcolm Y, Schaeffer A, Severs T, Wanekaya A (2010) Functionalized gold nanoparticles for the binding, stabilization, and delivery of therapeutic DNA, RNA, and other biological macromolecules. Nanotechnol Sci Appl 3:53
Deng XY, Chen Z (2004) Preparation of nano-NiO by ammonia precipitation and reaction in solution and competitive balance. Mater Lett 58:276–280. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-577X(03)00469-5
Desalegn T, Ravikumar CR, Murthy HC (2021) Eco-friendly synthesis of silver nanostructures using medicinal plant Vernoniaamygdalina Del. leaf extract for multifunctional applications. Appl Nanosci 11:535–551. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-020-01620-7
Douglas T, Strable E, Willits D, Aitouchen A, Libera M, Young M (2002) Protein engineering of a viral cage for constrained nanomaterials synthesis. Adv Mater 14:415–418. https://doi.org/10.1002/1521-4095
Gomathi AC, Rajarathinam SX, Sadiq AM, Rajeshkumar S (2020) Anticancer activity of silver nanoparticles synthesized using aqueous fruit shell extract of Tamarindus indica on MCF-7 human breast cancer cell line. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol 55:101376. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jddst.2019.101376
Gopalakrishnan V, Muniraj S (2021) Neem flower extract assisted green synthesis of copper nanoparticles–optimisation, characterisation and anti-bacterial study. Mater Today Proc 36:832–836. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.07.013
Graczyk A, Pawlowska R, Jedrzejczyk D, Chworos A (2020) Gold nanoparticles in conjunction with nucleic acids as a modern molecular system for cellular delivery. Molecules 25:204. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25010204
Gutierrez M, Henglein A (1993) Formation of colloidal silver by push-pull reduction of silver (1+). J Phys Chem 97:11368–11370. https://doi.org/10.1021/j100146a003
Hasan I, Khan RA, Alharbi W, Alharbi KH, Khanjer MA, Alslame A (2020) Synthesis, characterization and photo-catalytic activity of guar-gum-g-aliginate@ silver bionanocomposite material. RSC Adv 10:7898–7911. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0RA00163E
Hernandez P, Santiago-Cuevas A, Palacios-Cabrera C, Thangarasu P, Narayanan J, Kaur H, Sharma A (2022) Development and applications of Ru and Ce based iron oxides as photocatalysts. Mater Lett 313:131720. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2022.131720
Hu X, Wu L, Du M, Wang L (2022) Eco-friendly synthesis of size-controlled silver nanoparticles by using Areca catechu nut aqueous extract and investigation of their potent antioxidant and anti-bacterial activities. Arab J Chem 15:103763. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2022.103763
Huang YF, Chang HT, Tan W (2008) Cancer cell targeting using multiple aptamers conjugated on nanorods. Anal chem 80:567–572. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2022.131720
Hutchison JE (2008) Greener nanoscience: a proactive approach to advancing applications and reducing implications of nanotechnology. ACS Nano 2:395–402. https://doi.org/10.1021/nn800131j
Jadhav K, Deore S, Dhamecha D, Hr R, Jagwani S, Jalalpure S, Bohara R (2018) Phytosynthesis of silver nanoparticles: characterization, biocompatibility studies, and anticancer activity. ACS Biomater Sci Eng 4:892–899. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsbiomaterials.7b00707
Jaffri SB, Ahmad KS (2020) Biomimetic detoxifier PrunuscerasiferaEhrh silver nanoparticles: innate green bullets for morbific pathogens and persistent pollutants. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:9669–9685. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-07626-6
Joseph S, Mathew B (2015) Microwave-assisted green synthesis of silver nanoparticles and the study on catalytic activity in the degradation of dyes. J Mol Liq. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2015.01.027
Kakkar S, Harjani B, Ledwani N, Ledwani L (2020) Synthesis, characterization, and application of biogenic nanomaterials: an overview. Nanotechnol Energy Environ Eng. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-33774-2
Kalyane D, Raval N, Maheshwari R, Tambe V, Kalia K, Tekade RK (2019) Employment of enhanced permeability and retention effect (EPR): nanoparticle-based precision tools for targeting of therapeutic and diagnostic agent in cancer. Mater Sci Eng, C 98:1252–1276. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2019.01.066
Kasthuri J, Veerapandian S, Rajendiran N (2009) Biological synthesis of silver and gold nanoparticles using apiin as reducing agent. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 68:55–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2008.09.021
Kumar KV, Ramamurthi V, Sivanesan S (2005) Modeling the mechanism involved during the sorption of methylene blue onto fly ash. J Colloid Interface Sci 284:14–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2004.09.063
Lee KX, Shameli K, Yew YP, Teow SY, Jahangirian H, Rafiee-Moghaddam R, Webster TJ (2020) Recent developments in the facile bio-synthesis of gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) and their biomedical applications. Int J Nanomed 15:275
Li X, Ouyang S, Kikugawa N, Ye J (2008) Novel Ag2ZnGeO4 photocatalyst for dye degradation under visible light irradiation. Appl Catal A General 334:51–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcata.2007.09.033
Link S, El-Sayed MA (2003) Optical properties and ultrafast dynamics of metallic nanocrystals. Annu Rev Phys Chem 54:331–366. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.physchem.54.011002.103759
Liu R, An Y, Jia W, Wang Y, Wu Y, Zhen Y, Gao H (2020) Macrophage-mimic shape changeable nanomedicine retained in tumor for multimodal therapy of breast cancer. J Contr Release 321:589–601. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.02.043
Lops C, Ancona A, Di Cesare K, Dumontel B, Garino N, Canavese G, Cauda V (2019) Sonophotocatalytic degradation mechanisms of Rhodamine B dye via radicals generation by micro-and nano-particles of ZnO. Appl Catal B Environ 243:629–640. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2018.10.078
Magudapathy P, Gangopadhyay P, Panigrahi BK, Nair GM, Dhara S (2001) Electrical transport studies of Ag nanoclusters embedded in glass matrix. Phys B: Condens Matter 299:142–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0921-4526(00)00580-9
Miri A, Sarani M, Bazaz MR, Darroudi M (2015) Plant-mediated biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using Prosopisfarcta extract and its antibacterial properties. Spectrochimicaacta Part A Mol Biomol Spectr 141:287–291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2015.01.024
Mirzajani F, Ghassempour A, Aliahmadi A, Esmaeili MA (2011) Antibacterial effect of silver nanoparticles on Staphylococcus aureus. Res Microbiol 162:542–549. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resmic.2011.04.009
Moharana A, Kumar A, Thakur A, Vo VN, Sharma A, Kumar D (2021) Role of nanostructured metal oxides in photocatalysis: an overview. Nanostruct Photocatal. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-823007-7.00010-9
Mohebbi H, Ebadzadeh T, Hesari FA (2008) Synthesis of nano-crystalline (Ni/NiO)–YSZ by microwave-assisted combustion synthesis method: the influence of pH of precursor solution. J Power Sour 178:64–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2007.12.054
Nadagouda MN, Speth TF, Varma RS (2011) Microwave-assisted green synthesis of silver nanostructures. Acc Chem Res 44:469–478. https://doi.org/10.1021/ar1001457
Noginov MA, Zhu G, Bahoura M, Adegoke J, Small CE, Ritzo BA, Shalaev VM (2006) Enhancement of surface plasmons in an Ag aggregate by optical gain in a dielectric medium. Opt Lett 31:3022–3024. https://doi.org/10.1364/OL.31.003022
Onyancha RB, Aigbe UO, Ukhurebor KE, Muchiri PW (2021) Facile synthesis and applications of carbon nanotubes in heavy-metal remediation and biomedical fields: a comprehensive review. J Mol Struct 1238:130462. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2021.130462
Ovais M, Khalil AT, Islam NU, Ahmad I, Ayaz M, Saravanan M, Mukherjee S (2018) Role of plant phytochemicals and microbial enzymes in biosynthesis of metallic nanoparticles. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 102(16):6799–6814. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-018-9146-7
Oves M, Aslam M, Rauf MA, Qayyum S, Qari HA, Khan MS, Ismail IM (2018) Antimicrobial and anticancer activities of silver nanoparticles synthesized from the root hair extract of Phoenix dactylifera. Mater Sci Eng C 89:429–443. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2018.03.035
Pradeep M, Kruszka D, Kachlicki P, Mondal D, Franklin G (2021) Uncovering the phytochemical basis and the mechanism of plant extract-mediated eco-friendly synthesis of silver nanoparticles using ultra-performance liquid chromatography coupled with a photodiode array and high-resolution mass spectrometry. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 10:562–571. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.1c06960
Pugazhendhi A, Prabhu R, Muruganantham K, Shanmuganathan R, Natarajan S (2019) Anticancer, antimicrobial and photocatalytic activities of green synthesized magnesium oxide nanoparticles (MgONPs) using aqueous extract of Sargassumwightii. J Photochem Photobiol B 190:86–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2018.11.014
Raghunandan D, Bedre MD, Basavaraja S, Sawle B, Manjunath SY, VenkataRaman A (2010) Rapid biosynthesis of irregular shaped gold nanoparticles from macerated aqueous extracellular dried clove buds (Syzygiumaromaticum) solution. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 79:235–240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2010.04.003
Raja K, Saravanakumar A, Vijayakumar R (2012) Efficient synthesis of silver nanoparticles from Prosopisjuliflora leaf extract and its antimicrobial activity using sewage. SpectrochimicaActa Part A Mol Biomol Spectr 97:490–494. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2012.06.038
Raveendran P, Fu J, Wallen SL (2003) Completely “green” synthesis and stabilization of metal nanoparticles. J Am Chem Soc 125:13940–13941. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja029267j
Robby AI, Kim SG, Jo HJ, Lee G, Lee HS, Lee KD, Park SY (2021) Tumor microenvironment-responsive touch sensor-based pH-triggered controllable conductive hydrogel. Appl Mater Today 25:101259. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apmt.2021.101259
Robinson T, McMullan G, Marchant R, Nigam P (2001) Remediation of dyes in textile effluent: a critical review on current treatment technologies with a proposed alternative. Bioresour Technol 77:247–255. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0960-8524(00)00080-8
Saif S, Tahir A, Chen Y (2016) Green synthesis of iron nanoparticles and their environmental applications and implications. Nanomaterials 6:209. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano6110209
Sankar R, Rahman PK, Varunkumar K, Anusha C, Kalaiarasi A, Shivashangari KS, Ravikumar V (2017) Facile synthesis of Curcuma longa tuber powder engineered metal nanoparticles for bioimaging applications. J Mol Struct 1129:8–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2016.09.054
Seal S, Jeyaranjan A, Neal CJ, Kumar U, Sakthivel TS, Sayle DC (2020) Engineered defects in cerium oxides: tuning chemical reactivity for biomedical, environmental, & energy applications. Nanoscale 12:6879–6899. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0NR01203C
Selvi KV, Sivakumar T (2012) Isolation and characterization of silver nanoparticles from Fusariumoxysporum. Int J Curr Microbiol Applsci 1:56–62
Shankaran DR, Miura N (2007) Recent progress and challenges in nanotechnology for biomedical applications: an insight into the analysis of neurotransmitters. Recent Patents on Nanotechnol 1:210–223. https://doi.org/10.2174/187221007782360484
Stavrovskaya AA (2000) Cellular mechanisms of multidrug resistance of tumor cells. Biochemistry C/c of Biokhimiia 65:95–106
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, Bray F (2021) Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA A Cancer J Clin 71:209–249. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21660
Tu W, Liu H (2000) Rapid synthesis of nanoscale colloidal metalclusters by microwave irradiation. J Mater Chem 10:2207–2211. https://doi.org/10.1039/B002232M
Vadivelan V, Kumar KV (2005) Equilibrium, kinetics, mechanism, and process design for the sorption of methylene blue onto rice husk. J Colloid Interface Sci 286:90–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2005.01.007
Weir HK, Thompson TD, Stewart SL, White MC (2021) Peer reviewed: cancer incidence projections in the United States between 2015 and 2050. Preventing Chronic Disease 18:E59. https://doi.org/10.5888/pcd18.210006
Yallappa S, Manjanna J, Peethambar SK, Rajeshwara AN, Satyanarayan ND (2013) Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Acacia farnesiana (Sweet Acacia) seed extract under microwave irradiation and their biological assessment. J Cluster Sci 24:1081–1092. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-013-0599-7
Zhan H, Zhou X, Cao Y, Jagtiani T, Chang TL, Liang JF (2017) Anti-cancer activity of camptothecinnanocrystals decorated by silver nanoparticles. J Mater Chem B 5:2692–2701. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7TB00134G
Acknowledgements
The work was financially supported by Karnataka DST-Ph.D. fellowship of Department of Science and Technology (DST), Govt. of Karnataka. (No: DST/KSTePS/Ph.D fellowship/CHE-05:2020-21) KSTePS, DST, Govt. of Karnataka, Bangalore, to the first author. PMG thanks VGST-SMYSR (GRD 503 and 952) and Rani Channamma University for Interdisciplinary Research Project 2022 (RCUB/PMEB/2021-22/5338).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Anigol, L.B., Sajjan, V.P., Gurubasavaraj, P.M. et al. Study on the effect of pH on the biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using Capparis moonii fruit extract: their applications in anticancer activity, biocompatibility and photocatalytic degradation. Chem. Pap. 77, 3327–3345 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-023-02707-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-023-02707-5