Abstract
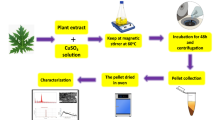
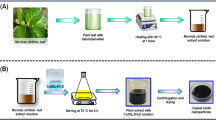
The aim of the present study was to synthesize biologically active cuprous oxide nanoparticles (Cu2O-NPs) using green nanotechnology from aqueous extract of Rubus ellipticus fruits. The structural characterization of aqueous extract-mediated cuprous oxide nanoparticles (Ru-Cu2O-NPs) was performed using X-ray powder diffraction (XRD), Transmission electron microscope (TEM), Field emission scanning electron microscope (FE-SEM), Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), and UV–Vis spectroscopy. Using standard techniques, Ru-Cu2O-NPs were also evaluated for their biological activities (antioxidant, antimicrobial, and anticancer) and toxicity. The XRD patterns and Rietveld refinement confirmed the phase purity of Ru-Cu2O-NPs with an average crystallite size of 25 nm. The FE-SEM and TEM images showed the formation of octahedron cages with a grain size of 0.82 ± 0.04 μm on average. The XPS analysis confirmed the presence of Cu1+ ions with many chemisorbed species on the surface. The determination of functional groups was carried out using FTIR with Cu–O stretching vibration at 635 cm−1. Tauc’s plot determined that the optical bandgap of the synthesized Ru-Cu2O-NPs was 1.28 eV. Compared to aqueous fruit extract, Ru-Cu2O-NPs showed significantly lower antioxidant activity. Furthermore, they showed higher antimicrobial activity (MIC) against Bacillus subtilis and Rosellinia necatrix (7.81 µg/mL), Staphylococcus aureus (15.62 µg/mL), and Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Fusarium oxysporum (31.2 µg/mL). The Ru-Cu2O-NPs showed no toxicity against BM MSCs and HC cells at 12.5 µg/mL concentration, whereas the Ru-Cu2O-NPs showed anticancer activity against colon cancer cell lines (SW480 and SW620) at 100 g/mL concentration. These results indicate that Ru-Cu2O-NPs have good antimicrobial and anticancer properties but have low toxicity thus making them suitable for use in pharmaceuticals and food industries.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adinarayana TV, Mishra A, Singhal I et al (2020) Facile green synthesis of silicon nanoparticles from Equisetum arvense for fluorescence based detection of Fe (III) ions. Nanoscale Adv 2:4125–4532. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0NA00307G
Ahmad W, Jaiswal KK, Soni S (2020) Green synthesis of titanium dioxide (TiO2) nanoparticles by using Mentha arvensis leaves extract and its antimicrobial properties. Inorg Nano-Met Chem 50:1032–1038. https://doi.org/10.1080/24701556.2020.1732419
Azimi H, Kuhri S, Osvet A et al (2014) Effective ligand passivation of Cu2O nanoparticles through solid-state treatment with mercaptopropionic acid. J Am Chem Soc 136:7233–7236. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja502221r
Banerjee D, Chakrabarti S, Hazra AK (2008) Antioxidant activity and total phenolics of some mangroves in Sundarbans. Afr J Biotechnol 7:805–810
Bauer AW (1966) Antibiotic susceptibility testing by a standardized single disc method. Am J Clin Pathol 45:149-158
Bezza FA, Tichapondwa SM, Chirwa EM (2020) Fabrication of monodispersed copper oxide nanoparticles with potential application as antimicrobial agents. Sci Rep 10:1–18. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-73497-z
Chauhan A, Verma R, Batoo KM et al (2021) Structural and optical properties of copper oxide nanoparticles: a study of variation in structure and antibiotic activity. J Mater Res 36:1496–1509. https://doi.org/10.1557/s43578-021-00193-7
Chauhan A, Verma R, Kumari S et al (2020) Photocatalytic dye degradation and antimicrobial activities of Pure and Ag-doped ZnO using Cannabis sativa leaf extract. Sci Rep 10:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-64419-0
Chenthamara D, Subramaniam S, Ramakrishnan SG et al (2019) Therapeutic efficacy of nanoparticles and routes of administration. Biomater Res 23:1–29. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40824-019-0166-x
Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (2012) M100–S22.Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing: 22nd informational supplement. PA CLSI, Wayne
Dhatwalia J, Kumari A, Chauhan A et al (2022) Rubus ellipticus Sm. fruit extract mediated zinc oxide nanoparticles: a green approach for dye degradation and biomedical applications. Materials 15:3470. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15103470
El-Saadony MT, El-Hack A, Taha ME et al (2020) Ecofriendly synthesis and insecticidal application of copper nanoparticles against the storage pest Tribolium castaneum. Nanomaterials 10(3):587. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10030587
Essien ER, Atasie VN, Okeafor AO et al (2020) Biogenic synthesis of magnesium oxide nanoparticles using Manihot esculenta (Crantz) leaf extract. Int Nano Lett 10:43–48. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40089-019-00290-w
Fidrianny I, Rizkiya A, Ruslan K (2015) Antioxidant activities of various fruit extracts from three solanum sp. using DPPH and ABTS method and correlation with phenolic, flavonoid and carotenoid content. J Chem Pharm Res 7:666–672
Gebremedhn K, Kahsay MH, Aklilu M (2019) Green synthesis of CuO nanoparticles using leaf extract of Catha edulis and its antibacterial activity. J Pharm Pharmacol 7:327–342. https://doi.org/10.17265/2328-2150/2019.06.007
Grover R, Moore J (1962) Toximetric studies of fungicides against brown rot organisms. Sclerotinia-Fructicola s-Laxa Phytopathol 52(9):876–879
Hayashi N, Machida K, Otawara K (2018) Polymer-soluble thermostable phosphate-ester copper complexes for near-infrared absorbing dyes with weak absorbance in the visible region. Opt Mater 77:111–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optmat.2018.01.020
Hussien A, Gawish SM, Mosleh SES (2019) Antimicrobial polypropylene loaded by cubic cuprous oxide micro particles. Egypt J Chem 62:1047–1055. https://doi.org/10.21608/ejchem.2019.13001.1813
Ijaz F, Shahid S, Khan SA (2017) Green synthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles using Abutilon indicum leaf extract: antimicrobial, antioxidant and photocatalytic dye degradation activities. Trop J Pharm Res 16:743–753. https://doi.org/10.4314/tjpr.v16i4.2
Iravani S, Korbekandi H, Mirmohammadi SV et al (2014) Synthesis of silver nanoparticles: chemical, physical and biological methods. Res Pharm Sci 9:385
Jiang P, Prendergast D, Borondics F et al (2013) Experimental and theoretical investigation of the electronic structure of Cu2O and CuO thin films on Cu (110) using X-ray photoelectron and absorption spectroscopy. J Chem Phys 138:024704. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4773583
Kang T, Guan R, Chen X (2013) In vitro toxicity of different-sized ZnO nanoparticles in Caco-2 cells. Nanoscale Res Lett 8:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1186/1556-276X-8-496
Kasana RC, Panwar NR, Kaul RK (2016) Copper nanoparticles in agriculture: biological synthesis and antimicrobial activity. Nanoscience Food Agric 3:129–143. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-48009-1_5
Kerour A, Boudjadar S, Bourzami R (2018) Eco-friendly synthesis of cuprous oxide (Cu2O) nanoparticles and improvement of their solar photocatalytic activities. J Solid State Chem 263:79–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jssc.2018.04.010
Khan S, Ansari AA, Khan AA (2017) In vitro evaluation of cytotoxicity, possible alteration of apoptotic regulatory proteins and antibacterial activity of synthesized copper oxide nanoparticles. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 153:320–326. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2017.03.005
Kumar V, Wadhwa R, Kumar N et al (2019) A comparative study of chemically synthesized and Camellia sinensis leaf extract-mediated silver nanoparticles. 3 biotech 9(1):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-018-1544-0
Kumar B, Smita K, Debut A et al (2021) Green synthesis of cuprous oxide nanoparticles using Andean Capuli (Prunus serotina Ehrh. var. Capuli) cherry. J Clust Sci 32:1753–1760. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-020-01924-2
Lal S, Verma R (2022) Chauhan A (2022) Antioxidant, antimicrobial, and photocatalytic activity of green synthesized ZnO-NPs from Myrica esculenta fruits extract. Inorg Chem Commun 141:109518. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inoche.2022.109518
Lalla R, Cheek MD, Nxumalo MM (2018) First assessment of naturalised Rubus ellipticus Sm. populations in South Africa-A potential invasion risk? S Afr J Bot 114:111–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sajb.2017.10.020
Li P, Lv W, Ai S (2016) Green and gentle synthesis of Cu2O nanoparticles using lignin as reducing and capping reagent with antibacterial properties. J Exp Nanosci 11:18–27. https://doi.org/10.1080/17458080.2015.1015462
Mahendran G, Kumari BR (2016) Biological activities of silver nanoparticles from Nothapodytesnimmoniana (Graham) Mabb. fruit extracts. Food Sci Hum Wellness 5:207–218. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fshw.2016.10.001
Maheshwaran G, Bharathi AN, Selvi MM (2020) Green synthesis of Silver oxide nanoparticles using Zephyranthes rosea flower extract and evaluation of biological activities. J Environ Chem Eng 8:104137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2020.104137
Marslin G, Siram K, Maqbool Q et al (2018) Secondary metabolites in the green synthesis of metallic nanoparticles. Materials 11:940. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11060940
Mensor LL, Menezes FS, Leitão GG et al (2001) Screening of Brazilian plant extracts for antioxidant activity by the use of DPPH free radical method. Phytother Res 15(2):127–130. https://doi.org/10.1002/ptr.687
Moller JK, Madsen HL, Aaltonen T et al (1999) Dittany (Origanum dictamnus) as a source of water-extractable antioxidants. Food Chem 64(2):215–219. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0308-8146(98)00143-5
Moharekar S, Raskar P, Wani A (2014) Synthesis and comparative study of zinc oxide nanoparticles with and without capping of pectin and its application. World J Pharm Pharm Sci 3(7):1255–1267
Muniyandi K, George E, Sathyanarayanan S et al (2019) Phenolics, tannins, flavonoids and anthocyanins contents influenced antioxidant and anticancer activities of Rubus fruits from Western Ghats, India. Food Sci Hum Well 8:73–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fshw.2019.03.005
Muthukumaran M, Dhinagaran G, Venkatachalam K et al (2020) Green synthesis of cuprous oxide nanoparticles for environmental remediation and enhanced visible-light photocatalytic activity. Optik 214:164849. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijleo.2020.164849
Nasrollahzadeh M, Sajadi SM, Maham M (2015) Green synthesis of palladium nanoparticles using Hippophaerhamnoides Linn leaf extract and their catalytic activity for the Suzuki–Miyaura coupling in water. J Mol Catal A Chem 396:297–303. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcata.2014.10.019
Nethravathi PC, Kumar MP, Suresh D et al (2015) Tinospora cordifolia mediated facile green synthesis of cupric oxide nanoparticles and their photocatalytic, antioxidant and antibacterial properties. Mater Sci Semicond Process 33:81–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mssp.2015.01.034
Ng CHB, Fan WY (2006) Shape evolution of Cu2O nanostructures via kinetic and thermodynamic controlled growth. J Phys Chem B 110:20801–20807. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp061835k
Pandey Y, Bhatt SS (2016) Overview of Himalayan yellow raspberry (Rubus ellipticus Smith): a nutraceutical plant. J Appl Nat Sci 8:494–499. https://doi.org/10.31018/jans.v8i1.824
Pankove JI (1975) Optical Processes in Semiconductors. Courier Corporation, Massachusetts
Ramesh P, Saravanan K, Manogar P et al (2021) Green synthesis and characterization of biocompatible zinc oxide nanoparticles and evaluation of its antibacterial potential. Sens Bio-Sens Res 31:100399. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbsr.2021.100399
Reddy NJ, Vali DN, Rani M (2014) Evaluation of antioxidant, antibacterial and cytotoxic effects of green synthesized silver nanoparticles by Piper longum fruit. Mater Sci Eng C 34:115–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2013.08.039
Regmi A, Bhandari J, Bhattarai S et al (2019) Synthesis, Characterizations and antimicrobial activity of cuprous oxide (Cu2O) nanoparticles. J Nepal Chem Soc 40:5–10. https://doi.org/10.3126/jncs.v40i0.27271
Rehana D, Mahendiran D, Kumar RS (2017) Evaluation of antioxidant and anticancer activity of copper oxide nanoparticles synthesized using medicinally important plant extracts. Biomed Pharmacother 89:1067–1077. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2017.02.101
Riss TL, Moravec RA (2004) Use of multiple assay endpoints to investigate the effects of incubation time, dose of toxin, and plating density in cell-based cytotoxicity assays. Assay Drug Dev Technol 2:51–62. https://doi.org/10.1089/154065804322966315
Saini R, Dangwal K, Singh H et al (2014) Antioxidant and antiproliferative activities of phenolics isolated from fruits of Himalayan yellow raspberry (Rubus ellipticus). J Food Sci Technol 51:3369–3375. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-012-0836-3
Sannigrahi S, Mazuder UK, Pal DK et al (2010) Antioxidant potential of crude extract and different fractions of Enhydra fluctuans Lour. Iran J Pharma Res 9(1):75
Sengul AB, Asmatulu E (2020) Toxicity of metal and metal oxide nanoparticles: a review. Environ Chem Lett 18:1659–1683. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-020-01033-6
Sharma D, Thakur N, Vashistt J (2018) Antibacterial evaluation of cuprous oxide nanoparticles synthesized using leaf extract of Callistemon viminalis. Indian J Pharm Educ Res 52:449–455. https://doi.org/10.5530/ijper.52.3.52
Sharma R, Garg R, Kumari A (2020) A review on biogenic synthesis, applications and toxicity aspects of zinc oxide nanoparticles. EXCLI J 19:1325. https://doi.org/10.17179/excli2020-2842
Shelari PV, Katkar AS (2018) Biological synthesis of Cu2O nanoshells and its optical properties. Int JChem Pharm Sci 7:75–80. https://doi.org/10.30731/ijcps.7.3.2018.75-80
Shende S, Gaikwad N, Bansod S (2016) Synthesis and evaluation of antimicrobial potential of copper nanoparticle against agriculturally important phytopathogens. Synthesis 1:41–47
Shirwaikar A, Shirwaikar A, Rajendran K et al (2006) In vitro antioxidant studies on the benzyl tetra isoquinoline alkaloid berberine. Biol Pharma Bull 29(9):1906–1910. https://doi.org/10.1248/bpb.29.1906
Sriramulu M, Shanmugam S, Ponnusamy VK (2020) Agaricus bisporus mediated biosynthesis of copper nanoparticles and its biological effects: an study. Colloid Interface Sci Commun 35:100254. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colcom.2020.100254
Thoka S, Lee AT, Huang MH (2019) Scalable synthesis of size-tunable small Cu2O nanocubes and octahedra for facet-dependent optical characterization and pseudomorphic conversion to Cu nanocrystals. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 7:10467–10476. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.9b00844
Velsankar K, RM AK, Preethi R (2020) Green synthesis of CuO nanoparticles via Allium sativum extract and its characterizations on antimicrobial, antioxidant, antilarvicidal activities. J Environ Chem Eng 8:104123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2020.104123
Viet PV, Nguyen HT, Cao TM et al (2016) Fusarium antifungal activities of copper nanoparticles synthesized by a chemical reduction method. J Nanomater 2016:7. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/1957612
Wang Y, Lu Y, Zhan W (2015) Synthesis of porous Cu2O/CuO cages using Cu-based metal–organic frameworks as templates and their gas-sensing properties. J Mater Chem A 3:12796–12803. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5TA01108F
Wongrakpanich A, Mudunkotuwa IA, Geary SM et al (2016) Size-dependent cytotoxicity of copper oxide nanoparticles in lung epithelial cells. Environ Sci Nano 3:365–374. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5EN00271K
Yedjou CG, Moore P, Tchounwou PB (2006) Dose-and time-dependent response of human leukemia (HL-60) cells to arsenic trioxide treatment. Int J Environ Res Public Health 3:136–140. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph2006030017
Zhang X, Zhang Y, Wang D et al (2014) Investigation of adsorption behavior of Cu2O submicro-octahedra towards congo red. J Nanomater 2014:3. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/619239
Zhao Y, Ran W, He J et al (2015) High-performance asymmetric supercapacitors based on multilayer MnO2/graphene oxide nanoflakes and hierarchical porous carbon with enhanced cycling stability. Small 11(11):1310–1319. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201401922
Zhou J, Wang C, Cunningham AJ et al (2019) Synthesis and characterization of size-controlled nano-Cu2O deposited on alpha-zirconium phosphate with excellent antibacterial property. Mater Sci Eng C 101:499–504. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2019.04.008
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There is no conflict of interest among the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Dhatwalia, J., Kumari, A., Chauhan, A. et al. Rubus ellipticus fruits extract-mediated cuprous oxide nanoparticles: in vitro antioxidant, antimicrobial, and toxicity study. Chem. Pap. 77, 1377–1393 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-022-02551-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-022-02551-z