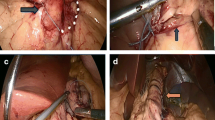
Abstract
Purpose
Laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy (LSG) is an effective bariatric procedure, yet can be followed by complications such as staple line leak and bleeding, vomiting, and gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). Various attempts have been described in the literature to improve the early outcome of LSG through various measures. This study aimed to assess the impact of adding T-shaped omentoplasty to LSG on the short-term outcome of the procedure.
Methods
This was a retrospective cohort study on patients with morbid obesity who underwent LSG in the period of November 2015 to November 2018. The outcome of patients with morbid obesity who underwent LSG combined with T-shaped omentoplasty (group I) was compared with that of a similar number of patients who underwent classical LSG without staple line fixation (group II). The main outcome measures were the rates of staple line bleeding and leak, postoperative nausea and vomiting (PONV), GERD, gastric axial rotation, other complications, and weight loss.
Results
The study included 106 patients of a mean BMI of 49.8 kg/m2. Group II had significantly higher PONV) scale at 1 week and 1 month than group I. Group I had significantly lower rates of staple line bleeding (0 vs 9.6%, p = 0.02) and GERD (3.7% vs 17.3%, p = 0.02) than group II. Both groups had similar rates of staple line leak and comparable operation time.
Conclusion
Staple line fixation using the T-shaped omentoplasty technique was associated with lower incidence of significant PONV, staple line bleeding, and GERD as compared with classical LSG.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Emile SH, Elfeki H, Elalfy K, et al. Laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy then and now: an updated systematic review of the progress and short-term outcomes over the last 5 years. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech. 2017;27(5):307–17. https://doi.org/10.1097/SLE.0000000000000418.
Alizadeh RF, Li S, Inaba CS, et al. Robotic versus laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy: a MBSAQIP analysis. Surg Endosc. 2019;33(3):917–22. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-018-6387-6.
Iannelli A, Treacy P, Sebastianelli L, et al. Perioperative complications of sleeve gastrectomy: review of the literature. J Minim Access Surg. 2019;15(1):1–7. https://doi.org/10.4103/jmas.JMAS_271_17.
Godoy E, Coelho D. Gastric sleeve fixation strategy in laparoscopic vertical sleeve gastrectomy. ABCD Arq Bras Cir Dig. 2013;26(Suplemento 1):79–82.
Abdallah E, Emile SH, Elfeki H. Laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy with or without staple line inversion and distal fixation to the transverse mesocolon: impact on early postoperative outcomes. Obes Surg. 2017;27(2):323–9.
Myles PS, Wengritzky R. Simplified postoperative nausea and vomiting impact scale for audit and post-discharge review. Br J Anaesth. 2012;108(3):423–9.
Brethauer SA, Kim J, El Chaar M, et al. Standardized outcomes reporting in metabolic and bariatric surgery. Obes Surg. 2015;25(4):587–606.
Ruiz-Tovar J, Zubiaga L, Muñoz JL, et al. Incidence of postoperative nausea and vomiting after laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy with staple line reinforcement with oversewing and staple line inversion vs buttressing material: a randomized clinical trial. Int J Surg. 2018;59:75–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijsu.2018.09.010.
Elbalshy MA, Fayed AM, Abdelshahid MA, et al. Role of staple line fixation during laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy. Int Surg J. 2018;5:156–61.
Santoro S. Technical aspects in sleeve gastrectomy. Obes Surg. 2007;17(11):1534–5.
Fallatah B, Shehry A, Abdelsamad L, et al. Comparison study of gastric emptying after performing sleeve gastrectomy with two different techniques. Glob J Surg. 2013;1(4):53–6.
Braghetto I, Davanzo C, Korn O, et al. Scintigraphic evaluation of gastric emptying in obese patients submitted to sleeve gastrectomy compared to normal subjects. Obes Surg. 2009;19(11):1515–21.
Sista F, Abruzzese V, Clementi M, et al. The effect of sleeve gastrectomy on GLP-1 secretion and gastric emptying: a prospective study. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2017;13(1):7–14.
Vives M, Molina A, Danús M, et al. Analysis of gastric physiology after laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy (LSG) with or without antral preservation in relation to metabolic response: a randomised study. Obes Surg. 2017;27:2836–44.
Emile SH. Gastroesophageal reflux disease after sleeve gastrectomy: the need to predict its onset and prevent its consequences. Obes Surg. 2019 Aug;29(8):2625–6.
Baumann T, Kuesters S, Grueneberger J, et al. Time-resolved MRI after ingestion of liquids reveals motility changes after laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy--preliminary results. Obes Surg. 2011;21(1):95–101.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Emad Abdallah designed the study. Emad Abdallah, Mahmoud Zakaria, Mahmoud Abdelnaby, Sabry Mahmoud, Waleed Gado, and Samy Elbaz followed the patients, collected the data, and critically revised the manuscript. Sameh Emile and Mohamed Fikry participated in data collection and analysis and writing and revision of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. Ethical approval for the study was obtained from the Research Ethics Committee.
Statement of Informed Consent
Informed consent does not apply as for this type of study; formal consent is not required.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abdallah, E., Zakaria, M., Fikry, M. et al. Laparoscopic Sleeve Gastrectomy with T-Shaped Omentoplasty: Impact on the Early Postoperative Outcomes. OBES SURG 30, 3735–3741 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11695-020-04743-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11695-020-04743-6