Abstract
Background
Nutritional deficiencies, especially micronutrient deficiencies, can occur in obese individuals. Surgical treatment may aggravate or cause these deficiencies, depending on the type of procedure, food intake and the use of multivitamins, minerals or other supplements. The objective of the study was to evaluate the nutrient intake of women who had undergone Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB) surgery.
Methods
A cross-sectional, controlled study was conducted among 44 women after RYGB (operated-group, OG; mean years post-operation = 3.4) and a control group of 38 healthy women (non-operated group, NOG) matched by age and economic condition. The women reported their dietary intake using a 4-day record. The Dietary Reference Intakes was used as a reference.
Results
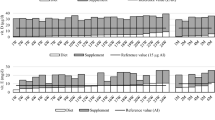
The macronutrient contributions to dietary energy intake presented an acceptable distribution for proteins and carbohydrates. Lipid intake was high among women in the OG and the NOG (43.2 and 55.3 %, respectively). In the evaluation of micronutrients, a statistically significant difference was observed between the groups for iron, zinc and vitamins B1 and B12. Both groups were at high risk for inadequate calcium intake, and the OG was at risk for inadequate zinc, iron and vitamin B1 intake.
Conclusions
The nutrient intake of women who had undergone RYGB is very similar to that of non-operated women, with the exception of a reduced intake of iron, zinc and vitamins B1 and B12, which may be due to the difficulty of consuming meat and a balanced diet. The findings of this study emphasize the importance of appropriate nutritional intervention and the regular use of multivitamin and mineral supplements for these patients.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
World Health Organization. Obesity and overweight. What are overweight and obesity? Março, 2011. Acesso em: 13 de julho de 2011. Disponível em: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs311/en/.
Instituto Brasileiro de Geografia e Estatística (IBGE). Pesquisa de Orçamentos Familiares 2008–2009: antropometria e estado nutricional de crianças, adolescentes e adultos. Rio de Janeiro, 2010.
Associação Brasileira para o Estudo da Obesidade e da Síndrome Metabólica (ABESO). Diretrizes brasileiras de obesidade 2009/2010. São Paulo, 2009.
Buchwald H, Oien DM. Metabolic/bariatric surgery worldwide 2008. Obes Surg. 2009;19:1605–11.
Shah M, Simha V, Garg A. Review: long-term impact of bariatric surgery on body weight, comorbidities, and nutritional status. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2010;91:4223–31.
Xanthakos SA. Nutritional deficiencies in obesity and after bariatric surgery. Pediatr Clin North Am. 2009;56:1105–21.
Farias LM, Coelho MP, Barbosa RF, et al. Aspectos nutricionais em mulheres obesas submetidas à gastroplastia vertical com derivação gastro-jejunal em Y-de-Roux. Rev Bras Nutr Clin. 2006;21:98–103.
Gasteyger C, Suter M, Gaillard RC, et al. Nutritional deficiencies after Roux-em-Y gastric bypass for morbid obesity often cannot be prevented by standard multivitamin supplementation. Am J Clin Nutr. 2008;87:1128–33.
Fujioka K. Commentary: follow-up of nutritional and metabolic problems after bariatric surgery. Diabetes Care. 2005;28:481–4.
Flancbaum L, Belsley S, Drake V, et al. Preoperative nutritional status of patients undergoing Roux-en-Y gastric bypass for morbid obesity. J Gastrointest Surg. 2006;10:1033–7.
Coupaye M, Puchaux K, Bogard C, et al. Nutritional consequences of adjustable gastric banding and gastric bypass: a 1-year prospective study. Obes Surg. 2009;19:56–65.
Slater GH, Ren CJ, Siegel N, et al. Serum fat-soluble vitamin deficiency and abnormal calcium metabolism after malabsorptive bariatric surgery. J Gastrointest Surg. 2004;8:48–55.
National Academy of Sciences. Dietary reference intakes: applications in dietary assessment. Washington, DC: National Academic; 2000.
World Health Organization (WHO). Obesity: preventing and managing the global epidemic. Report of a WHO consultation. WHO Technical Report Series 894. Geneva; 2000.
Associação Brasileira de Empresas de Pesquisa. São Paulo. Critério de classificação econômica no Brasil 2003: Base 2000. Acesso em: 14 de julho de 2011. Disponível em: http://www.abep.org/novo/Content.aspx?ContentID=302.
Pardini R, Matsudo S, Araujo T, et al. Validação do questionário internacional de nível de atividade física (IPAQ - versão 6): estudo piloto em adultos jovens brasileiros. Rev Bras Cien e Mov. 2001;9:45–51.
Programa de Apoio a Nutrição – NutWin [software]. Departamento de Informática em Saúde. Universidade Federal de São Paulo; 2005.
Institute of Medicine, Food and Nutrition Board. Dietary reference intakes for energy, carbohydrate, fiber, fat, fatty acids, cholesterol, protein, and amino acids. Washington (DC): National Academy; 2002.
Padovani RM, Amaya-Farfán J, Colugnati FAB, et al. Dietary reference intakes: aplicabilidade das tabelas em estudos nutricionais. Rev Nutr. 2006;19:741–60.
Institute of Medicine, Food and Nutrition Board. Dietary references intakes for calcium and vitamin D. Uncorrected proofs. Washington, DC: National Academies; 2010.
Colossi FG, Casagrande DS, Chatikin R, et al. Need for multivitamin use in the postoperative period of gastric bypass. Obes Surg. 2008;18:187–91.
AACE/TOS/ASMBS. Bariatric surgery guidelines. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2008;4:S109–84.
Dias MC, Ribeiro AG, Scabim VM, et al. Dietary intake of female bariatric patients after anti-obesity gastroplasty. Clinics. 2006;61:93–8.
Kruseman M, Leimgruber A, Zumbach F, et al. Dietary, weight, and psychological changes among patients with obesity, 8 years after gastric bypass. J Am Diet Assoc. 2010;110:527–34.
Olbers T, Björkman S, Lindroos A, et al. Body composition, dietary intake, and energy expenditure after laparoscopic Roux-en-y gastric bypass and laparoscopic vertical banded gastroplasty. Ann Surg. 2006;244:715–22.
Bavaresco M, Paganini S, Lima TP, et al. Nutritional course of patients submitted to bariatric surgery. Obes Surg. 2010;20:716–21.
Faria LS, Faria PO, Lopes TC, et al. Relation between carbohydrate intake and weight loss after bariatric surgery. Obes Surg. 2009;19:708–16.
Ruz M, Carrasco F, Rojas P, et al. Iron absorption and iron status are reduced after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. Am J Clin Nutr. 2009;90:527–32.
Goode LR, Brolin RE, Chowdhury HA, et al. Bone and gastric bypass surgery: effects of dietary calcium and vitamin D. Obes Res. 2004;12:40–7.
Sarwer DB, Wadden TA, Moore RH, et al. Preoperative eating behavior, postoperative dietary adherence and weight loss following gastric bypass surgery. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2008;4:640–6.
Cominetti C, Garrido Jr AB, Cozzolino SMF. Zinc nutritional status of morbidly obese patients before and after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass: a preliminary report. Obes Surg. 2006;16:448–53.
Behrns KE, Smith CD, Sarr MG. Prospective evaluation of gastric acid secretion and cobalamin absorption following gastric bypass for clinically severe obesity. Dig Dis Sci. 1994;39:315–20.
Sociedade Brasileira de Cardiologia. IV Diretriz Brasileira Sobre Dislipidemias e Prevenção da Aterosclerose. Arq Bras Cardiol. 2007;88:1–19.
Bult MJ, van Dalen T, Muller AF. Surgical treatment of obesity. Eur J Endocrinol. 2008;158:135–45.
Boesing F, Moreira EA, Wilhelm-Filho D, et al. Roux-en-Y bypass gastroplasty: markers of oxidative stress 6 months after surgery. Obes Surg. 2010;20:1236–44.
Aasheim ET, Johnson LK, Hofsø D, et al. Vitamin status after gastric bypass and lifestyle intervention: a comparative prospective study. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2012;8:169–75.
Aasheim ET, Björkman S, Søvik TT, et al. Vitamin status after bariatric surgery: a randomized study of gastric bypass and duodenal switch. Am J Clin Nutr. 2009;90:15–22.
Donadelli SP, Junqueira-Franco MV, de Mattos Donadelli CA, et al. Daily vitamin supplementation and hypovitaminosis after obesity surgery. Nutrition. 2012;28:391–6.
Muñoz M, Botella-Romero F, Gòmez-Ramírez S, et al. Iron deficiency and anaemia in bariatric surgical patients: causes, diagnosis and proper management. Nutr Hosp. 2009;24:640–54.
Instituto Brasileiro de Geografia e Estatística (IBGE). Pesquisa de orçamentos familiares 2008–2009: análise do consumo alimentar pessoal no Brasil. Rio de Janeiro; 2011.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Torres Rossi, R.G., dos Santos, M.T.A., de Souza, F.I.S. et al. Nutrient Intake of Women 3 Years After Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass Surgery. OBES SURG 22, 1548–1553 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11695-012-0688-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11695-012-0688-y