Abstract
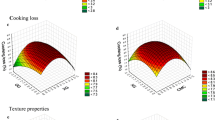
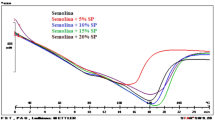
The effects of chicken meat, egg yolk, and seaweed supplementation on microwave-dried instant noodles were investigated to develop protein-enriched instant noodles. The influence of chicken meat significantly (P ≤ 0.05) increased the optimum cooking time and water absorption. Additionally, egg yolk improved the noodle quality by decreasing the cooking loss from 6.51 to 4.25% and increasing the maximum tension force and distance from 0.13 to 0.16 N and from 16.83 to 24.69 mm, respectively, which contrasted with the decrease in the maximum tension force and distance caused by seaweed addition. Scanning electron micrographs of the chicken addition presented large porous structures, while the egg yolk addition resulted in uniform porous structures with a finer connective network; confocal scanning laser micrographs also confirmed good protein distribution. Finally, instant noodles supplemented per 100 g of flour with chicken meat (10 g), egg yolk (10 g), and seaweed (2 g) were selected as optimal. The protein content significantly (P ≤ 0.05) increased from 11.42 to 16.73 g per 100 g dry matter, which was higher than in traditional wheat-based instant noodles and this developed product was preferred by panelists. This knowledge can support innovation in the development of instant noodles with a higher protein content.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Li, K.X. Zhu, X.N. Guo, K. Brijs, H.M. Zhou, Natural additives in wheat-based pasta and noodle products: opportunities for enhanced nutritional and functional properties. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food. Saf. 13, 347–357 (2014)
S.U. Kadam, P. Prabhasankar, Evaluation of cooking, microstructure, texture, and sensory quality characteristics of shrimp meat-based pasta. J. Texture Stud. 43, 268–274 (2012)
H.C. Chang, H.H. Chen, H.H. Hu, Textural changes in fresh egg noodles formulated with seaweed powder and full or partial replacement of cuttlefish paste. J. Texture Stud. 42, 61–71 (2011)
T. Liu, N. Hamid, K. Kantono, L. Pereira, M.M. Farouk, S.O. Knowles, Effects of meat addition on pasta structure, nutrition, and in vitro digestibility. Food Chem. 213, 108–114 (2016)
G.K. Pal, S.B. Kumar, P. Prabhasankar, P.V. Suresh, Inclusion of poultry based food ingredients in the formulation of noodles and their effects on noodle quality characteristics. J. Food Meas. Charact. 1–9 (2017)
D.D. Jayasena, S. Jung, Y.S. Bae, H.B. Park, J.H. Lee, C. Jo, Comparison of the amounts of endogenous bioactive compounds in raw and cooked meats from commercial broilers and indigenous chickens. J. Food Compos. Anal. 37, 20–24 (2015)
C. Alamprese, E. Casiraghi, M.A. Pagani, Development of gluten-free fresh egg pasta analogues containing buckwheat. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 225, 205–213 (2006)
S.U. Kadam, P. Prabhasankar, Marine foods as functional ingredients in bakery and pasta products. Food Res. Int. 43, 1975–1980 (2010)
P. Prabhasankar, P. Ganesan, N. Bhaskar, A. Hirose, N. Stephen, L.R. Gowda, M. Hosokawa, K. Miyashita, Edible Japanese seaweed, wakame (Undaria pinnatifida) as an ingredient in pasta: chemical, functional and structural evaluation. Food Chem. 115, 501–508 (2009)
S. Mohamed, S.N. Hashim, H.A. Rahman, Seaweeds: a sustainable functional food for complementary and alternative therapy. Trends Food Sci. Tech. 23, 83–96 (2012)
S. Chandrasekaran, S. Ramanathan, T. Basak, Microwave food processing—A review. Food Res. Int. 52, 243–261 (2013)
D. Setiady, M. Lin, F. Younce, B.A. Rasco, Incorporation of minced trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) into egg-based noodles. J. Food Process. Preserv. 31, 480–491 (2007)
C.M. Tudoricǎ, V. Kuri, C.S. Brennan, Nutritional and physicochemical characteristics of dietary fiber enriched pasta. J. Agric. Food Chem. 50, 347–356 (2002)
N. Rakhesh, C.M. Fellows, M. Sissons, Evaluation of the technological and sensory properties of durum wheat spaghetti enriched with different dietary fibres. J. Sci. Food 95, 2–11 (2015)
B.X. Fu, Asian noodles: history, classification, raw materials, and processing. Food Res. Int. 41, 888–902 (2008)
AACC, Approved Method of the American Association of Cereal, 10th edn. (American Association of Cereal Chemists, St. Paul, 2000)
A.A. Adedeji, L. Liu, M.O. Ngadi, Microstructural evaluation of deep-fat fried chicken nugget batter coating using confocal laser scanning microscopy. J Food Eng. 102, 49–57 (2011)
AOAC, Official Methods of Analysis of AOAC International, 19th edn. (Association of Official Analytical Chemists, Maryland, 2012)
E. Huff-Lonergan, S.M. Lonergan, Mechanisms of water-holding capacity of meat: the role of postmortem biochemical and structural changes. Meat Sci. 71, 194–204 (2005)
A. Marti, A. Barbiroli, M. Marengo, L. Fongaro, S. Iametti, M. Pagani, Structuring and texturing gluten-free pasta: egg albumen or whey proteins? Eur. Food Res. Technol. 238, 217–224 (2014)
P. Prabhasankar, P. Ganesan, N. Bhaskar, Influence of Indian brown seaweed (Sargassum marginatum) as an ingredient on quality, biofunctional, and microstructure characteristics of pasta. Food Sci. Technol. Int. 15, 471–479 (2009)
J. Filipović, L. Pezo, N. Filipović, V. Filipović, J. Brkljača, A. Jevtić-Vukmirović, Optimization of spelt pasta composition, regarding inulin HPX content and eggs quantity. J. Food Nutr. Res. 2, 167–173 (2014)
H. Khouryieh, T. Herald, F. Aramouni, Quality and sensory properties of fresh egg noodles formulated with either total or partial replacement of egg substitutes. J. Food Sci. 71, 433–437 (2006)
A.K. Khare, A.K. Biswas, S. Balasubramanium, M.K. Chatli, J. Sahoo, Optimization of meat level and processing conditions for development of chicken meat noodles using response surface methodology. J. Food Sci. Technol. 52, 3719–3729 (2015)
N.S. Ramya, P. Prabhasankar, L.R. Gowda, V.K. Modi, N. Bhaskar, Influence of freeze-dried shrimp meat in pasta processing qualities of Indian T. durum wheat. J. Aquat. Food Prod. Technol. 24, 582–596 (2015)
H.C. Chang, L.C. Wu, Texture and quality properties of Chinese fresh egg noodles formulated with green seaweed (Monostroma nitidum) powder. J. Food Sci. 73, 398–404 (2008)
C.S. Brennan, V. Kuri, C.M. Tudorica, Inulin-enriched pasta: effects on textural properties and starch degradation. Food Chem. 86, 189–193 (2004)
N. Aravind, M. Sissons, N. Egan, C. Fellows, Effect of insoluble dietary fibre addition on technological, sensory, and structural properties of durum wheat spaghetti. Food Chem. 130, 299–309 (2012)
L.J. Luo, X.N. Guo, K.X. Zhu, Effect of steaming on the quality characteristics of frozen cooked noodles. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 62, 1134–1140 (2015)
M. Li, L.J. Luo, K.X. Zhu, X.N. Guo, W. Peng, H.M. Zhou, Effect of vacuum mixing on the quality characteristics of fresh noodles. J. Food Eng. 110, 525–531 (2012)
M.E. Sosa-Morales, L. Valerio-Junco, A. López-Malo, H.S. García, Dielectric properties of foods: reported data in the 21st century and their potential applications. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 43, 1169–1179 (2010)
L. Zhang, J.G. Lyng, N.P. Brunton, The effect of fat, water and salt on the thermal and dielectric properties of meat batter and its temperature following microwave or radio frequency heating. J. Food Eng. 80, 142–151 (2007)
C. Niamnuy, S. Devahastin, S. Soponronnarit, Some recent advances in microstructural modification and monitoring of foods during drying: a review. J Food Eng. 123, 148–156 (2014)
Q. Lu, S. Guo, S. Zhang, Effects of flour free lipids on textural and cooking qualities of Chinese noodles. Food Res. Int. 42, 226–230 (2009)
E. Silva, M. Birkenhake, E. Scholten, L.M.C. Sagis, E. van der Linden, Controlling rheology and structure of sweet potato starch noodles with high broccoli powder content by hydrocolloids. Food Hydrocolloids 30, 42–52 (2013)
S. Jaturasitha, T. Srikanchai, M. Kreuzer, M. Wicke, Differences in carcass and meat characteristics between chicken indigenous to northern Thailand (Black-boned and Thai native) and imported extensive breeds (Bresse and Rhode Island red). Poult. Sci. 87, 160–169 (2008)
S. Wattanachant, S. Benjakul, D.A. Ledward, Composition, color, and texture of Thai indigenous and broiler chicken muscles. Poult. Sci. 83, 123–128 (2004)
FDA, Notification of Ministry of Public Health, (No. 182) B.E. 2541 (1998) Re: Nutrition Labeling (FDA, Bangkok, 1998)
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the Researcher for Industry (RRI) Program of the Thailand Research Fund and the Thai President Foods Public Company Limited for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that we do not have any conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pongpichaiudom, A., Songsermpong, S. Evaluation of microstructure and quality characteristics of microwave-dried instant noodles enriched with chicken meat, egg yolk, and seaweed. Food Measure 12, 22–34 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11694-017-9613-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11694-017-9613-3