Abstract
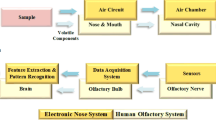
There are mainly two selection methods for different features of electronic nose (E-nose) which is used to identify different samples, namely visual inspection and correct rate of discrimination result. The visual inspection is not a quantitative method. Besides, when the correct rates of discrimination result are identical for different features, the identification difference of different features is not evaluated accurately and quantitatively. To get a better feature vector for identifying different samples, a selection method was studied in-depth in which Wilks Λ–statistic was employed as a selection index for different features. At the same time, three different kinds of Chinese vinegar and three of Chinese milk were taken and tested by an E-nose. Five different features were extracted from the E-nose signals which are variance value (VARV), integral value (INV), mean value of relative steady-state responses (MVRSR), mean-differential coefficient value (MDCV) and energy value of wavelet packet decomposition (WE). The best feature vectors of these five features were obtained using the selection method and its effectiveness was respectively proved by the visual inspection and Fisher discriminant analysis (FDA) correct rate of vinegar and milk samples.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. Gutierrez-Osuna, H.T. Nagle, S.S. Schiffman, Transient response analysis of an electronic nose using multi-exponential models. Sens. Actuators B 61, 170–182 (1999)
M. Aleixandre, I. Sayago, M.C. Horrillo, Analysis of neural networks and analysis of feature selection with genetic algorithm to discriminate among pollutant gas. Sens. Actuators B 103, 22–128 (2004)
L. Carmel, S. Levy, D. Lancet, D. Harel, A feature extraction method for chemical sensors in electronic nose. Sens. Actuators B 93, 66–76 (2003)
M. Padilla, I. Montoliu, A. Pardo, A. Perera, S. Marco, Feature extraction on three way enose signals. Sens. Actuators B 116, 145–150 (2006)
Y. Yin, X. Tian, Classification of Chinese drinks by a gas sensors array and combination of the PCA with Wilks distribution. Sens. Actuators B 124, 393–397 (2007)
H. Ding, H. Ge, J. Liu, High performance of gas identification by wavelet transform-based fast feature extraction from temperature modulated semiconductor gas sensors. Sens. Actuators B 107, 749–755 (2005)
R. Haddad, L. Carmel, D. Harel, A feature extraction algorithm for multi-peak signals in electronic noses. Sens. Actuators B 120, 467–472 (2007)
A. Leone, C. Distante, N. Ancona, K.C. Persaud, E. Stella, P. Siciliano, A powerful method for feature extraction and compression of electronic nose responses. Sens. Actuators B 105, 378–392 (2005)
S. Panigrahi, S. Balasubramanian, H. Gu, C. Logue, M. Marchello, Neural network integrated electronic nose system for identification of spoiled beef. LWT 39, 135–145 (2006)
Y. Yin, H. Yu, H. Zhang, A feature extraction method based on wavelet packet analysis for discrimination of Chinese vinegars using a gas sensors array. Sens. Actuators B 134, 1005–1009 (2008)
C. Distante, M. Leo, P. Siciliano, K.C. Persaud, On the study of feature extraction methods for an electronic nose. Sens. Actuators B 87, 274–288 (2002)
S. Zhang, C. Xie, M. Hu, H. Li, Z. Bai, D. Zeng, An entire feature extraction method of metal oxide gas sensors. Sens. Actuators B 132, 81–89 (2008)
S. Zhang, C. Xie, Z. Bai, M. Hu, H. Li, D. Zeng, Spoiling and formaldehyde-containing detections in octopus with an E-nose. Food Chem. 113, 1346–1350 (2009)
M. Penza, G. Cassano, F. Tortorella, G. Zaccaria, Classification of food, beverages and perfumes by WO3 thin-film sensors array and pattern recognition techniques. Sens. Actuators B 73, 76–86 (2001)
C.D. Natale, F.A.M. Davide, A. D’Amico, P. Nelli, S. Groppellli, G. Sberveglieri, An electronic nose for the recognition of the vineyard of a red wine. Sens. Actuators B 33, 83–88 (1996)
J. Lozano, J.P. Santos, M.C. Horrillo, Enrichment sampling methods for wine discrimination with gas sensors. J. Food Compos. Anal. 21, 716–723 (2008)
L. Pillonel, J.O. Bosset, R. Tabacchi, Rapid preconcentration and enrichment techniques for the analysis of food volatile, a review. LWT 35, 1–14 (2002)
H. Yu, J. Wang, H. Zhang, Y. Yu, C. Yao, Identification of green tea grade using different feature of response signal from E-nose sensors. Sens. Actuators B 128, 455–461 (2008)
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) under Grant No. 31171685, the authors acknowledge the support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yin, Y., Chu, B., Yu, H. et al. A selection method for feature vectors of electronic nose signal based on wilks Λ–statistic. Food Measure 8, 29–35 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11694-013-9162-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11694-013-9162-3