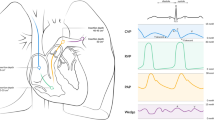
Abstract
Blood pressure monitoring has come a long way from the initial observations made by Reverend Hales in the 18th century. There are none that deny the importance of monitoring perioperative blood pressure; however, the limited ability of the current prevalent technology (oscillometric blood pressure monitoring) to offer continuous blood pressure measurements leaves room for improvement. Invasive monitoring is able to detect beat-to-beat blood pressure measurement, but the risks inherent to the procedure make it unsuitable for routine use except when this risk is outweighed by the benefits. This review focuses on the discoveries which have led up to the current blood pressure monitoring technologies, and especially the creation of those offering non-invasive but continuous blood pressure monitoring capabilities, including their methods of measurement and limitations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Society of Anesthesiologists. Standards of the American Society of Anesthesiologists: Standards for Basic Anesthetic Monitoring.; Available from: http://www.asahq.org/For-Healthcare-Professionals/~/media/For%2520Members/documents/Standards%2520Guidelines%2520Stmts/Basic%2520Anesthetic%2520Monitoring%25202011.ashx (Accessed on January 12, 2012)
Cannesson M, Pestel G, Ricks C, Hoeft A, Perel A. Hemodynamic monitoring and management in patients undergoing high risk surgery: a survey among North American and European anesthesiologists. Crit Care 2011; 15(4): R197
Bijker JB, van Klei WA, Kappen TH, van Wolfswinkel L, Moons KG, Kalkman CJ. Incidence of intraoperative hypotension as a function of the chosen definition: literature definitions applied to a retrospective cohort using automated data collection. Anesthesiology 2007; 107(2): 213–220
Bijker JB, Persoon S, Peelen LM, Moons KG, Kalkman CJ, Kappelle LJ, van Klei WA. Intraoperative hypotension and perioperative ischemic stroke after general surgery: a nested casecontrol study. Anesthesiology 2012; 116(3): 658–664
Monk TG, Saini V, Weldon BC, Sigl JC. Anesthetic management and one-year mortality after noncardiac surgery. Anesth Analg 2005; 100(1): 4–10
Saager L, Greenwald SD, Kelley SD, Schubert A, Sessler DI.. Duration of a “triple low” of blood pressure, BIS, and anesthestic concentration predicts poor outcome. Anesthesiology 2009; 111: A880
Tassoudis V, Vretzakis G, Petsiti A, Stamatiou G, Bouzia K, Melekos M, Tzovaras G. Impact of intraoperative hypotension on hospital stay in major abdominal surgery. J Anesth 2011; 25(4): 492–499
Ramsey M3rd. Blood pressure monitoring: automated oscillometric devices. J Clin Monit 1991; 7(1): 56–67
Smulyan H, Safar ME. Blood pressure measurement: retrospective and prospective views. Am J Hypertens 2011; 24(6): 628–634
Kroeker EJ, Wood EH. Comparison of simultaneously recorded central and peripheral arterial pressure pulses during rest, exercise and tilted position in man. Circ Res 1955; 3(6): 623–632
Bailey RH, Knaus VL, Bauer JH. Aneroid sphygmomanometers. An assessment of accuracy at a university hospital and clinics. Arch Intern Med 1991; 151(7): 1409–1412
Marks LA, Groch A. Optimizing cuff width for noninvasive measurement of blood pressure. Blood Press Monit 2000; 5(3): 153–158
Finnie KJ, Watts DG, Armstrong PW. Biases in the measurement of arterial pressure. Crit Care Med 1984; 12(11): 965–968
Glasser SP, Ramsey MR 3rd. An automated system for blood pressure determination during exercise. Circulation 1981; 63(2): 348–353
Bur A, Herkner H, Vlcek M, Woisetschläger C, Derhaschnig U, Delle Karth G, Laggner AN, Hirschl MM. Factors influencing the accuracy of oscillometric blood pressure measurement in critically ill patients. Crit Care Med 2003; 31(3): 793–799
Alpert BS. Oscillometric blood pressure values are algorithmspecific. Am J Cardiol 2010; 106(10): 1524, author reply 1524–1525
Amoore JN, Geake WB, Scott DH. Oscillometric non-invasive blood pressure measurements: the influence of the make of instrument on readings? Med Biol Eng Comput 1997; 35(2): 131–134
Gorback MS, Quill TJ, Graubert DA. The accuracy of rapid oscillometric blood pressure determination. Biomed Instrum Technol 1990; 24(5): 371–374
Sy WP. Ulnar nerve palsy possibly related to use of automatically cycled blood pressure cuff. Anesth Analg 1981; 60(9): 687–688
Bause GS, Weintraub AC, Tanner GE. Skin avulsion during oscillometry. J Clin Monit 1986; 2(4): 262–263
Scheer B, Perel A, Pfeiffer UJ. Clinical review: complications and risk factors of peripheral arterial catheters used for haemodynamic monitoring in anaesthesia and intensive care medicine. Crit Care 2002; 6(3): 199–204
Brzezinski M, Luisetti T, London MJ. Radial artery cannulation: a comprehensive review of recent anatomic and physiologic investigations. Anesth Analg 2009; 109(6): 1763–1781
Hamilton WF, Dow P. An experimental study of the standing waves in the pulse propagated through the aorta. Am J Physiol 1938; (125): 48–59
O’Rourke MF, Pauca A, Jiang XJ. Pulse wave analysis. Br J Clin Pharmacol 2001; 51(6): 507–522
Avolio AP, Van Bortel LM, Boutouyrie P, Cockcroft JR, McEniery CM, Protogerou AD, Roman MJ, Safar ME, Segers P, Smulyan H. Role of pulse pressure amplification in arterial hypertension: experts’ opinion and review of the data. Hypertension 2009; 54(2): 375–383
Laurent S, Cockcroft J, Van Bortel L, Boutouyrie P, Giannattasio C, Hayoz D, Pannier B, Vlachopoulos C, Wilkinson I, Struijker-Boudier H; European Network for Non-invasive Investigation of Large Arteries. Expert consensus document on arterial stiffness: methodological issues and clinical applications. Eur Heart J 2006; 27(21): 2588–2605
Lamia B, Chemla D, Richard C, Teboul JL. Clinical review: interpretation of arterial pressure wave in shock states. Crit Care 2005; 9(6): 601–606
Cannesson M, Le Manach Y, Hofer CK, Goarin JP, Lehot JJ, Vallet B, Tavernier B. Assessing the diagnostic accuracy of pulse pressure variations for the prediction of fluid responsiveness: a “gray zone” approach. Anesthesiology 2011; 115(2): 231–241
Peňáz J. Photoelectric measurement of blood pressure, volume and flow in the finger. Digest of the 10th International Conference on Medical and Biological Engineering-Dresden, 1973
Imholz BP, Wieling W, van Montfrans GA, Wesseling KH. Fifteen years experience with finger arterial pressure monitoring: assessment of the technology. Cardiovasc Res 1998; 38(3): 605–616
Wesseling KH, Settels JJ, van der Hoeven GM, Nijboer JA, Butijn MW, Dorlas JC. Effects of peripheral vasoconstriction on the measurement of blood pressure in a finger. Cardiovasc Res 1985; 19(3): 139–145
Kemmotsu O, Ueda M, Otsuka H, Yamamura T, Winter DC, Eckerle JS. Arterial tonometry for noninvasive, continuous blood pressure monitoring during anesthesia. Anesthesiology 1991; 75(2): 333–340
Hansen S, Staber M. Oscillometric blood pressure measurement used for calibration of the arterial tonometry method contributes significantly to error. Eur J Anaesthesiol 2006; 23(9): 781–787
Janelle GM, Gravenstein N. An accuracy evaluation of the T-Line Tensymeter (continuous noninvasive blood pressure management device) versus conventional invasive radial artery monitoring in surgical patients. Anesth Analg 2006; 102(2): 484–490
Dueck R, Goedje O, Clopton P. Noninvasive continuous beat-tobeat radial artery pressure via TL-200 applanation tonometry. J Clin Monit Comput 2012; 26(2): 75–83
Lane JD, Greenstadt L, Shapiro D, Rubinstein E. Pulse transit time and blood pressure: an intensive analysis. Psychophysiology 1983; 20(1): 45–49
Marie GV, Lo CR, Van Jones J, Johnston DW. The relationship between arterial blood pressure and pulse transit time during dynamic and static exercise. Psychophysiology 1984; 21(5): 521–527
Drzewiecki GM, Melbin J, Noordergraaf A. Arterial tonometry: review and analysis. J Biomech 1983; 16(2): 141–152
Biais M, Vidil L, Roullet S, Masson F, Quinart A, Revel P, Sztark F. Continuous non-invasive arterial pressure measurement: evaluation of CNAP device during vascular surgery. Ann Fr Anesth Reanim 2010; 29(7–8): 530–535
Imholz BP, van Montfrans GA, Settels JJ, van der Hoeven GM, Karemaker JM, Wieling W. Continuous non-invasive blood pressure monitoring: reliability of Finapres device during the Valsalva manoeuvre. Cardiovasc Res 1988; 22(6): 390–397
Lemson J, Hofhuizen CM, Schraa O, Settels JJ, Scheffer GJ, van der Hoeven JG. The reliability of continuous noninvasive finger blood pressure measurement in critically ill children. Anesth Analg 2009; 108(3): 814–821
Maggi R, Viscardi V, Furukawa T, Brignole M. Non-invasive continuous blood pressure monitoring of tachycardic episodes during interventional electrophysiology. Europace 2010; 12(11): 1616–1622
Hofhuizen CM, Lemson J, Hemelaar AE, Settels JJ, Schraa O, Singh SK, van der Hoeven JG, Scheffer GJ. Continuous non-invasive finger arterial pressure monitoring reflects intra-arterial pressure changes in children undergoing cardiac surgery. Br J Anaesth 2010; 105(4): 493–500
Jeleazcov C, Krajinovic L, Münster T, Birkholz T, Fried R, Schüttler J, Fechner J. Precision and accuracy of a new device (CNAPTM) for continuous non-invasive arterial pressure monitoring: assessment during general anaesthesia. Br J Anaesth 2010; 105(3): 264–272
Eckert S, Horstkotte D. Comparison of Portapres non-invasive blood pressure measurement in the finger with intra-aortic pressure measurement during incremental bicycle exercise. Blood Press Monit 2002; 7(3): 179–183
Schramm C, Baat L, Plaschke K. Continuous noninvasive arterial pressure: assessment in older and high-risk patients under analgesic sedation. Blood Press Monit 2011; 16(6): 270–276
Hahn R, Rinösl H, Neuner M, Kettner SC. Clinical validation of a continuous non-invasive haemodynamic monitor (CNAP™; 500) during general anaesthesia. Br J Anaesth 2012 108(4):581–585
Ilies C, Bauer M, Berg P, Rosenberg J, Hedderich J, Bein B, Hinz J, Hanss R. Investigation of the agreement of a continuous noninvasive arterial pressure device in comparison with invasive radial artery measurement. Br J Anaesth 2012; 108(2): 202–210
Garnier RP, van der Spoel AG, Sibarani-Ponsen R, Markhorst DG, Boer C. Level of agreement between Nexfin non-invasive arterial pressure with invasive arterial pressure measurements in children. Br J Anaesth 2012; 109(4): 609–615
Martina JR, Westerhof BE, van Goudoever J, de Beaumont EM, Truijen J, Kim YS, Immink RV, Jöbsis DA, Hollmann MW, Lahpor JR, de Mol BA, van Lieshout JJ. Noninvasive continuous arterial blood pressure monitoring with Nexfin®. Anesthesiology 2012; 116(5): 1092–1103
Akkermans J, Diepeveen M, Ganzevoort W, van Montfrans GA, Westerhof BE, Wolf H. Continuous non-invasive blood pressure monitoring, a validation study of Nexfin in a pregnant population. Hypertens Pregnancy 2009; 28(2): 230–242
Eeftinck Schattenkerk DW, van Lieshout JJ, van den Meiracker AH, Wesseling KR, Blanc S, Wieling W, van Montfrans GA, Settels JJ, Wesseling KH, Westerhof BE. Nexfin noninvasive continuous blood pressure validated against Riva-Rocci/Korotkoff. Am J Hypertens 2009; 22(4): 378–383
Tanaka H, Thulesius O, Yamaguchi H, Mino M, Konishi K. Continuous non-invasive finger blood pressure monitoring in children. Acta Paediatr 1994; 83(6): 646–652
Sipkens LM, Treskes K, Ariese-Beldman K, Veerman DP, Boer C. Application of Nexfin noninvasive beat-to-beat arterial blood pressure monitoring in autonomic function testing. Blood Press Monit 2011; 16(5): 246–251
Martina JR, Westerhof BE, Van Goudoever J, De Jonge N, Van Lieshout JJ, Lahpor JR, De Mol BA. Noninvasive blood pressure measurement by the Nexfin monitor during reduced arterial pulsatility: a feasibility study. ASAIO J 2010; 56(3): 221–227
Siebig S, Rockmann F, Sabel K, Zuber-Jerger I, Dierkes C, Brünnler T, Wrede CE. Continuous non-invasive arterial pressure technique improves patient monitoring during interventional endoscopy. Int J Med Sci 2009; 6(1): 37–42
Chen G, Chung E, Meng L, Alexander B, Vu T, Rinehart J, Cannesson M. Impact of non invasive and beat-to-beat arterial pressure monitoring on intraoperative hemodynamic management. J Clin Monit Comput 2012; 26(2): 133–140
Lu Z, Mukkamala R. Continuous cardiac output monitoring in humans by invasive and noninvasive peripheral blood pressure waveform analysis. J Appl Physiol 2006; 101(2): 598–608
Rang S, de Pablo Lapiedra B, van Montfrans GA, Bouma BJ, Wesseling KH, Wolf H. Modelflow: a new method for noninvasive assessment of cardiac output in pregnant women. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2007; 196(3): 235 e1–8
Bogert LW, Wesseling KH, Schraa O, Van Lieshout EJ, de Mol BA, van Goudoever J, Westerhof BE, van Lieshout JJ. Pulse contour cardiac output derived from non-invasive arterial pressure in cardiovascular disease. Anaesthesia 2010; 65(11): 1119–1125
Broch O, Renner J, Gruenewald M, Meybohm P, Schöttler J, Caliebe A, Steinfath M, Malbrain M, Bein B. A comparison of the Nexfin® and transcardiopulmonary thermodilution to estimate cardiac output during coronary artery surgery. Anaesthesia 2012; 67(4): 377–383
van der Spoel AG, Voogel AJ, Folkers A, Boer C, Bouwman RA. Comparison of noninvasive continuous arterial waveform analysis (Nexfin) with transthoracic Doppler echocardiography for monitoring of cardiac output. J Clin Anesth 2012; 24(4): 304–309
Chen G, Meng L, Alexander B, Tran NP, Kain ZN, Cannesson M. Comparison of noninvasive cardiac output measurements using the Nexfin monitoring device and the esophageal Doppler. J Clin Anesth 2012; 24(4): 275–283
Fischer MO, Avram R, Cârjaliu I, Massetti M, Gérard JL, Hanouz JL, Fellahi JL. Non-invasive continuous arterial pressure and cardiac index monitoring with Nexfin after cardiac surgery. Br J Anaesth 2012; 109(4): 514–521
McCarthy T, Telec N, Dennis A, Griffiths J, Buettner A. Ability of non-invasive intermittent blood pressure monitoring and a continuous non-invasive arterial pressure monitor (CNAP™) to provide new readings in each 1-min interval during elective caesarean section under spinal anaesthesia. Anaesthesia 2012; 67(3): 274–279
Kemmotsu O, Ueda M, Otsuka H, Yamamura T, Okamura A, Ishikawa T, Winter DC, Eckerle JS. Blood pressure measurement by arterial tonometry in controlled hypotension. Anesth Analg 1991; 73(1): 54–58
Sato T, Nishinaga M, Kawamoto A, Ozawa T, Takatsuji H. Accuracy of a continuous blood pressure monitor based on arterial tonometry. Hypertension 1993; 21(6 Pt 1): 866–874
Weiss BM, Spahn DR, Rahmig H, Rohling R, Pasch T. Radial artery tonometry: moderately accurate but unpredictable technique of continuous non-invasive arterial pressure measurement. Br J Anaesth 1996; 76(3): 405–411
Kemmotsu O, Ohno M, Takita K, Sugimoto H, Otsuka H, Morimoto Y, Mayumi T. Noninvasive, continuous blood pressure measurement by arterial tonometry during anesthesia in children. Anesthesiology 1994; 81(5): 1162–1168
Harasawa K, Yamane M, Morimoto Y, Kemmotsu O. Performance of a tonometer for arterial pressure measurement during anesthesia in the elderly. J Anesth 2004; 18(4): 316–317
Papaioannou TG, Stamatelopoulos KS, Gialafos E, Vlachopoulos C, Karatzis E, Nanas J, Lekakis J. Monitoring of arterial stiffness indices by applanation tonometry and pulse wave analysis: reproducibility at low blood pressures. J Clin Monit Comput 2004; 18(2): 137–144
O’Rourke MF, Seward JB. Central arterial pressure and arterial pressure pulse: new views entering the second century after Korotkov. Mayo Clin Proc 2006; 81(8): 1057–1068
O’Rourke MF, Adji A. An updated clinical primer on large artery mechanics: implications of pulse waveform analysis and arterial tonometry. Curr Opin Cardiol 2005; 20(4): 275–281
Saugel B, Fassio F, Hapfelmeier A, Meidert AS, Schmid RM, Huber W. The T-Line TL-200 system for continuous non-invasive blood pressure measurement in medical intensive care unit patients. Intensive Care Med 2012; 38(9): 1471–1477
Szmuk P, Pivalizza E, Warters RD, Ezri T, Gebhard R. An evaluation of the T-Line Tensymeter continuous noninvasive blood pressure device during induced hypotension. Anaesthesia 2008; 63(3): 307–312
Poon CC, Zhang YT. Cuff-less and noninvasive measurements of arterial blood pressure by pulse transit time. Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc 2005; 6: 5877–5880
Ahlstrom C, Johansson A, Uhlin F, Länne T, Ask P. Noninvasive investigation of blood pressure changes using the pulse wave transit time: a novel approach in the monitoring of hemodialysis patients. J Artif Organs 2005; 8(3): 192–197
Fung P, Dumont G, Ries C, Mott C, Ansermino M. Continuous noninvasive blood pressure measurement by pulse transit time. Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc 2004; 1: 738–741
Lansdorp B, Ouweneel D, de Keijzer A, van der Hoeven JG, Lemson J, Pickkers P. Non-invasive measurement of pulse pressure variation and systolic pressure variation using a finger cuff corresponds with intra-arterial measurement. Br J Anaesth 2011; 107(4): 540–545
Monnet X, Dres M, Ferré A, Le Teuff G, Jozwiak M, Bleibtreu A, Le Deley MC, Chemla D, Richard C, Teboul JL. Prediction of fluid responsiveness by a continuous non-invasive assessment of arterial pressure in critically ill patients: comparison with four other dynamic indices. Br J Anaesth 2012; 109(3): 330–338
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chung, E., Chen, G., Alexander, B. et al. Non-invasive continuous blood pressure monitoring: a review of current applications. Front. Med. 7, 91–101 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11684-013-0239-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11684-013-0239-5