Abstract
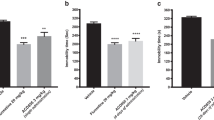
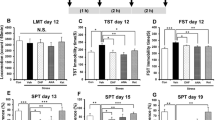
Ketamine exerts rapid and robust antidepressant properties in both animal models and depressed patients and tramadol possesses potential antidepressant effects. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) is an important biomarker for mood disorders and tropomyosin-related kinase B (TrkB) is a high affinity catalytic receptor for BDNF.We hypothesized that tramadol pretreatment might reinforce ketamine-elicited antidepressant effects with significant changes in hippocampal BDNF and TrkB levels in rats. Immobility time of rats receiving different treatment in the forced swimming test (FST) was observed. Levels of BDNF and TrkB in hippocampus were measured by enzyme linked immunosorbent assay. Results showed that tramadol (5 mg/kg) administrated alone neither elicited antidepressant effects nor altered BDNF or TrkB level. However, pretreatment with tramadol (5 mg/kg) enhanced the ketamine (10 mg/kg) -elicited antidepressant effects and upregulated the BDNF and TrkB levels in hippocampus. In conclusion, tramadol pretreatment reinforces the ketamine-elicited antidepressant effects, which is associated with the increased levels of BDNF and TrkB in rat hippocampus.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zarate CA Jr, Brutsche NE, Ibrahim L, Franco-Chaves J, Diazgranados N, Cravchik A, Selter J, Marquardt CA, Liberty V, Luckenbaugh DA. Replication of ketamine’s antidepressant efficacy in bipolar depression: a randomized controlled add-on trial. Biol Psychiatry 2012; 71(11): 939–946
Li N, Liu RJ, Dwyer JM, Banasr M, Lee B, Son H, Li XY, Aghajanian G, Duman RS. Glutamate N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonists rapidly reverse behavioral and synaptic deficits caused by chronic stress exposure. Biol Psychiatry 2011; 69(8): 754–761
Barber J. Examining the use of tramadol hydrochloride as an antidepressant. Exp Clin Psychopharmacol 2011; 19(2): 123–130
Yalcin I, Aksu F, Bodard S, Chalon S, Belzung C. Antidepressantlike effect of tramadol in the unpredictable chronic mild stress procedure: possible involvement of the noradrenergic system. Behav Pharmacol 2007; 18(7): 623–631
Hashimoto K. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor as a biomarker for mood disorders: an historical overview and future directions. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 2010; 64(4): 341–357
Russo-Neustadt A, Ha T, Ramirez R, Kesslak JP. Physical activityantidepressant treatment combination: impact on brain-derived neurotrophic factor and behavior in an animal model. Behav Brain Res 2001; 120(1): 87–95
Siuciak JA, Lewis DR, Wiegand SJ, Lindsay RM. Antidepressantlike effect of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF). Pharmacol Biochem Behav 1997; 56(1): 131–137
Garcia LS, Comim CM, Valvassori SS, Réus GZ, Barbosa LM, Andreazza AC, Stertz L, Fries GR, Gavioli EC, Kapczinski F, Quevedo J. Acute administration of ketamine induces antidepressant- like effects in the forced swimming test and increases BDNF levels in the rat hippocampus. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 2008; 32(1): 140–144
Castrén E, Võikar V, Rantamäki T. Role of neurotrophic factors in depression. Curr Opin Pharmacol 2007; 7(1): 18–21
Saarelainen T, Hendolin P, Lucas G, Koponen E, Sairanen M, MacDonald E, Agerman K, Haapasalo A, Nawa H, Aloyz R, Ernfors P, Castrén E. Activation of the TrkB neurotrophin receptor is induced by antidepressant drugs and is required for antidepressant- induced behavioral effects. J Neurosci 2003; 23(1): 349–357
Rantamäki T, Knuuttila JE, Hokkanen ME, Castrén E. The effects of acute and long-term lithium treatments on TrkB neurotrophin receptor activation in the mouse hippocampus and anterior cingulate cortex. Neuropharmacology 2006; 50(4): 421–427
Detke MJ, Rickels M, Lucki I. Active behaviors in the rat forced swimming test differentially produced by serotonergic and noradrenergic antidepressants. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1995; 121(1): 66–72
Porsolt RD, Le Pichon M, Jalfre M. Depression: a new animal model sensitive to antidepressant treatments. Nature 1977; 266(5604): 730–732
Jesse CR, Bortolatto CF, Savegnago L, Rocha JB, Nogueira CW. Involvement of L-arginine-nitric oxide-cyclic guanosine monophosphate pathway in the antidepressant-like effect of tramadol in the rat forced swimming test. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 2008; 32(8): 1838–1843
Beurel E, Song L, Jope RS. Inhibition of glycogen synthase kinase-3 is necessary for the rapid antidepressant effect of ketamine in mice. Mol Psychiatry 2011; 16(11): 1068–1070
Li N, Liu RJ, Dwyer JM, Banasr M, Lee B, Son H, Li XY, Aghajanian G, Duman RS. Glutamate N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonists rapidly reverse behavioral and synaptic deficits caused by chronic stress exposure. Biol Psychiatry 2011; 69(8): 754–761
Bamigbade TA, Davidson C, Langford RM, Stamford JA. Actions of tramadol, its enantiomers and principal metabolite, Odesmethyltramadol, on serotonin (5-HT) efflux and uptake in the rat dorsal raphe nucleus. Br J Anaesth 1997; 79(3): 352–356
Nishimura M, Sato K, Okada T, Yoshiya I, Schloss P, Shimada S, Tohyama M. Ketamine inhibits monoamine transporters expressed in human embryonic kidney 293 cells. Anesthesiology 1998; 88(3): 768–774
Markowitz JS, Patrick KS. Venlafaxine-tramadol similarities. Med Hypotheses 1998; 51(2): 167–168
Raffa RB, Friderichs E, Reimann W, Shank RP, Codd EE, Vaught JL. Opioid and nonopioid components independently contribute to the mechanism of action of tramadol, an “atypical” opioid analgesic. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 1992; 260(1): 275–285
Valverde O, Micó JA, Maldonado R, Mellado M, Gibert-Rahola J. Participation of opioid and monoaminergic mechanisms on the antinociceptive effect induced by tricyclic antidepressants in two behavioural pain tests in mice. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 1994; 18(6): 1073–1092
Nibuya M, Morinobu S, Duman RS. Regulation of BDNF and trkB mRNA in rat brain by chronic electroconvulsive seizure and antidepressant drug treatments. J Neurosci 1995; 15(11): 7539–7547
Machado-Vieira R, Yuan P, Brutsche N, DiazGranados N, Luckenbaugh D, Manji HK, Zarate CA Jr. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor and initial antidepressant response to an N-methyl-Daspartate antagonist. J Clin Psychiatry 2009; 70(12): 1662–1666
Faron-Górecka A, Kuśmider M, Inan SY, Siwanowicz J, Piwowarczyk T, Dziedzicka-Wasylewska M. Long-term exposure of rats to tramadol alters brain dopamine and alpha 1-adrenoceptor function that may be related to antidepressant potency. Eur J Pharmacol 2004; 501(1–3): 103–110
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, C., Li, X., Wang, N. et al. Tramadol reinforces antidepressant effects of ketamine with increased levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and tropomyosin-related kinase B in rat hippocampus. Front. Med. 6, 411–415 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11684-012-0226-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11684-012-0226-2