Abstract
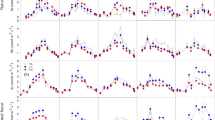
Nitrogen (N) deposition to alpine forest ecosystems is increasing gradually, yet previous studies have seldom reported the effects of N inputs on soil CO2 flux in these ecosystems. Evaluating the effects of soil respiration on N addition is of great significance for understanding soil carbon (C) budgets along N gradients in forest ecosystems. In this study, four levels of N (0, 50, 100, 150 kg N ha−1 a−1) were added to soil in a Picea baifouriana and an Abies georgei natural forest on the Tibetan Plateau to investigate the effect of the N inputs on soil respiration. N addition stimulated total soil respiration (Rt) and its components including heterotrophic respiration (Rh) and autotrophic respiration (Ra); however, the promoted effects declined with an increase in N application in two coniferous forests. Soil respiration rate was a little greater in the spruce forest (1.05 μmol CO2 m−2 s−1) than that in the fir forest (0.97 μmol CO2 m−2 s−1). A repeated measures ANOVA indicated that N fertilization had significant effects on Rt and its components in the spruce forest and Rt in the fir forest, but had no obvious effect on Rh or Ra in the fir forest. Rt and its components had significant exponential relationships with soil temperature in both forests. N addition also increased temperature sensitivity (Q10) of Rt and its components in the two coniferous forests, but the promotion declined as N in put increased. Important, soil moisture had great effects on Rt and its components in the spruce forest (P < 0.05), but no obvious impacts were observed in the fir forest (P > 0.05). Following N fertilization, Ra was significantly and positively related to fine root biomass, while Rh was related to soil enzymatic activities in both forests. The mechanisms underlying the effect of simulated N deposition on soil respiration and its components in this study may help in forecasting C cycling in alpine forests under future levels of reactive N deposition.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson TH (1998) The influence of acid irrigation and liming on the soil microbial biomass in a Norway spruce (Picea abies [L.] K.) stand. Plant Soil 199:117–122
Bowden RD, Davidson E, Savage K, Arabia C, Steudler P (2004) Chronic nitrogen additions reduce total soil respiration and microbial respiration in temperate forest soils at the Harvard Forest. For Ecol Manag 196:43–56
Buchmann N (2000) Biotic and abiotic factors controlling soil respiration rates in Picea abies stands. Soil Biol Biochem 32:1625–1635
Burton AJ, Pregitzer KS, Crawford JN, Zogg GP, Zak DR (2004) Simulated chronic NO3 − deposition reduces soil respiration in northern hardwood forests. Global Chang Biol 10:1080–1091
Chen BY, Liu SR, Ge JP, Chu JX (2010) Annual and seasonal variations of Q 10 soil respiration in the sub-alpine forests of the eastern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, China. Soil Biol Biochem 42:1735–1742
Dai M, Zhang ZM, Zhao Y, Hu MJ (2015) The difference of soil respiration for typical forest ecosystems in China. J Central China Norm Univ (Natl Sci) 49:237–245 (in Chinese)
Davidson E, Belk E, Boone RD (1998) Soil water content and temperature as independent or confounded factors controlling soil respiration in a temperate mixed hardwood forest. Glob Chang Biol 4:217–227
Davidson EA, Ishida FY, Nepstad DC (2004) Effects of an experimental drought on soil emissions of carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and nitric oxide in a moist tropical forest. Glob Chang Biol 10:718–730
Detwiler RP, Charles ASH (1988) Tropical forests and the global carbon cycle. Science 239:42–47
Eivazi F, Tabatabai M (1988) Glucosidases and galactosidases in soils. Soil Biol Biochem 20:601–606
Fang JY, Zhu JL, Wang SP, Yue C, Shen HH (2011) Global warming, human-induced carbon emissions, and their uncertainties. Sci China Earth Sci 54:1458–1468
Fang H, Cheng S, Yu G, Zheng J, Zhang P, Xu M, Li Y, Yang X (2012) Responses of CO2 efflux from an alpine meadow soil on the Qinghai Tibetan Plateau to multi-form and low-level N addition. Plant Soil 351:177–190
Galloway JN, Cowling EB (2002) Reactive nitrogen and the world: 200 years of change. AMBIO J Hum Environ 31:64–71
Gao W, Huang Z, Ye G, Yue X, Chen Z (2017) Effects of forest cover types and environmental factors on soil respiration dynamics in a coastal sand dune of subtropical China. J For Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11676-017-0565-6
Guan S, Zhang D, Zhang Z (1986) Soil enzyme and its research methods. Agricultural Press, Beijing, pp 291–294 (in Chinese)
Hanson PJ, Edwards NT, Garten CT, Andrews JA (2000) Separating root and soil microbial contributions to soil respiration: a review of methods and observations. Biogeochemistry 48:115–146
Holland EA, Braswell BH, Sulzman J, Lamarque JF (2005) Nitrogen deposition onto the United States and Western Europe: synthesis of observations and models. Ecol Appl 15:38–57
Hu H, Hu T, Sun L (2016) Spatial heterogeneity of soil respiration in a Larix gmelinii forest and the response to prescribed fire in the Greater Xing’an Mountains, China. J For Res 27:1–10
Huang S, Li J, Ye G, Nie S, Chen Z, Huang L (2014) Response of respiraiton of different components to nitrogen addition in a Castanea mollissima plantation. Sci Soil Water Conserv 12:95–100 (in Chinese)
Janssens IA, Dieleman W, Luyssaert S, Subke J-A, Reichstein M, Ceulemans R, Ciais P, Dolman AJ, Grace J, Matteucci G, Papale D, Piao SL, Schulze E-D, Tang J, Law BE (2010) Reduction of forest soil respiration in response to nitrogen deposition. Nat Geosci 3:315–322
Jassal RS, Black TA, Roy R, Ethier G (2011) Effect of nitrogen fertilization on soil CH4 and N2O fluxes, and soil and bole respiration. Geoderma 162:182–186
Jiang J, Zong N, Song M, Shi P, Ma W, Fu G, Shen Z, Zhang X, Ouyang H (2013) Responses of ecosystem respiration and its components to fertilization in an alpine meadow on the Tibetan Plateau. Eur J Soil Biol 56:101–106
Jiang J, Shi P, Zong N, Fu G, Shen Z, Zhang X, Song M (2015) Climatic patterns modulate ecosystem and soil respiration responses to fertilization in an alpine meadow on the Tibetan Plateau, China. Ecol Res 30:3–13
Lee KH, Jose S (2003) Soil respiration, fine root production, and microbial biomass in cottonwood and loblolly pine plantations along a nitrogen fertilization gradient. For Ecol Manag 185:263–273
Liu XJ, Lei Duan, Mo JM, Du EZ, Shen JL, Lu XK, Zhang Y, Zhou XB, He CE, Zhang FS (2011) Nitrogen deposition and its ecological impact in China: an overview. Environ Pollut 159:2251–2264
Liu Q, Zhao C, Cheng X, Yin H (2015) Soil respiration and carbon pools across a range of spruce stand ages, eastern Tibetan Plateau. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 61:440–449
Lo CM, Morillas L, Ochoahueso R, Munzi S, Roales J, Hasselquist NJ, Manrique E, Spano D, Jaoudé RA, Mereu S (2017) Contrasting effects of nitrogen addition on soil respiration in two mediterranean ecosystems. Environ Sci Pollut R 2017:1–12
Ma HP, Guo QQ, Li JR, Zhou CN (2016) Soil Respiration and its affecting factors relative to type of forest in the Sygera Mountains of Southeast Tibetan Plateau. Acta Pedol Sin 53:253–260 (in Chinese)
Mo J, Zhang W, Zhu W, Gundersen P, Fang Y, Li D, Wang H (2008) Nitrogen addition reduces soil respiration in a mature tropical forest in southern China. Glob Chang Biol 14:403–412
Peng S, Shilong P, Tao W, Sun J, Shen Z (2009) Temperature sensitivity of soil respiration in different ecosystems in China. Soil Biol Biochem 41:1008–1014
Post WM, Emanuel WR, Zinke PJ, Stangenberger AG (1982) Soil carbon pools and world life zones. Nature 298:156–159
Pregitzer KS, King JS, Burton AJ, Brown SE (2000) Responses of tree fine roots to temperature. New Phytol 147:105–115
Raich J, Schlesinger WH (1992) The global carbon dioxide flux in soil respiration and its relationship to vegetation and climate. Tellus B 44:81–99
Rayment MB, Jarvis PG (2000) Temporal and spatial variation of soil CO2 efflux in a Canadian boreal forest. Soil Biol Biochem 32:35–45
Ren F, Yang X, Zhou H, Zhu W, Zhang Z, Chen L, Gao G, He J (2017) Corrigendum: contrasting effects of nitrogen and phosphorus addition on soil respiration in an alpine grassland on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Sci Rep-UK 6:34786
Rodeghiero M, Cescatti A (2005) Indirect partitioning of soil respiration in a series of evergreen forest ecosystems. Plant Soil 284:7–22
Shi PL, Zhang XZ, Zhong ZM, Ouyang H (2006) Diurnal and seasonal variability of soil CO2 efflux in a cropland ecosystem on the Tibetan Plateau. Agric For Meteorol 137:220–233
Stursova M, Crenshaw CL, Sinsabaugh RL (2006) Microbial responses to long-term N deposition in a semiarid grassland. Microb Ecol 51:90–98
Sun ZZ, Liu LL, Ma YC, Yin GD, Zhao C, Zhang Y, Piao SL (2014) The effect of nitrogen addition on soil respiration from a nitrogen-limited forest soil. Agric For Meteorol 197:103–110
Tian HQ, Chen GS, Zhang C, Melillo JM, Hall CAS (2010) Pattern and variation of C:N: P ratios in China’s soils: a synthesis of observational data. Biogeochemistry 98:139–151
Tu LH, Hu TX, Zhang J, Li XW, Hu HL, Liu L, Xiao YL (2013) Nitrogen addition stimulates different components of soil respiration in a subtropical bamboo ecosystem. Soil Biol Biochem 58:255–264
Wang J (2017) The effects of changing environment on soil respiration and its components in the spruce and fir forests in Tibet Plateau. University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Doctoral Dissertation) (in Chinese)
Wang J, Wang GX, Hu ZY (2017) Short-term effect of nitrogen addition on microbial and root respiration in an alpine spruce ecosystem. Int J Bioautomat 21:145–159
Widén B (2002) Seasonal variation in forest-floor CO2 exchange in a Swedish coniferous forest. Agr Forest Meteorol 111:283–297
Xu Z, Tang S, Xiong L, Yang W, Yin H, Tu L, Wu H, Chen L, Tan B (2015a) Temperature sensitivity of soil respiration in China’s forest ecosystems: patterns and controls. Appl Soil Ecol 93:105–110
Xu Z, Zhou F, Yin H, Liu Q (2015b) Winter soil CO2 efflux in two contrasting forest ecosystems on the eastern Tibetan Plateau, China. J For Res 26:1–8
Yuan YL, Si GC, Wang J, Luo TX, Zhang GX (2014) Bacterial community in alpine grasslands along an altitudinal gradient on the Tibetan Plateau. Eur J Soil Sci 66:1033–1043
Zhang W, Parker K, Luo Y, Wan S, Wallace L, Hu S (2005) Soil microbial responses to experimental warming and clipping in a tallgrass prairie. Glob Chang Biol 11:266–277
Zhang Y, Duan B, Xian JR, Korpelainen H, Li CY (2011) Links between plant diversity, carbon stocks and environmental factors along a successional gradient in a subalpine coniferous forest in Southwest China. For Ecol Manag 262:361–369
Zhang CP, Niu DC, Hall SJ, Wen HY, Li XD, Fu H, Wan CG, Elser JJ (2014) Effects of simulated nitrogen deposition on soil respiration components and their temperature sensitivities in a semiarid grassland. Soil Biol Biochem 75:113–123
Zhao N, Meng P, Yu X (2017) Separating component parts of soil respiration under Robinia pseudoacacia plantation in the Taihang Mountains, China. J For Res 28:529–537
Zhou X, Zhang Y (2014) Seasonal pattern of soil respiration and gradual changing effects of nitrogen addition in a soil of the Gurbantunggut Desert, northwestern China. Atmos Environ 85:187–194
Zhou X, Zhang Y, Downing A (2012) Non-linear response of microbial activity across a gradient of nitrogen addition to a soil from the Gurbantunggut Desert, northwestern China. Soil Biol Biochem 47:67–77
Zhou LY, Zhou XH, Shao JJ, Nie YY, He YH, Jiang LL, Wu ZT, Bai SH (2016) Interactive effects of global change factors on soil respiration and its components: a meta-analysis. Glob Chang Biol. https://doi.org/10.1111/gcb.13253
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the Chinese Academy of Sciences Key Research Project for Frontier Science (QYZDJ-SSW-DQC006) and by the “Strategic Priority Research Program” of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (XDA01020304). We thank the Southeast Tibet Station for Alpine Environment, Observation and Research, Chinese Academy of Sciences for its great support. We are also very grateful to the anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Project funding: This research was supported by the Chinese Academy of Sciences Key Research Project for Frontier Science (QYZDJ-SSW-DQC006) and by the “Strategic Priority Research Program” of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (XDA01020304).
The online version is available at http://www.springerlink.com
Corresponding editor: Chai Ruihai.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J., Wang, G., Fu, Y. et al. Short-term effects of nitrogen deposition on soil respiration components in two alpine coniferous forests, southeastern Tibetan Plateau. J. For. Res. 30, 1029–1041 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11676-018-0678-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11676-018-0678-6