Abstract
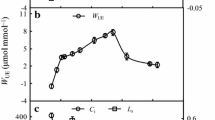
We investigated the combined effects of soil moisture and light intensity on the growth, development and ecophysiological characteristics of one-year old Amorpha fruticosa seedlings. Soil moisture and light intensity influenced the ecophysiological characteristics of Amorpha fruticosa seedlings. Soil moisture resulted in the decreases of growth rate, individual size, net photosynthetic rate, transpiration rate, leaf water loss rate (WLR), and biomass accumulation of plant parts, and led to increased leaf water saturation deficit (WSD). Under water stress, more photosynthetic products were allocated to root growth. With decreasing light intensity, net photosynthetic rate, transpiration rate, chla/b, water saturation deficit, water use efficiency, water loss rate and biomass accumulation declined, while Chla, Chlb, Chla+b and carotenoids (Car) increased and more photosynthetic products were allocated to stem and leaf growth. Maximum growth vigor, net photosynthetic rate and total biomass accumulation in Amorpha fruticosa seedlings was recorded at 75–80% soil water-holding capacity and 100% light density in greenhouse environments.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berry JA, Downton WJS. 1982. Environmental regulation of photosynthesis. In: Govindjee (ed.), Photosynthesis. New York: Academic Press, 263–343.
Bertamini M, Neduncheanian N. 2003. Photoinhibition of photosynthesis in mature and young leaves of grapevine. Plant Science, 164(4): 635–644.
Guo WH, Li B, Zhang XS, Wang RQ. 2007. Architectural plasticity and growth responses of Hippophae rhamnoides and Caragana intermedia seedlings to simulated water stress. Journal of Arid Environments, 69: 385–399.
Guo XY, Yang YF, Li JD. 2003. Research on photosynthetic characteristics of reed in different dry habitats of Songnen plain. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 12(3): 16–21.
He CX, Li JY, Guo M, Wang YT, Chen C. 2008. Changes of leaf photosynthetic characteristics and water use efficiency along tree height of four tree species. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 28(7): 3008–3016.
Huang J, Guo SR, Wu Z, Huang J, Guo SR, Wu Z, Li SJ. 2007. Effects of weak light on photosynthetic characteristics and chloroplast ultrastructure of non-heading Chinese cabbage. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, l8(2): 352–358 (in Chinese).
Ji WD, Shi GX, Yang HY, Xu QS, Xu Y, Zhang H. 2007. Effects of Cu2+ stress on leaf physiological indice and ultrastructure of Potamogeton malaianus. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 18(12): 2727–2732.
Jin J, Zhong ZC, Liu JC, He YJ. 2005. Response of the phenotypic plasticity of Cajannus cajan seedlings to relative soil water content in limestone areas. Journal of Southwest Agricultural University (Natural Science), 27(1): 89–92.
Krause GH. 1988. Photoinhibition of photosynthesis-An evaluation of damaging and protective mechanisms. Physiologia Plantarum, 74: 566–574.
Lichtenthaler HK, Wellburn AR. 1983. Determination of total carotenoids and chlorophylls a and b of leaf extracts in different solvents. Biochemical Society Transactions, 11: 591–592.
Li JY, Zhou P, Zhao LJ. 2002. Influence of drought stress on transpiring water-consumption of seedlings. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 22(9): 1380–1386.
Ma JY, Zhou R, Cheng BS. 1997. The relationship between Carotenoids and reactive nitrogen metabolism. Journal of Shandong Agricultural University, 28(4): 518–522.
Pell EJ, Sinn JP, Eckardt N, Johansen CV, Winner WE, Mooney HA. 1993. Response of radish to multiple stresses. II. Influence of season and genotype on plant response to ozone and soil moisture deficit. New Phytologist, 123(l): 153–163.
Tjus SE, Moiler BL, Scheller HV. 1999. Photoinhibition of photosystem I damage both reaction center proteins PS I-A and PS I-B and acceptor side located small photosystem I polypeptides. Photosynthesis Research, 60: 75–86.
Wang M, Tao DL. 1998. Drought-tolerance of main tree species in Changbai Mountain. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 9(1): 7–10.
Willekens H, Camp WV, Montagu MV, Inze D, Langebartels C, Jr HS. 1994. Ozone, sulfur dioxide and ultraviolet-B have similar effects on mRNA accumulation of antioxidant genes in Nicotiana plumbaginifolia L. Plant Physiol, 106: 1007–1014.
Xiao DM, Wang M, Ji LZ. 2004. Influence of water stress on growth and biomass allocation of dominant tree species in mixed forest of broad-leaved and Korean pine at Changbai Mountain. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 23(5): 93–97.
Yamamoto HY. 1975. Biochemistry of the violaxanthin cycle in higher plants. Pure and Applied Chemistry, 51: 639–648.
Yang YF, Li JD. 2003. Biomass allocation and growth analysis on the ramets of Phragmites ammumis populations in different habitats in the Songnen Plains of China. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 14(1): 30–34.
Zhang SQ, Shan L. 2002. Plant water use efficiency and its research progress. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas, 20(4): 1–5.
Zhang SR, Gao RF, Wang LJ. 2004. Response of oxygen evolution activity of photosystemII, photosynthetic pigments and chloroplast ultrastructure of hybrid poplar clones to light stress. Acta Phytoecologica Sinica, 28(2): 143–149.
Zhang XF, Yu XC, Zhang ZX. 2002. Effect of soil water on the growth and physiological characteristics of grafted and non-grafted cucumber in greenhouse. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, l3(11): 1399–1402 (in Chinese)
Zhang XZ. 1989. Experimental techniques in plant physiology. Shenyang: Liaoning Science and Technology Press, 47–48.
Zhang YL, Zhang XQ, Wang RQ. 2005. Preliminary studies on the flora in the Luzhong Mountains. Journal of Shandong Forestry Science and Technology, 34(1): 1–5.
Zhang ZA, Zhang MS, Wei RH. 2004. Experimental guide of plant Physiology. Beijing: Chinese Agricultural Science and Technology Press, 64–68
Zhao LJ, Li JY, Yu JF, Bertin S. 2003. Daily variation in transpiring water-consumption rates of seedlings in different drought stress. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 25(3): 42–47.
Zheng SH, Yang CR. 2006. The ecophysiological and morphological characteristics of maize in seedling stage under water stress. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 26(4): 1138–1143.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Fund project: This work was financially supported by National Science Foundation of China (No.31270374), Independent Innovation Foundation of Shandong University (No.2011DX008) and Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province, China (No.2009ZRB01875; ZR2010CM062).
The online version is available at http://www.springerlink.com
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Xr., Tan, Xf., Wang, Rq. et al. Effects of soil moisture and light intensity on ecophysiological characteristics of Amorpha fruticosa seedlings. Journal of Forestry Research 24, 293–300 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11676-013-0352-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11676-013-0352-y