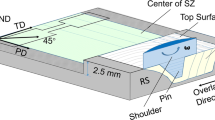
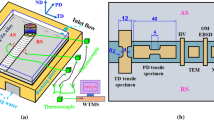
Abstract
Ten-millimeter-thick strain-hardened AZ31B-H24 magnesium sheets were subjected to friction stir processing (FSP) in air and submerged friction stir processing (SFSP) under water to investigate their microstructures and microhardness properties. Different rotational speeds of 500, 630, 800, and 1000 rpm and traverse speeds of 50, 100, 200, and 350 mm/min were employed for processing the materials. For SFSPed samples, the rotational speed of 500 rpm and 200 mm/min of traverse speed resulted in an ultra-fine-grained structure with a minimum grain size of about 400-500 nm, which is half compared to that of FSPed. It was found that both processes led to variation of crystallographic orientation, and enhancing the rotational speed and lowering the traverse speed promoted the development of a {0002} basal texture. The microhardness of SFSPed material increased significantly up to 110% (~ 95 Hv), while the microhardness was 45% (~ 65 Hv) higher than the base metal (~ 45 Hv) for FSPed material.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
S.H. Chowdhury, D.L. Chen, S.D. Bhole, X. Cao, and P. Wanjara, Friction Stir Welded AZ31 Magnesium Alloy: Microstructure, Texture, and Tensile Properties, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2013, 44(A), p 323–336
Y. Morisada, H. Fujii, T. Nagaoka, and M. Fukusumi, Nanocrystallized Magnesium Alloy—Uniform Dispersion of C60 Molecules, Scr. Mater., 2006, 55, p 1067–1070
C.J. Lee and J.C. Huang, High Strain Rate Super Plasticity of Mg Based Composites Fabricated by Friction Stir Processing, Mater. Trans., 2006, 47, p 2773–2778
T.A. Samman and G. Gottstein, Dynamic Recrystallization During High Temperature Deformation of Magnesium, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2008, 490, p 411–420
J.Q. Su, T.W. Nelson, and C.J. Sterling, Friction Stir Processing of Large-Area Bulk UFG Aluminum Alloys, Scr. Mater., 2005, 52, p 135–140
H.S. Arewal, H.S. Singh, S. Singh, B.K. Dhindaw, D. McPhail, B. Shollock, R. Chater, and S. Mukherjee, Microstructure-Property Relationship for Friction Stir Processed Magnesium Alloy, Adv. Eng. Mater., 2014, 16(1), p 94–102
B. Mansoor and A.K. Ghosh, Microstructure and Tensile Behavior of a Friction Stir Processed Magnesium Alloy, Acta Mater., 2012, 60(13–14), p 5079–5088
C.W. Yang, Effect of Friction Stir Processing on the Microstructural Evolution and Tensile Behaviors of an α/β Dual-Phase Mg-Li-Al-Zn Alloy, Mater. Trans., 2014, 55(2), p 371–377
J. Chen, H. Fujii, Y. Sun, Y. Morisada, and R. Ueji, Fine Grained Mg-3Al-1Zn Alloy with Randomized Texture in the Double-Sided Friction Stir Welded Joints, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2013, 580, p 83–91
R. Xin, D. Liu, B. Li, L. Sun, Z. Zhou, and Q. Liu, Mechanisms of Fracture and Inhomogeneous Deformation on Transverse Tensile Test of Friction-Stir-Processed AZ31 Mg Alloy, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2013, 565, p 333–341
B.M. Darras, M.K. Khraisheh, F.K. Abu-Farha, and M.A. Omar, Friction Stir Processing of Commercial AZ31 Magnesium Alloy, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2007, 191, p 77–81
C.I. Chang, X.H. Du, and J.C. Huang, Achieving Ultrafine Grain Size in Mg-Al-Zn Alloy by Friction Stir Processing, Scr. Mater., 2007, 57, p 209–212
H. Zhang and H. Liu, Characteristics and Formation Mechanisms of Welding Defects in Underwater Friction Stir Welded Aluminum Alloy, Metall. Microsc. Anal., 2012, 1, p 269–281
M.A. Wahid, Z.A. Khan, and A.N. Siddiquee, Review on Underwater Friction Stir Welding: A Variant of Friction Stir Welding with Great Potential of Improving Joint Properties, Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China, 2018, 28, p 193–219
N. Bhadouria, L. Thakur, P. Kumar, and N. Arora, An Investigation of Normal and Submerged Condition on Microstructural and Tribological Properties of Friction Stir Processed AZ91-D Magnesium Alloy, Can. J. Metall. Mater. Sci., Can. Metall. Q., 2017, 56, p 94–103
G. Cao and D. Zhang, Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Submerged Friction Stir Processing Mg-Y-Nd Alloy, Mater. Sci. Forum, 2015, 816, p 404–410
S. Benavides, Y. Li, L.E. Murr, D. Brown, and J.C. Mcclurr, Low-Temperature Friction-Stir Welding of 2024 Aluminum, Scr. Mater., 1999, 41, p 809–815
K.S. Wang, J.L. Wu, W. Wang, L.H. Zhou, Z.X. Lin, and L. Kong, Underwater Friction Stir Welding of Ultrafine Grained 2017 Aluminum Alloy, J. Cent. South Univ., 2012, 19(8), p 2081–2085
X. Feng, H. Liu, and J.C. Lippold, Microstructure Characterization of the Stir Zone of Submerged Friction Stir Processed Aluminum Alloy 2219, Mater. Charact., 2013, 82, p 97–102
M.A. Mofid, A. Abdollah-Zadeh, F. Malek Ghaini, and C. Hakan Gur, Submerged Friction-Stir Welding (SFSW) Underwater and Under Liquid Nitrogen: An Improved Method to Join Al Alloys to Mg Alloys, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2012, 43(13), p 5106–5114
B. Darras and E. Kishta, Submerged Friction Stir Processing of AZ31 Magnesium Alloy, Mater. Des., 2013, 47, p 133–137
F. Chai, D. Zhang, and Y. Li, Microstructures and Tensile Properties of Submerged Friction Stir Processed AZ91 Magnesium Alloy, J. Magn. Alloys, 2015, 3, p 203–209
G.K. Padhy, C.S. Wu, and S. Gao, Friction Stir Based Welding and Processing Technologies-Processes, Parameters, Microstructures and Applications: A Review, Mater. Sci. Technol., 2018, 34, p 1–38
M.J. Zehetbauer and Y.T. Zhu, Ed., Bulk Nanostructured Materials, Wiley, Weinheim, 2009
J.C. Huang, I.C. Hsiao, T.D. Wang, and B.Y. Lou, EBSD Study on Grain Boundary Characteristics in Fine-Grained Al Alloys, Scr. Mater., 2000, 43, p 213–217
A.J. Ardell, Precipitation Hardening, Metall. Trans. A, 1985, 16, p 2131–2165
C.G. Rhodes, M.W. Mahoney, W.H. Bingel, and M. Calabrese, Fine-Grain Evolution in Friction-Stir Processed 7050 Aluminum, Scr. Mater., 2003, 48, p 1451–1455
Y.N. Wang, C.I. Chang, C.J. Lee, H.K. Lin, and J.C. Huang, Texture and Weak Grain Size Dependence in Friction Stir Processed Mg-Al-Zn Alloy, Scr. Mater., 2006, 55, p 637–640
S. Goel, G. Naveen, A. Gupta, and P. Gulati, Effect of Process Parameters on Mechanical and Metallurgical Properties of Friction Stir Processed AZ31 Mg Alloy, Mater. Today Proc., 2018, 5, p 4575–4583
W.Y. Li, T. Fu, L. Hütsch, J. Hilgert, F.F. Wang, J.F. dos Santos, and N. Huber, Effects of Tool Rotational and Welding Speed on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Bobbin-Tool Friction-Stir Welded Mg AZ31, Mater. Des., 2014, 64, p 714–720
Y.N. Wang and J.C. Huang, Transition of Dominant Diffusion Process During Superplastic Deformation in AZ61 Magnesium Alloys, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2002, 35(2), p 555–562
C.I. Chang, C.J. Lee, and J.C. Hung, Relationship Between Grain Size and Zener–Holloman Parameter During Friction Stir Processing in AZ31 Mg Alloys, Scr. Mater., 2004, 51, p 509–514
M. Jones, P. Heurtier, C. Desrayaud, F. Montheillet, D. Allehaux, and J. Driver, Correlation Between Microstructure and Microhardness in a Friction Stir Welded 2024 Aluminium Alloy, Scr. Mater., 2005, 52, p 693–697
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shahnam, A., Karimzadeh, F., Golozar, M.A. et al. Microstructure Evolution of Ultra-Fine-Grained AZ31 B Magnesium Alloy Produced by Submerged Friction Stir Processing. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 28, 4593–4601 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-019-04198-6
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-019-04198-6