Abstract
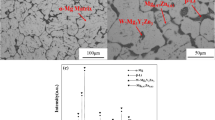
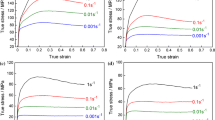
Hot deformation behavior of the cast-homogenized Mg-6.0Zn-0.5Mn-0.5Er alloy was studied using dynamic recrystallization (DRX) kinetic model and processing map. The compressing tests were conducted in the temperature range of 250-450 °C and strain rates of 0.001-1 s−1. According to the evolution of microstructures, under lower strain rates, the main DRX mechanism of Mg-6.0Zn-0.5Mn-0.5Er alloy is continuous DRX (CDRX); twinning induced DRX (TDRX) and CDRX both become the main DRX mechanism under higher strain rates. The DRX kinetics model of Mg-6.0Zn-0.5Mn-0.5Er alloy is calculated as \(X_{\text{DRX}} = 1 - \exp \left[ { - 1.9463\left( {\frac{{\varepsilon - \varepsilon_{\text{c}} }}{{\varepsilon^{*} }}} \right)^{1.4608} } \right]\), which is corresponding to the microstructure evolutions of DRX under different deformation conditions. The contour map of DRX was proposed based on the calculation results of DRX kinetics model. The processing maps are constructed to predict processing parameters of the alloy, and the predictability was evaluated combining with the contour map of DRX and dynamic materials model (DMM) processing map. It is deduced from the microstructures evolution and processing map that the optimum processing domain is mainly at 380-450 °C and 0.01-0.001 s−1, and 410-420 °C and 0.01-1 s−1.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Abbasi, A. Abdollahzadeh, B. Bagheri, and H. Omidvar, The Effect of SIC Particle Addition During FSW on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of AZ31 Magnesium Alloy, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2015, 24, p 5037–5045
Z.L. Liu, Y. Liu, X.Q. Liu, and M.M. Wang, Effect of Minor Zn Additions on the Mechanical and Corrosion Properties of Solution-Treated AM60-2%Re Magnesium Alloy, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2016, 25, p 2855–2865
M. Shalbafi, R. Roumina, and R. Mahmudi, Hot Deformation of the Extruded Mg-10Li-1Zn Alloy: Constitutive Analysis and Processing Maps, J. Alloys Compd., 2017, 696, p 1269–1277
B. Inem, Dynamic Recrystallization in a Thermomechanically Processed Metal Matrix Composite, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 1995, 197, p 91–95
T.Y. Kwak, H.K. Lim, and W.J. Kim, Hot Compression Characteristics and Processing Maps of a Cast Mg-9.5Zn-2.0Y Alloy with Icosahedral Quasicrystalline Phase, J. Alloys Compd., 2015, 644, p 645–653
N. Tahreen, D.F. Zhang, F.S. Pan, X.Q. Jiang, D.Y. Li, and D.L. Chen, Hot Deformation and Processing Map of an As-Extruded Mg-Zn-Mn-Y Alloy Containing I, and W Phases, Mater. Design., 2015, 87, p 245–255
H. Zhou, Q.D. Wang, B. Ye, and W. Guo, Hot Deformation and Processing Maps of As-Extruded Mg-9.8Gd-2.7Y-0.4Zr Mg Alloy, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2013, 576, p 101–107
X.H. Chen, X.L. Wang, and Z.H. Zhang, Research Status of Dynamic Recrystallization of Magnesium Alloys, Ordnance Mater. Sci. Eng., 2013, 36, p 148–152
C.M. Liu, Z.J. Liu, X.R. Zhu, and H.T. Zhou, Research and Development Progress of Dynamic Recrystallization in Pure Magnesium and Its Alloys, Trans. Nonferrous Metal. Soc., 2006, 16, p 1–12
B.J. Lv, J. Peng, D.W. Shi, A.T. Tang, and F.S. Pan, Constitutive Modeling of Dynamic Recrystallization Kinetics and Processing Maps of Mg-2.0Zn-0.3Zr Alloy Based on True Stress–Strain Curves, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2013, 560, p 727–733
B.J. Lv, J. Peng, Y.J. Wang, X.Q. An, L.P. Zhong, A.T. Tang, and F.S. Pan, Dynamic Recrystallization Behavior and Hot Workability of Mg-2.0Zn-0.3Zr-0.9Y Alloy by Using Hot Compression Test, Mater. Des, 2014, 53, p 357–365
B.J. Lv, J. Peng, Y. Peng, A.T. Tang, and F.S. Pan, The Effect of LPSO Phase on Hot Deformation Behavior and Dynamic Recrystallization Evolution of Mg-2.0 Zn-0.3 Zr-5.8 Y Alloy, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2013, 579, p 209–216
B.J. Lv, J. Peng, L.L. Zhu, Y.J. Wang, and A.T. Tang, The Effect of 14H LPSO Phase on Dynamic Recrystallization Behavior and Hot Workability of Mg-2.0Zn-0.3Zr-5.8Y Alloy, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2014, 599, p 150–159
B.J. Lv, J. Peng, and Z. Chu, The Effect of Icosahedral Phase on Dynamic Recrystallization Evolution and Hot Workability of Mg-2.0Zn-0.3Zr-0.2Y Alloy, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2015, 24, p 3502–3512
B. Chen and J. Zhang, Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of ZK60-Er Magnesium Alloys, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2015, 633, p 154–160
Q. Wang, K. Liu, Z. Wang, S. Li, and W. Du, Microstructure, Texture and Mechanical Properties of As-Extruded Mg-Zn-Er Alloys Containing W-Phase, J. Alloys Compd., 2014, 602, p 32–39
J. Zhang, B. Chen, and C. Liu, An Investigation of Dynamic Recrystallization Behavior of ZK60-Er Magnesium Alloy, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2014, 612, p 253–266
C.C. Sun, K. Liu, Z.H. Wang, S.B. Li, X. Du, and W.B. Du, Hot Deformation Behaviors and Processing Maps of Mg-Zn-Er Alloys Based on Gleeble-1500 Hot Compression Simulation, Trans. Nonferrous Metal. Soc., 2016, 26, p 3123–3134
T. Sakai and J.J. Jonas, Overview No. 35 Dynamic Recrystallization: Mechanical and Microstructural Considerations, Acta Mater., 1984, 32, p 189–209
X. Kai, Z. Li, G. Fan, Q. Guo, Z. Tan, W. Zhang, Y. Su, W. Lu, W.J. Moon, and D. Zhang, Strong and Ductile Particulate Reinforced Ultrafine-Grained Metallic Composites Fabricated by Flake Powder Metallurgy, Scr. Mater., 2013, 68, p 555–558
A. Laasraoui and J.J. Jonas, Prediction of Steel Flow Stresses at High Temperatures and Strain Rates, Metall. Trans. A, 1991, 22, p 1545–1558
C. Roucoules, S. Yue, and J.J. Jonas, Effect of Alloying Elements on Metadynamic Recrystallization in HSLA Steels, Metall. Trans. A, 1995, 26, p 181–190
C.M. Sellars, Modelling Microstructural Development During Hot Rolling, Mater. Sci. Technol. Lond., 2013, 6, p 1072–1081
Y. Cai, L. Wan, Z.H. Guo, C.Y. Sun, D.J. Yang, Q.D. Zhang, and Y.L. Li, Hot Deformation Characteristics of AZ80 Magnesium Alloy: Work Hardening Effect and Processing Parameter Sensitivities, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2017, 687, p 113–122
Y. Xu, L. Hu, and Y. Sun, Deformation Behaviour and Dynamic Recrystallization of AZ61 Magnesium Alloy, J. Alloys Compd., 2013, 580, p 262–269
S.I. Kim and Y.C. Yoo, Dynamic Recrystallization Behavior of AISI, 304 Stainless Steel, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2001, 311, p 108–113
E.I. Poliak and J.J. Jonas, A One-Parameter Approach to Determining the Critical Conditions for the Initiation of Dynamic Recrystallization, Acta Mater., 1996, 44, p 127–136
H. Li, H. Wang, Z. Li, C. Liu, and H. Liu, Flow Behavior and Processing Map of As-Cast Mg-10Gd-4.8Y-2Zn-0.6Zr Alloy, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2010, 528, p 154–160
H.C. Xiao, S.N. Jiang, B. Tang, W.H. Hao, Y.H. Gao, Z.Y. Chen, and C.M. Liu, Flow Behavior and Processing Map of As-Cast Mg-10Gd-4.8Y-2Zn-0.6Zr Alloy, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2015, 628, p 311–318
O. Sivakesavam and Y.V.R.K. Prasad, Characteristics of Superplasticity Domain in the Processing Map for Hot Working of As-Cast Mg-11.5Li-1.5Al Alloy, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2002, 323, p 270–277
Z. Zhou, Q. Fan, Z. Xia, A. Hao, W. Yang, W. Ji, and H. Cao, Constitutive Relationship and Hot Processing Maps of Mg-Gd-Y-Nb-Zr Alloy, J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 2017, 33, p 637–644
Y.V.R.K. Prasad, H.L. Gegel, S.M. Doraivelu, J.C. Malas, J.T. Morgan, K.A. Lark, and D.R. Barker, Modeling of Dynamic Material Behavior in Hot Deformation: Forging of Ti-6242, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1984, 15, p 1883–1892
H. Ziegler, Progress in Solid Mechanics, Vol 4, I.N. Sneddon and R. Hill, Ed., Wiley, New York, 1963, p 93–191
Acknowledgments
This research was financially supported by Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province, China (Project No. ZR2016EMQ08), Chinese Postdoctoral Science Foundation (Project No. 2017M612224) and Shandong Province Higher Education Science and Technology Program, China (Project Nos. J16LB06, J17KA055).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lv, BJ., Guo, F., Che, QL. et al. A New Method for Optimizing Hot Processing Parameters of Mg-6.0Zn-0.5Mn-0.5Er Alloy Based on Kinetic Model of Dynamic Recrystallization and Processing Map. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 27, 3773–3782 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-018-3443-2
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-018-3443-2