Abstract
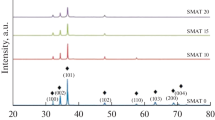
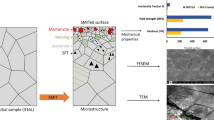
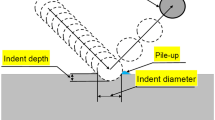
In the present work, the influence of surface mechanical attrition treatment (SMAT) parameters on the microstructural and mechanical properties of an aluminum-magnesium-silicon alloy AA 6061 was studied using design of experiment technique. Balls of three different diameters were used, and SMAT was done for three different durations. The microstructural features of the surface layer fabricated by SMAT were characterized by cross-sectional scanning electron microscopic observations, x-ray diffraction technique and transmission electron microscopy. The microindentation hardness, nanoindentation hardness and surface roughness were determined. Due to SMAT, nanocrystallites formed on the surface and near-surface regions, and hardness and surface roughness increased. The ball diameter was the most influencing SMAT parameter compared to the treatment duration. However, interaction between ball diameter and treatment duration could not be ignored. Regression equations were developed relating the process parameters to the surface properties. The ball diameter and treatment duration could thus be properly selected as per the required values of roughness and/or the hardness.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. Lu and J. Lu, Nanostructured Surface Layer on Metallic Materials Induced by Surface Mechanical Attrition Treatment, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2004, 375, p 38–45
H. Gleiter, Nanostructured Materials: Basic Concepts and Microstructure, Acta Mater., 2000, 48, p 1–29
K.S. Kumar, H. Van Swygenhoven, and S. Suresh, Mechanical Behavior of Nanocrystalline Metals and Alloys, Acta Mater., 2003, 51, p 5743–5774
J.L. Liu, M. Umemoto, Y. Todaka, and K. Tsuchiya, Formation of a Nanocrystalline Surface Layer on Steels by Air Blast Shot Peening, J. Mater. Sci., 2007, 42, p 7716–7720
K. Dai, J. Villegas, Z. Stone, and L. Shaw, Finite Element Modeling of the Surface Roughness of 5052 Al Alloy Subjected to a Surface Severe Plastic Deformation Process, Acta Mater., 2004, 52, p 5771–5782
G. Liu, J. Lu, and K. Lu, Surface Nanocrystallization of 316L Stainless Steel Induced by Ultrasonic Shot Peening, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2000, 286, p 91–95
X. Wu, N. Tao, Y. Hong, B. Xu, J. Lu, and K. Lu, Microstructure and Evolution of Mechanically-Induced Ultrafine Grain in Surface Layer of Al-Alloy Subjected to USSP, Acta Mater., 2002, 50, p 2075–2084
H.W. Chang, P.M. Kelly, Y.N. Shi, and M.X. Zhang, Effect of Eutectic Si on Surface Nanocrystallization of Al–Si Alloys by Surface Mechanical Attrition Treatment, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2011, 530, p 304–314
H.W. Chang, P.M. Kelly, Y.-N. Shi, and M.-X. Zhang, Thermal Stability of Nanocrystallized Surface Produced by Surface Mechanical Attrition Treatment in Aluminum Alloys, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2012, 206, p 3970–3980
Y. Liu, B. Jin, and J. Lu, Mechanical Properties and Thermal Stability of Nanocrystallized Pure Aluminum Produced by Surface Mechanical Attrition Treatment, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2015, 636, p 446–451
L. Wen, Y. Wang, Y. Zhou, L. Guo, and J. Ouyang, Iron-Rich Layer Introduced by SMAT and Its Effect on Corrosion Resistance and Wear Behavior of 2024 Al Alloy, Mater. Chem. Phys., 2011, 126, p 301–309
L. Wen, Y. Wang, Y. Zhou, L. Guo, and J. Ouyang, Microstructure and Corrosion Resistance of Modified 2024 Al Alloy Using Surface Mechanical Attrition Treatment Combined with Microarc Oxidation Process, Corros. Sci., 2011, 53, p 473–480
B. Arifvianto, Suyitno, M. Mahardika, P. Dewo, P.T. Iswanto, and U.A. Salim, Effect of Surface Mechanical Attrition Treatment (SMAT) on Microhardness, Surface Roughness and Wettability of AISI 316L, Mater. Chem. Phys., 2011, 125, p 418–426
T. Roland, D. Retraint, K. Lu, and J. Lu, Fatigue Life Improvement Through Surface Nanostructuring of Stainless Steel by Means of Surface Mechanical Attrition Treatment, Scr. Mater., 2006, 54, p 1949–1954
N.R. Tao, M.L. Sui, J. Lu, and K. Lu, Surface Nanocrystallization of Iron Induced by Ultrasonic Shot Peening, Nano Mater., 1999, 11, p 433–440
X. Yong, G. Liu, and K. Lu, Characterization and Properties of Nanostructured Surface Layer in a Low Carbon Steel Subjected to Surface Mechanical Attrition, J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 2003, 19, p 1–4
K.Y. Zhu, A. Vassel, F. Brisset, K. Lu, and J. Lu, Nanostructure Formation Mechanism of α-Titanium Using SMAT, Acta Mater., 2004, 52, p 4101–4110
Y.S. Zhang and Z. Han, Fretting Wear Behavior of Nanocrystalline Surface Layer of Pure Copper Under Oil Lubrication, Tribol. Lett., 2007, 27, p 53–59
S. Anand Kumar, S. Ganesh Sundara Raman, T.S.N. Sankara Narayanan, and R. Gnanamoorthy, Influence of Surface Mechanical Attrition Treatment on Fretting Wear Behavior of Ti-6Al-4V, Adv. Mater. Res., 2012, 463–464, p 316–320
S. Anand Kumar, S. Ganesh Sundara Raman, T.S.N. Sankara Narayanan, and R. Gnanamoorthy, Fretting Wear Behaviour of Surface Mechanical Attrition Treated Alloy 718, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2012, 206, p 4425–4432
Y.S. Zhang, K. Wang, Z. Han, and G. Liu, Dry Sliding Wear Behavior of Copper with Nano-scaled Twins, Wear, 2007, 262, p 1463–1470
S. Anand Kumar, S. Ganesh Sundara Raman, and T.S.N. Sankara Narayanan, Influence of Surface Mechanical Attrition Treatment Duration on Fatigue Lives of Ti-6Al-4V, Trans. Indian Inst. Met., 2014, 67(1), p 137–141
S. Anand Kumar, S. Ganesh Sundara Raman, and T.S.N. Sankara Narayanan, Effect of Surface Mechanical Attrition Treatment on Fatigue Lives of Alloy 718, Trans. Indian Inst. Met., 2012, 65, p 473–477
T. Balusamy, S. Kumar, and T.S.N. Sankara Narayanan, Effect of Surface Nanocrystallization on the Corrosion Behavior of AISI, 409 Stainless Steel, Corros. Sci., 2010, 52, p 3826–3834
P.J. Ross, Taguchi Techniques for Quality Engineering, McGraw-Hill, New York, 1996
L. Wagner, Mechanical Surface Treatments on Titanium, Aluminum and Magnesium Alloys, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 1999, 263, p 210–216
Y. Fu, J. Wei, and A.W. Batchelor, Some Considerations on the Mitigation of Fretting Damage by the Application of Surface-Modification Technologies, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2000, 99, p 231–245
C. Colombie, Y. Berthier, A. Floquet, L. Vincent, and M. Godet, Fretting Load-Carrying Capacity of Wear Debris, ASME J. Tribol., 1984, 106, p 185–194
R.K. Roy, A Primer on Taguchi Method, Van Noshtrand Reinhold Int. Co. Ltd, New York, 1990
H. Saitoh, T. Ochi, M. Kubota, Formation of surface nanocrystalline structure in steels by air blast shot peening, in Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Shot Peening, (2008), p. 488–493
B.N. Mordyuk and G.I. Prokopenko, Ultrasonic Impact Peening for the Surface Properties’ Management, J. Sound Vib., 2007, 308, p 855–866
V.S. Sarma, J. Wang, W.W. Jian, A. Kauffmann, H. Conrad, J. Freudenberger, and Y.T. Zhu, Role of Stacking Fault Energy in Strengthening Due to Cryo-Deformation of FCC Metals, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2010, 527, p 7624–7630
D.E. Stegall, M.A. Mamun, and A.A. Elmustafa, The Role of Stacking Fault Energy on the Indentation Size Effect of FCC Pure Metals and Alloys, Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc., 2012, 1424, p 7–12
B.D. Cullity, Elements of x-ray Diffraction, Addison Wesley, Massachusetts, 1978
H. Chen, Y.L. Yao, J.W. Kysar, I.C. Noyan, and Y. Wang, Fourier Analysis of x-ray Micro-diffraction Profiles to Characterize Laser Shock Peened Metals, Int. J. Solids Struct., 2005, 42, p 3471–3485
S. Anand Kumar, R. Sundar, S. Ganesh Sundara Raman, H. Kumar, R. Gnanamoorthy, R. Kaul, K. Ranganathan, S.M. Oak, and L.M. Kukreja, Fretting Wear Behavior of Laser Peened Ti-6Al-4V, Tribol. Trans., 2012, 55, p 615–623
L. Zhu, B. Xu, H. Wang, and C. Wang, Effect of Residual Stress on the Nanoindentation Response of (100) Copper Single Crystal, Mater. Chem. Phys., 2012, 136, p 561–565
A.C. Fischer-Cripps, Nanoindentation, Springer, New York, 2011
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Anand Kumar, S., Satish Kumar, P., Ganesh Sundara Raman, S. et al. Influence of SMAT Parameters on Microstructural and Mechanical Properties of Al-Mg-Si Alloy AA 6061. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 26, 1947–1957 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-017-2612-z
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-017-2612-z