Abstract
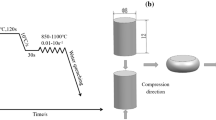
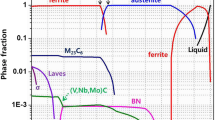
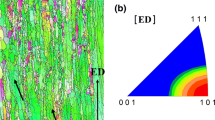
High-phosphorus steels are important for structural applications where corrosion resistance is required and are subjected to hot deformation processing. Therefore, hot deformation behavior of Fe-0.05C-0.13P steel is studied by conducting hot compression tests in the temperature range 750-1050 °C after austenitization at 1050 °C for 10 s. The strain rates ranged from 0.001 to 10 s−1. Optical and scanning electron microscopy was performed to determine the microstructural evolution. EBSD measurement on selected samples was used to determine the microstructural changes in the ferrite phase. Processing windows were determined using modified dynamic material model in order to determine the safe hot working domains and these are correlated with the microstructural developments.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
B.E. Hopkins and H.R. Tipler, The Effect of Phosphorus on the Tensile and Notch-Impact Properties of High-Purity Iron and Iron-Carbon Alloys, J. Iron Steel Inst., 1958, 188, p 218-237
J.W. Stewart, J.A. Charles, and E.R. Wallach, Iron-phosphorus-Carbon System, Part 1—Mechanical Properties of Low Carbon Iron-Phosphorus Alloys, Mater. Sci. Technol., 2000, 16, p 275–282
G. Sahoo and R. Balasubramaniam, Mechanical Behavior of Novel Phosphoric Irons for Concrete Reinforcement Applications, Scripta Mater., 2007, 56, p 117–120
G. Sahoo and R. Balasubramaniam, On the Corrosion Behaviour of Phosphoric irons in Simulated Concrete Pore Solution, Corros. Sci., 2008, 50, p 131–143
S.I. Kim, S.H. Choi, and Y. Lee, Influence of Phosphorous and Boron on Dynamic Recrystallization and Microstructures of Hot-Rolled Interstitial Free Steel, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2005, 406, p 125–133
M.F. Ashby and H.J. Frost, Deformation-Mechanism Maps: The Plasticity and Creep of Metals and Ceramics, Pergamon Press, London, 1982, ISBN 978-0080293387
Y.V.R.K. Prasad, H.L. Gegel, S.M. Doraivelu, J.C. Malas, J.T. Morgan, K.A. Lark, and D.R. Barker, Modeling of Dynamic Material Behavior in Hot Deformation: Forging of Ti-6242, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1984, 15(10), p 1883–1892
Y.V.R.K. Prasad, Author’s Reply: Dynamic Materials Model: Basis and Principles, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1996, 27, p 235–236
S.V.S. Narayana Murty and B. Nageswara Rao, Ziegler’s Criterion on the Instability Regions in Processing Maps, Mater. Sci. Lett., 1998, 17, p 1203–1205
S.V.S. Narayana, B. Murty, and B.P. Nageswara Rao, Kashyap, Development and Validation of a Processing Map for Zirconium Alloys, Modell. Simul. Mater. Eng., 2002, 10, p 503–520
S.V.S. Narayana Murty, B. Nageswara Rao, and B.P. Kashyap, on the Hot Working Characteristics of 6061Al-SiC and 6061-Al2O3 Particulate Reinforced Metal Matrix Composites, Comput. Sci. Technol., 2003, 63, p 119–135
S.V.S. Murty, B.N. Rao, and B.P. Kashyap, On the Hot Working Characteristics of 2014 Al-20 vol% Al2O3 Metal Matrix Composite, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2005, 166, p 279–285
J.K. Chakravartty, G.K. Dey, S. Banerjee, and Y.V.R.K. Prasad, Characterization of Hot Deformation Behaviour of Zr-2.5Nb-0.5Cu Using Processing Maps, J. Nucl. Mater., 1995, 218, p 247–255
S.K. Rajput, M. Dikovits, G.P. Chaudhari, S.K. Nath, C. Poletti, F. Warchomicka, V. Pancholi, and S.K. Nath, Physical simulation of hot deformation and microstructural evolution of AISI, 1016 steel using processing maps, Mat Sci Eng A-Struct, 2013, 587, p 291–300
H. Ziegler, E. Becker, B. Budiansky, H.A. Lauwerier, and T. Koiter, An Introduction to Thermodynamics, 2nd ed., North-Holland, New York, 1983
F. Montheillet, J.J. Jonas, and K.W. Neale, Modeling of Dynamic Material Behavior: A Critical Evaluation of the Dissipator Power Co-content Approach, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1996, 27, p 232–235
S.K. Rajput, G.P. Chaudhari, and S.K. Nath, Physical Simulation of Hot Deformation of Low-Carbon Ti-Nb Micro-alloyed Steel and Microstructural Studies, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2014, 23(8), p 2930–2942
C.M. Sellars and W.J. McG, Tegart, On the Mechanism of Hot Deformation, Acta Metall., 1966, 14, p 1136–1138
J. Zhang, H. Di, X. Wanga, Y. Cao, J. Zhang, and T. Ma, Constitutive Analysis of the Hot Deformation Behavior of Fe–23Mn–2Al–0.2C Twinning Induced Plasticity Steel in Consideration of Strain, Mater. Design, 2013, 44, p 354–364
H.J. McQueen, S. Yue, N.D. Ryan, and E. Fry, Hot Working Characteristics of Steels in Austenitic State, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 1995, 53, p 293–310
H.J. McQueen, Elevated-Temperature Deformation at Forming Rates of 10−2 to 102 s−1, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2002, 33, p 345–362
K.P. Rao, Y.K.D.V. Prasad, and E.B. Hawbolt, Hot Deformation Studies on a Low-Carbon Steel: Part 1-Flow Curves and the Constitutive Relationship, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 1996, 56, p 897–907
Y.D. Huang and L. Froyen, Important Factors to Obtain Homogeneous and Ultrafine Ferrite–Pearlite Microstructure in Low Carbon Steel, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2002, 124, p 216–226
R.L. Goetz and S.L. Semiatin, The Adiabatic Correction Factor for Deformation Heating During the Uniaxial Compression Test, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2001, 10(6), p 710–717
N. Tsuji, B.Y. Matsu, and Y. Saito, Dynamic Recrystallization of Ferrite in Interstitial Free Steel, Scripta Mater., 1997, 37, p 477–484
H. Dong, D. Cai, Z. Zhao, Z. Wang, Y. Wang, Q. Yang, and B. Liao, Investigation on Static Softening Behaviors of a Low Carbon Steel Under Ferritic Rolling Condition, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2010, 19(2), p 151–154
J.W. Stewart, J.A. Charles, and E.R. Wallach, Iron–Phosphorus–Carbon System, Part 3 – Metallography of Low Carbon Iron–Phosphorus Alloys, Mater Sci Tech Ser, 2000, 16, p 291–303
W.D. Callister, Material Science and Engineering—An Introduction, 2nd ed., Wiley, New Delhi, 2014, p 261
H. Erhart and H.J. Grabke, Site Competition in Grain Boundary Segregation of Phosphorus and Nitrogen in Iron, Scripta Metall Mater, 1981, 15, p 531–534
K.B. Gove and J.A. Charles, Met. Technol., 1974, 1, p 279–283
S.M. Abbasi and A. Momeni, Hot Working Behavior of Fe–29Ni–17Co Analyzed by Mechanical Testing and Processing Map, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2012, 552, p 330–335
S.V.S. Narayana Murty, B. Nageswara Rao, and B.P. Kashyap, Instability Criteria for Hot Deformation of Materials, Int. Mater. Rev., 2000, 45, p 15–26
R. Vogel, On the System Iron-Phosphorus-Carbon, Arch Eisenhuttenwes., 1929, 3(5), p 369–371(in German)
N.E. Dowling, Mechanical Behaviour of Materials: Engineering Methods for Deformation, Fracture and Fatigue, 3rd ed., Pearsons Prentice Hall, NJ, 2007
J.M. Cabrera, A.A.L. Omar, J.J. Jonas, and J.M. Prado, Modeling the Flow Behavior of a Medium Carbon Microalloyed Steel Under Hot Working Conditions, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1997, 28, p 2233–2244
T.E. Mitchell, J.P. Hirth, and A. Misra, Apparent Activation Energy and Stress Exponent in Materials with a Peierls Stress, Acta Mater., 2002, 50, p 1087–1093
C.W. Siyasiya and W.E. Stumpf, Constitutive Constants for Hot Working of Steels: The Critical Strain for Dynamic Recrystallisation in C-Mn Steels, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2015, 24(1), p 468–476
R. Bobbili and V. Madhu, An Investigation into Hot Deformation Characteristics and Processing Maps of High-Strength Armor Steel, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2015, 24, p 4728–4735
Acknowledgment
The authors wish to thank Ajay Aggarwal, Vaishnav Steel Private Limited, Muzaffarnagar, India for making the castings of the Fe-0.05C-0.13P alloy for research purpose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mehta, Y., Rajput, S.K., Dabhade, V.V. et al. Physical Simulation of Hot Deformation and Microstructural Evolution of Fe-0.05C-0.13P Steel. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 25, 1376–1383 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-016-1992-9
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-016-1992-9