Abstract
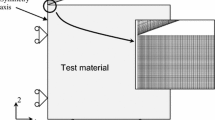
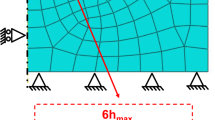
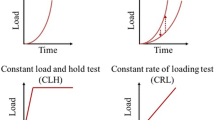
The use of instrumented indentation to characterize power-law creep is studied by computational modeling. Systematic finite element analyses were conducted to examine how indentation creep tests can be employed to retrieve the steady-state creep parameters pertaining to regular uniaxial loading. The constant indentation load hold and constant indentation-strain-rate methods were considered, first using tin (Sn)-based materials as a model system. The simulated indentation-strain rate-creep stress relations were compared against the uniaxial counterparts serving as model input. It was found that the constant indentation-strain-rate method can help establish steady-state creep, and leads to a more uniform behavior than the constant-load hold method. An expanded parametric analysis was then performed using the constant indentation-strain-rate method, taking into account a wide range of possible power-law creep parameters. The indentation technique was found to give rise to accurate stress exponents, and a certain trend for the ratio between indentation strain rate and uniaxial strain rate was identified. A contour-map representation of the findings serves as practical guidance for determining the uniaxial power-law creep response based on the indentation technique.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
M.F. Ashby, Materials Selection in Mechanical Design, 4th ed., Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford, 2011
M.A. Meyers and K.K. Chawla, Mechanical Behavior of Materials, 2nd ed., Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 2009
R.E. Smallman and A.H.W. Ngan, Modern Physical Metallurgy, 8th ed., Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford, 2014
S.N.G. Chu and J.C.M. Li, Impression Creep; A New Creep Test, J. Mater. Sci., 1977, 12, p 2200–2208
J.C.M. Li, Impression Creep and Other Localized Tests, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2002, 322, p 23–42
F. Yang and J.C.M. Li, Impression Test—A Review, Mater. Sci. Eng. R, 2013, 74, p 233–253
Y.J. Liu, B. Zhao, B.X. Xu, and Z.F. Yue, Experimental and Numerical Study of the Method to Determine the Creep Parameters from the Indentation Creep Testing, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2007, 456, p 103–108
M.J. Mayo, R.W. Siegel, A. Narayanasamy, and W.D. Nix, Mechanical Properties of Nanophase TiO2 as Determined by Nanoindentation, J. Mater. Res., 1990, 5, p 1073–1082
V. Raman and R. Berriche, An Investigation of the Creep Processes in Tin and Aluminum Using a Depth-Sensing Indentation Technique, J. Mater. Res., 1992, 7, p 627–638
M. Fujiwara and M. Otsuka, Indentation Creep of β-Sn and Sn-Pb Eutectic Alloy, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2001, 319-321, p 929–933
H. Takagi, M. Dao, M. Fujiwara, and M. Otsuka, Experimental and Computational Creep Characterization of Al-Mg Solid-Solution Alloy through Instrumented Indentation, Phil. Mag., 2003, 83, p 3959–3976
C.Z. Liu and J. Chen, Nanoindentation of Lead-Free Solders in Microelectronic Packaging, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2007, 448, p 340–344
C.L. Wang, Y.H. Lai, J.C. Huang, and T.G. Nieh, Creep of Nanocrystalline Nickel: A Direct Comparison between Uniaxial and Nanoindentation Creep, Scr. Mater., 2010, 62, p 175–178
R. Goodall and T.W. Clyne, A Critical Appraisal of the Extraction of Creep Parameters from Nanoindentation Data Obtained at Room Temperature, Acta Mater., 2006, 54, p 5489–5499
L. Shen, W.C.D. Cheong, Y.L. Foo, and Z. Chen, Nanoindentation Creep of Tin and Aluminium: A Comparative Study between Constant Load and Constant Strain Rate Methods, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2012, 532, p 505–510
J. Dean, A. Bradbury, G. Aldrich-Smith, and T.W. Clyne, A Procedure for Extracting Primary and Secondary Creep Parameters from Nanoindentation Data, Mech. Mater., 2013, 65, p 124–134
M. Tehrani, M. Safdari, and M.S. Al-Haik, Nanocharacterization of Creep Behavior of Multiwall Carbon Nanotubes/Epoxy Nanocomposite, Int. J. Plast., 2011, 27, p 887–901
J.L. Hay and G.M. Pharr, Instrumented Indentation Testing, ASM Handbook Volume 8: Mechanical Testing and Evaluation, H. Kuhn and D. Medlin, Ed., ASM International, Materials Park, OH, 2000,
B.N. Lucas and W.C. Oliver, Indentation Power-Law Creep of High-Purity Indium, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1999, 30A, p 601–610
Y.-T. Cheng and C.-M. Cheng, What is Indentation Hardness?, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2000, 133-134, p 417–424
L. Shen, P. Lu, S. Wang, and Z. Chen, Creep Behaviour of Eutectic SnBi Alloy and its Constituent Phases using Nanoindentation Technique, J. Alloy. Compd., 2013, 574, p 98–103
G. Xiao, G. Yuan, C. Jia, X. Yang, Z. Li, and X. Shu, Strain Rate Sensitivity of Sn-3.0Ag-0.5Cu Solder Investigated by Nanoindentation, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2014, 613, p 336–339
C. Su, E.G. Herbert, S. Sohn, J.A. LaManna, W.C. Oliver, and G.M. Pharr, Measurement of Power-Law Creep Parameters by Instrumented Indentation Methods, J. Mech. Phys. Solids, 2013, 61, p 517–536
W.H. Poisl, W.C. Oliver, and B.D. Fabes, The Relationship between Indentation and Uniaxial Creep in Amorphous Selenium, J. Mater. Res., 1995, 10, p 2024–2032
H. Takagi, M. Dao, and M. Fujiwara, Prediction of the Constitutive Equation for Uniaxial Creep of a Power-Law Material through Instrumented Microindentation Testing and Modeling, Maters. Trans., 2014, 55, p 275–284
M.E. Cordova and Y.-L. Shen, Indentation versus Uniaxial Power-Law Creep: A Numerical Assessment, J. Mater. Sci., 2015, 50, p 1394–1400
A.C. Fischer-Cripps, Nanoindentation, Springer, New York, 2002
D.R. Lide, Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 76th ed., CRC Press, Boca Raton, 1995
G. Tang, Y.-L. Shen, D.R.P. Singh, and N. Chawla, Indentation Behavior of Metal-Ceramic Multilayers at the Nanoscale: Numerical Analysis and Experimental Verification, Acta Mater., 2010, 58, p 2033–2044
N. J. Martinez, M.S. Thesis, University of New Mexico, 2015.
D.S. Tabor, The Hardness of Metals, Clarendon Press, Oxford, 1951
K.L. Johnson, The Correlation of Indentation Experiments, J. Mech. Phys. Solids, 1970, 18, p 115–126
S.S. Chiang, D.B. Marshall, and A.G. Evans, The Response of Solids to Elastic/Plastic Indentation. I. Stresses and Residual Stresses, J. Appl. Phys., 1982, 53, p 298–311
A. Bolshakov and G.M. Pharr, Influences of Pileup on the Measurement of Mechanical Properties by Load and Depth Sensing Indentation Techniques, J. Mater. Res., 1998, 13, p 1049–1058
P. Hosemann, J.G. Swadener, D. Kiener, G.S. Was, S.A. Maloy, and N. Li, An Exploratory Study to Determine Applicability of Nano-Hardness and Micro-Compression Measurements for Yield Stress Estimation, J. Nucl. Mater., 2008, 375, p 135–143
R.S. Sidhu, X. Deng, and N. Chawla, Microstructure Characterization and Creep Behavior of Pb-Free Sn-Rich Solder Alloys: Part II. Creep Behavior of Bulk Solder and Solder/Copper Joints, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2008, 39A, p 349–362
N. Chawla, Thermomechanical Behaviour of Environmentally Benign Pb-Free Solders, Int. Mater. Rev., 2009, 54, p 368–384
A.F. Bower, Applied Mechanics of Solids, CRC Press, Boca Raton, 2010
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Martinez, N.J., Shen, YL. Analysis of Indentation-Derived Power-Law Creep Response. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 25, 1109–1116 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-016-1934-6
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-016-1934-6