Abstract
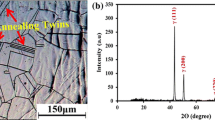
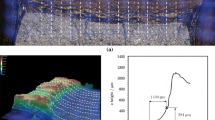
The mechanisms of loss of hot ductility and the mechanical behavior of 17-4 PH alloys were investigated using hot tensile testing at temperatures between 700 and 1100 °C and strain rates of 10−4, 10−2, and 10−1 s−1. Scanning electron microscopy was used in conjunction with the results of the tensile tests to find the temperature region of loss of ductility and correlate it with cracking observed during processing by hot upsetting prior to ring rolling. It is reported that 17-4 PH alloys lose ductility in a temperature range around 900 °C near to the duplex austenite + ferrite phase field. Furthermore, it is found that niobium carbides precipitated at austenite/ferrite interfaces and grain boundaries have a pronounced effect on the mechanical behavior of the alloy during high-temperature deformation.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. Mirzadeh, A. Najafizadeh, and M. Moazeny, Flow Curve Analysis of 17-4 PH Stainless Steel Under Hot Compression Test, Metall. Mater. Trans., 2009, 40, p 2950–2958
H. Mirzadeh and A. Najafizadeh, The Rate of Dynamic Recrystallization in 17-4 PH Stainless Steel, Mater. Des., 2010, 31, p 4577–4583
M. Yazdani, S.M. Abbasi, A. Momeni, and A. KarimiTaheri, Hot Ductility of a Fe–Ni–Co Alloy In Cast and Wrought Conditions, Mater. Des., 2011, 32, p 2956–2962
I. Mejía, A. Bedolla-Jacuinde, C. Maldonado, and J.M. Cabrera, Hot Ductility Behavior of a Low Carbon Advanced High Strength Steel (AHSS) Microalloyed with boron, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2011, 528, p 4468–4474
F. Equihua-Guillen and A. Salinas-Rodriguez, Role of the austenite-ferrite transformation start temperature on the high-temperature ductility of electrical steels, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2011, 20(1), p 102–107
K.R. Carpenter, R. Dippenaar, and C.R. Killmore, Hot Ductility of Nb- and Ti-Bearing Microalloyed Steels and the Influence of Thermal history, Metall. Mater. Trans., 2009, 40, p 573–580
G.I.S.L. Cardoso and S. Yue. Hot Ductility of Three Low Carbon Steels in Continuously Cast Slabs. Iron and Steel Society, Inc, p. 585–593, 1990.
J. Wang, H. Zou, C. Li, S. Qiu, and B. Shen, The Spinodal Decomposition in 17-4PH Stainless Steel Subjected to Long-Term Aging at 350ºC, Mater. Charact., 2008, 59, p 587–591
J. Calvo, J.M. Cabrera, and J.M. Prado, Ductilidad en caliente y mecanismos de fractura de un acero de construcción, Rev. Metal., 2006, 42(1), p 11–17
R. Abushosha, S. Ayyad, and B. Mintz, Influence of Cooling Rate on Hot Ductility of C-Mn-Al and C-Mn-Nb-Al Steels, Mater. Sci. Technol., 1998, 14, p 346–351
E.O. García-Sánchez, E.A. Treviño-Luna, A. Salinas-Rodríguez, and L.A. Leduc-Lezama, Mecanismos de fractura a alta temperatura en aceros eléctricos no-orientados, Rev. Metal. Madrid, 2007, 43(4), p 272–277
S. Serejzadeh and A. KarimiTaheri, An Investigation on the Effect of Carbon and Silicon on Flow Behavior of Steel, Mater. Des., 2002, 23, p 271–276
K. Banks, A. Koursaris, F. Verdoorn, and A. Tuling, Precipitation and Hot Ductility of low C-V and Low C-V-Nb Microalloyes Steels During Thin Slab Casting, Mater. Sci. Technol., 2001, 17, p 1596–1604
H. Matsuoka, K. Osawa, M. Ono, and M. Ohmura, Influence of Cu and Sn on Hot Ductility of Steels with Various C Content, ISIJ Int., 1997, 37(3), p 255–262
B. Mintz, A. Tuling, and A. Delgado, Influence of Silicon, Aluminum, Phosphorus and Boron on Hot Ductility of Transformation Induced Plasticity Assisted Steels, Mater. Sci. Technol., 2003, 19, p 1721–1726
B. Mintz, A. Cowley, C. Talian, D.N. Crowther, and R. Abushosha, Influence of P on Hot Ductility of High C, Al, and Nb Containing Steels, Mater. Sci. Technol., 2003, 19, p 184–188
K.W. Andrews, J. Iron Steel Inst., 1965, 203, p 721
B. Mintz, S. Yue, and J.J. Jonas, Hot Ductility of Steels and Its Relationship to the Problem of Transverse Cracking During Continuous Casting, Int. Mater. Rev., 1991, 36(5), p 187–217
S. Nemat-Nasser, W.-G. Guo, and D.P. Kihl, Thermomechanical Response of AL-6XN Stainless Steel Over a Wide Range of Strain Rates and Temperatures, J. Mech. Phys. Solids, 2001, 49, p 1823–1846
J. Lewis, J.J. Jonas, and B. Mintz, The Formation of Deformation Induced Ferrite During Mechanical Testing, ISIJ Int., 1998, 38(3), p 300–309
S.K. Kim, J.S. Kim, and N.J. Kim, Effect of Boron on the Hot Ductility of Nb-Containing Steel, Metall. Mater. Trans, 2002, 33A, p 701–704
S.C. Seo, H.J. Kim, B.H. Park, K.S. Son, S.K. Lee, S.B. Kang, and D. Kim, Effect of Low-Cycle Fatigue on the Hot Ductility of Plain Carbon Steel, Metal. Mater. Int., 2006, 12(3), p 273–277
N.A. Viktorov, Hot Ductility of Steel 08kh18n10t, Met. Sci. Heat Treat., 2011, 53(5–6), p 263–264
C. Yin-li, W. Yan, and Z. Ai-min, Precipitation of AlN and MnS in Low Carbon Aluminium-Killed Steel, J. Iron Steel Res. Int., 2012, 19(4), p 51–56
K.C. Cho, D.J. Munb, Y.M. Koo, and J.S. Lee, Effect of Niobium and Titanium Addition on the Hot Ductility of Boron Containing Steel, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2011, 528, p 3556–3561
Y. Maehara, H. Tomono, and Y. Ohmori, Stress Relaxation and Hot Ductility of Steels in Intermittent Tensile Deformation at Temperatures from 700 to 1300 °C, ISIJ Int., 1987, 73(9), p 1170–1177
R. Abushosha, S. Ayyad, and B. Mintz, Influence of Cooling Rate and MnS Inclusions on Hot Ductility of Steels, Mater. Sci Technol., 1998, 14, p 227–235
B. Mintz, Influence of Nitrogen on Hot Ductility of Steels and Its Relationship to Problem of Transverse Cracking, Ironmak. Steelmak., 2000, 27(5), p 343–347
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Herrera Lara, V., Guerra Fuentes, L., Covarrubias Alvarado, O. et al. Hot Ductility of the 17-4 PH Stainless Steels. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 25, 1041–1046 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-016-1895-9
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-016-1895-9