Abstract
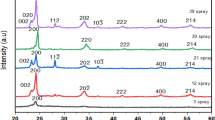
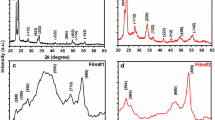
Studies on effect of the substrate temperature on physicochemical properties of WO3 thin films prepared using spray pyrolysis technique have been presented. Raman spectra of the film shows presence of W-O-W network with stretching and bending vibrations which revealed monoclinic structure of WO3 which is confirmed by XRD studies. XPS studies show that films are sub-stoichiometric and O/W ratio is 2.87, with W present in two valence states W+5 and W+6 with ratio of 0.21. Smallest crystallite size (28 nm) is observed for the film deposited at 425 °C, and on either side crystallite size is larger. Optical studies show band gap energy 2.6 eV and NUV, blue and green photo-emissions from WO3 films. Scanning electron micrographs depict wired network of the WO3, and AFM shows rough nature of the films. The thermo-emf is found to be linearly changing with temperature difference and decreases with increase in the substrate temperature.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Deepa, D.P. Singh, S.M. Shivaprasad, and S.A. Agnihotry, A Comparison of Electrochromic Properties of Sol-Gel Derived Amorphous and Nanocrystalline Tungsten Oxide Films, Curr. Appl. Phys., 2007, 7, p 220–229
J.M. O-Rueda de Leon, D.R. Acosta, U. Pal, and L. Castaneda, Improving Electrochromic Behavior of Spray Pyrolised WO3 Thin Solid Films by Mo Doping, Electrochim. Acta, 2011, 56, p 2599–2605
S.K. Deb, Opportunities and Challenges in Science and Technology of WO3 for Electrochromic and Related Applications, Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells, 2008, 92, p 245–258
A. Kaushal, N. Choudhary, N. Kaur, and D. Kaur, VO2-WO3 Nanocomposite Thin Films Ynthesized by Pulsed Laser Deposition Technique, App. Surf. Sci., 2011, 257, p 8937–8944
C.W. Lai, and S. Sreekantan, Preparation of Hybrid WO3-TiO2 Nanotube Photoelectrodes Using Anodization and Wet Impregnation: Improved Water-Splitting Hydrogen Generation Performance, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2013, 38, 2156–2166
D.S. Lee, K.H. Nam, and D.D. Lee, Effect of Substrate on NO2 Sensing Properties of WO3 Thin Film Gas Sensors, Thin Solid Films, 2000, 375, p 142–146
M.N. Spallart and S.B. Sadale, Photoelectrocatalysis with Drop-Cast Tungsten Trioxide Films, J. New Mater. Electrochem. Syst., 2010, 13, p 127–131
G. Wang, Y. Ji, R. Huang, Q. Yang, P. Gouma, and M. Dudley, Fabrication and Characterization of Polycrystalline WO3 Nanofibers and Their Application for Ammonia Sensing, J. Phys. Chem. B 110 (2006), p 23777–23782
G. Shaw, I.P. Parkin, K.F.E. Pratt, and D.E. Williams, Control of Semiconducting Oxide Gas-Sensor Microstructure by Application of an Electric Field During AEROSOL-ASSISTED CHEMICAL VAPOUR DEPOSITION, J. Mater. Chem., 2005, 15, p 149–154
M. Akiyama, J. Tamaki, N. Miura, and N. Yamazoe, Tungsten Oxide-Based Semiconductor Sensor Highly Sensitive to NO and NO2, Chem. Lett., 1991, 20, p 1611–1614
J. Shieh, H.M. Feng, M.H. Hon, and H.Y. Juang, WO3 and W-Ti-O Thin-Film Gas Sensor Prepared by Sol-Gel Dip-Coasting, Sensors Actuators B, 2002, 86, p 75–80
A.A. Tomchenko, G.P. Harmer, B.T. Marquis, and J.W. Allen, Semiconducting Metal Oxide Sensor Array for the Selective Detection of Combustion Gases, Sensors Actuators B, 2003, 93, p 126–134
C.S. Blackman and I.P. Parkin, Atmospheric Pressure Chemical Vapor Deposition of Crystalline Monoclinic WO3 and WO3-x Thin Films from Reaction of WCl6 with O-Containing Solvents and Their Photochromic and Electrochromic Properties, Chem. Mater., 2005, 17, p 1583–1590
W.J. Lee, P.S. Shinde, G.H. Go, and C.H. Doh, Enhanced Photoelectrochemical Performance of WO3/Ti Photoanode Due to In Situ Formation of a Thin Interfacial Composite Layer, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2013, 270, p 267–271
M.H. Yaacob, M.Z. Ahmad, A.Z. Sadek, J.Z. Ou, J. Campbell, K. Kalantar-zadeh, and W. Wlodarski, Optical Response of WO3 Nanostructured Thin Films Sputtered on Different Transparent Substrates Towards Hydrogen of Low Concentration, Sensors Actuators B, 2013, 177, p 981–988
I.M. Szilagyi, L. Wang, P.I. Gouma, C. Balazsi, J. Madarasz, and G. Pokol, Preparation of Hexagonal WO3 from Hexagonal Ammonium Tungsten Bronze for Sensing NH3, Mater. Res. Bull., 2009, 44, p 505–508
O. Pyper, R. Schollhorn, J.T.M. Donkers, and L.H.M. Krings, Nanocrystalline Structure of WO3 Thin Films Prepared by the Sol-Gel Technique, Mater. Res. Bull., 1998, 33, p 1095–1101
X. Su, Y. Li, J. Jian, and J. Wang, In Situ Etching WO3 Nanoplates: Hydrothermal Synthesis, Photoluminescence and Gas Sensor Properties, Mater. Res. Bull., 2010, 45, p 1960–1963
D.S. Martinez, A.M. Cruz, and E. Lopez-Cuellar, Synthesis of WO3 Nanoparticles by Citric Acid-Assisted Precipitation and Evaluation of Their Photocatalytic Properties, Mater. Res. Bull., 2013, 48, p 691–697
C.N.J. Wagner, Local Arrangement for X-ray Diffraction, chap 7, Gordon and Breach, New York, 1966
S. Thanikaikarasan, T. Mahalingam, A. Kathalingam, Y.D. Kim, and T. Kim, Growth and Characterization of Electrosynthesized Iron Selenide Thin Films, Vacuum, 2009, 83, p 1066–1072
P. Biloen and G.T. Pott, X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy Study of Supported Tungsten Oxide, J. Catal., 1973, 30, p 169–174
A.R. Babar, S.S. Shinde, A.V. Moholkar, C.H. Bhosale, J.H. Kim, and K.Y. Rajpure, Sensing Properties of Sprayed Antimony Doped Tin Oxide Thin Films: Solution Molarity, J. Alloys Compd., 2011, 509, p 3108–3115
J. Gabrusenoks, A. Veispals, A. Czarnowski, and K.H. Meiwes-Broer, Infrared and Raman spectroscopy of WO3 and CdWO4, J. Electrochim. Acta, 2001, 46, p 2229–2231
C. Santato, M. Odziemkowski, M. Ulmann, and J. Augustynski, Crystallographically Oriented Mesoporous WO3 Films: Synthesis, Characterization, and Applications, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2001, 123, p 10639–10649
E. Salje, The Orthorhombic Phase of WO3, Acta. Crystallogr., 1977, B33, p 574–577
M. Daniel, B. Desbat, J. Lassegues, B. Gerand, and M. Figlarz, Infrared and Raman Study of W03 Tungsten Trioxides and WO3, xHzO Tungsten Trioxide Hydrates, J. Solid State Chem., 1987, 67, p 235–247
J.L. Solis, J. Rodriguez, and W. Estrada, Highly Porous Tungsten-Oxide-Based Films Obtained by Spray-Gel for Gas Sensing Applications, Revista Mexicana Defisica, 2006, 52, p 29–31
K.Y. Rajpure, C.D. Lokhande, and C.H. Bhosale, A Comparative Study of the Properties of Spray-Deposited Sb2Se3 Thin Films Prepared from Aqueous and Nonaqueous Media, Mater. Res. Bull., 1999, 34, p 1079–1087
H.L. Hartnagel, A.L. Dawar, A.K. Jain, C. Jagadish, Semiconducting Transparent Thin Films, Institute of Physics Publishing, Bristol, 1995, p 244
M.A. Damian, Y. Rodriguez, J.L. Solis, and W. Estrada, Characterization and Butanolyethanol Sensing Properties of Mixed Tungsten Oxide and Copper Tungstate films Obtained by Spray-Sol-Gel, Thin Solid Films, 2003, 444, p 104–110
M. Manfredi, C. Paracchini, G.C. Salviati, and G. Schianchi, Conductive Processes in Transparent WO3 Films Irradiated with Ultraviolet Light, Thin Solid Films, 1981, 79, p 161–166
J.Y. Luo, F.L. Zhao, L. Gong, H.J. Chen, and J. Zhou, Ultraviolet-Visible Emission from Three-Dimensional WO3-x Nanowire Networks, Appl. Phys. Lett., 2007, 91, p 093124
J. Diaz-Reyes, J.E. Lores-Mena, J.M. Gutierrez-Arias, M.M. Morincastillo, H. Azucena-Courtecatl, M. Galvan, P. Rodriguwz-Fragoso, and A. Mendez-Lopez, Optical and Structural Properties of WO3 as a Function of the Annealing Temperature, Advances in Sensors, Signals and Materials, p 99–104, ISBN: 978-960-474-248-6
V.S. Sawant, S.S. Shinde, R.J. Deokate, C.H. Bhosale, B.K. Chougule, and K.Y. Rajpure, Effect of Calcining Temperature on Electrical and Dielectric Properties of Cadmium Stannate, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2009, 255, p 6675–6678
R.C. Kambale, N.R. Adhate, B.K. Chougule, and Y.D. Kolekar, Magnetic and dielectric properties of mixed spinel Ni-Zn ferrites synthesized by citrate-nitrate combustion method, J. Alloys Compd., 2010, 491, p 372–377
Acknowledgment
This work is supported by UGC through financial support by major research project entitled “Photocatalytic degradation of waste water using sprayed tungsten trioxide (WO3) thin films”. No. 41-869/2012. One of the authors (V. V. Ganbavle) is thankful to UGC New Delhi, for awarding fellowship through UGC-BSR scheme.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ganbavle, V.V., Agawane, G.L., Moholkar, A.V. et al. Structural, Optical, Electrical, and Dielectric Properties of the Spray-Deposited WO3 Thin Films. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 23, 1204–1213 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-014-0873-3
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-014-0873-3