Abstract
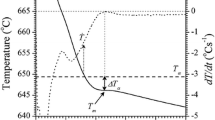
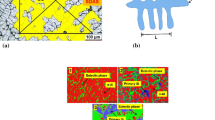
The effect of AlTi5B1 grain refinement and different solidification rates on metallurgical and mechanical properties of a secondary AlSi7Cu3Mg alloy is reported. While the Ti content ranges from 0.04 up to 0.225 wt.%, the cooling rate varies between 0.1 and 5.5 °C/s. Metallographic and thermal analysis techniques have been used to quantitatively examine the macro- and microstructural changes occurring with grain refiner addition at various cooling rates. The results indicate that a small AlTi5B1 addition produces the greatest refinement, while no significant reduction of grain size is obtained with a great amount of grain refiner. On increasing the cooling rate, a lower amount of AlTi5B1 master alloy is necessary to produce a uniform grain size throughout the casting. The combined addition of AlTi5B1 and Sr does not produce any reciprocal interaction or effect on primary α-Al and eutectic solidification. The grain refinement improves the plastic behavior of the alloy and increases the reliability of castings, as evidenced by the Weibull statistics.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Zehnder, R. Pritzlaff, S. Lundberg, and B. Gilmont, Aluminium in Transport, Aluminium in Commercial Vehicles, 2nd ed., European Aluminium Association, 2011, p 7–13
EAA, Aluminium in Cars, 1st ed., European Aluminium Association, 2007, p 1–15
F. Bonollo, I. Carturan, G. Cupitò, and R. Molina, Life Cycle Assessment in the Automotive Industry: Comparison Between Aluminium and Cast Iron Cylinder Blocks, Mater. Sci. Technol., 2006, 24(2), p 3–8
U.J.M. Boin and M. Bertram, Melting Standardized Aluminum Scrap, JOM, 2005, 57(8), p 26–33
M.E. Schlesinger, Aluminum Recycling, 1st ed., CRC Press, Boca Raton, 2007, p 176–192
J.E. Gruzleski and B.M. Closset, The Treatment of Liquid Aluminum-Silicon Alloys, American Foundrymen’s Society Inc., Illinois, 1990
D.G. McCartney, Grain Refining of Aluminum and Its Alloys Using Inoculants, Int. Mater. Rev., 1989, 34(5), p 247–260
Y. Birol, An Improve Practice to Manufacture Al-Ti-B Master Alloys by Reacting Halide Salts with Molten Aluminum, J. Alloy. Compd., 2006, 420(1–2), p 71–76
M. Easton and D. StJohn, Grain Refinement of Aluminium Alloys: Part I. The Nucleant and Solute Paradigms—A Review of the Literature, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1999, 30(6), p 1613–1623
A.L. Greer, P.S. Cooper, M.W. Meredith, W. Schneider, P. Schumacher, J.A. Spittle, and A. Tronche, Grain Refinement of Aluminium Alloys by Inoculation, Adv. Eng. Mater., 2003, 5(1–2), p 81–91
M. Easton and D. StJohn, An Analysis of the Relationship Between Grain Size, Solute Content, and the Potency and Number Density of Nucleant Particles, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2005, 36(7), p 1911–1920
Y.C. Lee, A.K. Dahle, D.H. StJohn, and J.E.C. Hutt, The Effect of Grain Refinement and Silicon Content on Grain Formation in Hypoeutectic Al-Si Alloys, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 1999, 259(1), p 43–52
Y. Birol, Performance of AlTi5B1, AlTi3B3 and AlB3 Master Alloys in Refining Grain Structure of Aluminium Foundry Alloys, Mater. Sci. Technol., 2012, 28(4), p 481–486
M. Johnsson, L. Bäckerud, and G.K. Sigworth, Study of the Mechanism of Grain Refinement of Aluminum After Additions of Ti and B Containing Master Alloys, Metall. Trans. A, 1993, 24(2), p 481–491
P. Schumacher, A.L. Greer, J. Worth, P.V. Evans, M.A. Kearns, P. Fisher, and A.H. Green, New Studies of Nucleation Mechanisms in Aluminium Alloys: Implications for Grain Refinement in Practice, Mater. Sci. Technol., 1998, 14(5), p 394–404
P. Schumacher and B.J. McKay, TEM Investigation of Heterogeneous Nucleation Mechanisms in Al-Si Alloys, J. Non-Cryst. Solids, 2003, 317(1–2), p 123–128
T. Chandrashekar, M.K. Muralidhara, K.T. Kashyap, and P. Raghothama Rao, Effect of Growth Restricting Factor on Grain Refinement of Aluminum Alloys, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 2009, 40(3–4), p 234–241
M.N. Binney, D.H. StJohn, A.K. Dahle, J.A. Taylor, E.C. Burhop, and P.S. Cooper, Grain Refinement of Secondary Aluminium-Silicon Casting Alloys, TMS Light Metals, March 2–6, 2003 (San Diego, CA, USA), Minerals, Metals and Materials Society (TMS), 2003, p 917–921
J.A. Spittle and S. Sadli, The Influence of Zirconium and Chromium on the Grain-Refining Efficiency of Al-Ti-B Inoculants, Cast Met., 1995, 7(4), p 247–253
A.M. Bunn, P. Schumacher, M.A. Kearns, C.B. Boothroyd, and A.L. Greer, Grain Refinement by Al-Ti-B Alloys in Aluminium Melts: A Study of the Mechanisms of Poisoning by Zirconium, Mater. Sci. Technol., 1999, 15(10), p 1115–1123
EN 1706:2010, Aluminium and Aluminium Alloys—Castings—Chemical Composition and Mechanical Properties, European Committee for Standardization, p 24–25
L. Bäckerud, G. Chai, and J. Tamminen, Solidification Characteristics of Aluminum: Foundry Alloys, Vol 2, 1st ed., American Foundrymen’s Society Inc., Des Plaines, IL, 1990
G.F. Vander Voort, Metallography: Principles and Practice, McGraw-Hill, New York, NY, 1984, p 612
ASTM E112-12, Standard Test Methods for Determining Average Grain Size, American Society for Testing Materials, p 9–11
M. Drouzy, S. Jacob, and M. Richard, Interpretation of Tensile Results by Means of Quality Index and Probable Yield Strength, AFS Int. Cast Met. J., 1980, 5(2), p 43–50
C.H. Cáceres, A Rationale for the Quality Index of Al-Si-Mg Casting Alloys, Int. J. Cast Met. Res., 1998, 10(5), p 293–299
N.D. Alexopoulos and Sp.G. Pantelakis, Evaluation of the Effects of Variations in Chemical Composition on the Quality of Al-Si-Mg, Al-Cu, and Al-Zn-Mg Cast Aluminum Alloys, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2003, 12(2), p 196–205
N.D. Alexopoulos, Definition of Quality in Cast Aluminum Alloys and Its Characterization with Appropriate Indices, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2006, 15(1), p 59–66
Q. Wang, Y.X. Li, and X.C. Li, Grain Refinement of Al-7Si Alloys and the Efficiency Assessment by Recognition of Cooling Curves, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2003, 34(5), p 1175–1182
L. Lu and A.K. Dahle, Effects of Combined Additions of Sr and AlTiB Grain Refiners in Hypoeutectic Al-Si Foundry Alloys, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2006, 435–436, p 288–296
A.K. Dahle, K. Nogita, S.D. McDonald, C. Dinnis, and L. Luc, Eutectic Modification and Microstructure Development in Al-Si Alloys, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2005, 413–414, p 243–248
S.D. McDonald, K. Nogita, and A.K. Dahle, Eutectic Nucleation in Al-Si Alloys, Acta Mater., 2004, 52(14), p 4273–4280
A. Knuutinen, K. Nogita, S.D. McDonald, and A.K. Dahle, Modification of Al-Si Alloys with Ba, Ca, Y and Yb, J. Light Met., 2001, 1(4), p 229–240
T.N. Ware, A.K. Dahle, S. Charles, and M.J. Couper, Effect of Sr, Na, Ca & P on the Castability of Foundry Alloy A356.2, ASM Materials Solutions 2002 Conference & Exposition, 2nd International Aluminium Casting Technology Symposium, Columbus, OH, USA, October 2002
A. Manente and G. Timelli, Influence of Strontium Modification and Solidification History on the Microstructure of Cast Al-Si Alloys, Metall. Ital., 2008, 100(11–12), p 37–50
Q.G. Wang, D. Apelian, and D.A. Lados, Fatigue Behavior of A356/357 Aluminum Cast Alloys. Part 2—Effect of Microstructural Constituents, J. Light Met., 2001, 1(1), p 85–97
L.A. Dobrzanski, R. Maniara, J. Sokołowski, and W. Kasprzak, Effect of Cooling Rate on the Solidification Behavior of AC AlSi7Cu2 Alloy, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2007, 191(1–3), p 317–320
S. Kahn and R. Elliot, Quench Modification of Aluminium-Silicon Eutectic Alloys, J. Mater. Sci., 1996, 31(14), p 3731–3737
Q.G. Wang and C.H. Cáceres, Fracture Mode in Al-Si-Mg Casting Alloys, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 1998, 241(1–2), p 72–82
Q.G. Wang, C.H. Cáceres, and J.R. Griffiths, Damage by Eutectic Particle Cracking in Aluminum Casting Alloys A356/357, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2003, 34(12), p 2901–2912
F. Grosselle, G. Timelli, and F. Bonollo, Doe Applied to Microstructural and Mechanical Properties of Al-Si-Cu-Mg Casting Alloys for Automotive Applications, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2010, 527(15), p 3536–3545
F. Grosselle, G. Timelli, F. Bonollo, A. Tiziani, and E. Della Corte, Correlation Between Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Al-Si Cast Alloys, Metall. Ital., 2009, 101(6), p 25–32
X. Teng, H. Mae, and Y. Bai, Probability Characterization of Tensile Strength of an Aluminum Casting, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2010, 527(16–17), p 4169–4176
N.R. Green and J. Campbell, Statistical Distributions of Fracture Strengths of Cast Al-7Si-Mg Alloy, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 1993, 173(1–2), p 261–266
W. Weibull, A Statistical Distribution Function of Wide Applicability, J. Appl. Mech., 1951, 18(3), p 293–297
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the contribution of Teksid Aluminum Spa (Carmagnola, Italy) for supporting this research. Many thanks to Dr. R. Molina and Mr. R. Di Matteo.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Timelli, G., Camicia, G. & Ferraro, S. Effect of Grain Refinement and Cooling Rate on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Secondary Al-Si-Cu Alloys. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 23, 611–621 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-013-0757-y
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-013-0757-y