Abstract
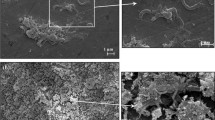
This article reports about the tests carried to investigate microbial-induced corrosion on stainless steels due to sulfate-reducing bacteria sp. Desulfotomaculum nigrificans in different host media. Stainless steel 304L, 316L, and 2205 were selected for the test. Modified Baar’s media (BM), sodium chloride solution, and artificial sea water (SW) were used as test solutions in anaerobic conditions. Electrochemical polarization and immersion test were performed to estimate the extent of corrosion rate and pitting on stainless steels. SEM/EDS were used to study the details inside/outside pits formed on the corroded samples. Biofilm formed on corroded coupons was analyzed for its components by UV/Visible spectroscopy. Corrosion attack on the test samples was observed maximum in case of exposure to SW followed by NaCl solution, both having sulfide and chloride whereas stainless steel exposed to BM, having sulfide, showed minimum attack. Tendency of extracellular polymeric substances to bind metal ions is observed to be responsible for governing the extent of corrosion attack.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
W.A. Hamilton, Sulfate-Reducing Bacteria and Anaerobic Corrosion, Annu. Rev. Microbiol., 1985, 39, p 195–217
I.B. Beech, Sulfate-Reducing Bacteria in Biofilms on Metallic Materials and Corrosion, Microbiol. Today, 2003, 30, p 115–117
R.K. Nilsen, J. Beeder, T. Thorstenson, and T. Torsvik, Distribution of Thermophilic Marine Sulphate Reducers in North Sea Oil Field Waters and Oil Reservoirs, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 1996, 62, p 1793–1798
P. Cristiani and U. Giancola, Heat Exchanger Fouling Mitigation and Cleaning Technologies, H. Muller-Steinhagen, Ed., Publico Publications, Essen, 2000, p 334–349.
P. Cristiani, G. Perboni, and A. Debenedetti, Effect of Chlorination on the Corrosion of Cu/Ni 70/30 Condenser Tubing, Electrochim. Acta, 2008, 54, p 100–107
R.C. Newman, H.S. Isaacs, and B. Alman, Effects of Sulfur Compounds on the Pitting Behavior of Type 304 Stainless Steel in Near-Neutral Chloride Solutions, Corrosion, 1982, 38, p 261–265
S.E. Werner, C.A. Johnson, N.J. Laycock, P.T. Wilson, and B.J. Webster, Pitting of Type 304 Stainless Steel in the Presence of a Biofilm Containing Sulphate Reducing Bacteria, Corros. Sci., 1998, 40, p 465–480
T.J. Marchesani, J.A. Ellor, and G.A Gehring Jr., Effect of Target Chlorination on the Corrosion Behavior of Copper-Nickel Condenser Tubing, EPRI TR-101405, Ocean City Research Corporation, Final Report, October 1992
R. J. Ferrara, E. Taschenberg, and P.J. Moran, The Effect of Chlorinated Sea Water on Galvanic Corrosion Behavior of Alloys Used in Seawater Piping Systems. Corrosion 85, Boston, MA, Paper No. 211, 1985
R. Toress-Sanchez, A. Magana-Vazuez, and J.M. Sanchez-Yanez, High Temperature Microbial Corrosion in the Condenser of a Geothermal Electric Power Unit, Mater. Performance, 1997, 36, p 43–46
M.A.N. Almeida and F.P. de Franca, Thermophilic and Mesophilic Bacteria in Biofilms Associated with Corrosion in a Heat Exchanger, World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 1999, 15, p 439–442
A.V.R. Kumar, R. Singh, and R.K. Nigam, Moissbauer Spectroscopy of Corrosion Products of Mild Steel due to Microbiologically Influenced Corrosion, J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem., 1999, 242, p 131–137
R. Alfaro-Cuevas-Villanueva, R. Cortes-Martinez, J.J. García-Díaz, R. Galvan-Martinez, and R. Torres-Sanchez, Microbiologically Influenced Corrosion of Steels by Thermophilic and Mesophilic Bacteria, Mater. Corros., 2006, 57, p 543–548
D. Çetin, S. Bilgiç, S. Dönmez, and G. Dönmez, Determination of Biocorrosion of Low Alloy Steel by Sulfate-Reducing Desulfotomaculum sp. Isolated from Crude Oil Field, Mater. Corros., 2007, 58, p 841–847
D. Çetin, S. Bilgiç, and G., Dönmez, Biocorrosion of Low Alloy Steel by Desulfotomaculum sp. and Effect of Biocides on Corrosion Control, ISIJ Int., 2007, 47, p 1023–1028
D. Çetin and M.L. Aksu, Corrosion Behavior of Low-Alloy Steel in the Presence of Desulfotomaculum sp., Corros. Sci., 2009, 51, p 1584–1588
B. Anandkumar, J.H. Choi, G. Venkatachari, and S. Maruthamuthu, Molecular Characterization and Corrosion Behavior of Thermophilic (55°C) SRB Desulfotomaculum kuznetsovii Isolated from Cooling Tower in Petroleum Refinery, Mater. Corros., 2009, 60, p 730–737
B. Anandkumar, A. Rajasekar, G. Venkatachari, and S. Maruthamuthu, Effect of Thermophilic Sulphate-Reducing Bacteria (Desulfotomaculum geothermicum) Isolated from Indian Petroleum Refinery on the Corrosion of Mild Steel, Curr. Sci., 2009, 97, p 342–348
H. El Hajj, A. Abdelouas, B. Grambow, C. Martin, and M. Dion, Microbial Corrosion of P235GH Steel Under Geological Condition, Phys. Chem. Earth, 2010, 35, p 248–253
P.J. Antony, S. Chonmdar, P. Kumar, and R. Raman, Corrosion of 2205 Duplex Stainless Steel in Chloride Medium Containing Sulfate-Reducing Bacteria, Electrochim. Acta, 2007, 52, p 3985–3994
E.I. Sungur, N. Cansever, and A. Cotuk, Microbial Corrosion of Galvanized Steel by a Freshwater Strain of Sulphate Reducing Bacteria (Desulfovibrio sp.), Corros. Sci., 2007, 49, p 1097–1109
P. Angell, J.-S. Luo, and D.C. White, Microbially Sustained Pitting Corrosion of 304 Stainless Steel in Anaerobic Seawater, Corros. Sci., 1995, 37, p 1085–1096
“Standard Reference Test Method for Making Potentiostatic and Potentiodynamic Anodic Polarization Measurements”, G5-87, Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 03.02, ASTM, p 73–79
“Standard Practice for Laboratory Immersion Corrosion Testing of Metals”, G31-72, Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 03.02, ASTM, p 102–109
H. Liu and H.H.P. Fang, Extraction of Extracellular Polymeric Substances (EPS) of Sludges, J. Biotechnol., 2002, 95, p 249–256
A. Nigam, Lab Manual in Biochemistry, Immunology and Biotechnology, Tata McGraw-Hill Publishing Company Limited, New Delhi, 2007
K. Mojica, D. Elsey, and M.J. Cooney, Quantitative Analysis of Biofilm EPS Uronic Acid Content, J. Microbiol. Method, 2007, 71, p 61–65
E.G. Bligh and W.J. Dyer, A Rapid Method of Total Lipid Extraction and Purification, Biochem. Physiol., 1959, 37, p 911–917
G. Rouser, S. Fleischer, and A. Yamamoto, Two Dimensional Thin Layer Chromatography Separation of Polar Lipid and Determination of Phospholipids by Phosphorous Analysis of Spots, Lipid, 1970, 5, p 494–496
A.D. Karkhanis, J.Y. Zeltner, and D.J.C. Carlo, A New and Improved Microassay to Determine 2-Keto-3-deoxyoctonate in Lipopolysaccharide of Gram-Negative Bacteria, Anal. Biochem., 1978, 85, p 595–601
I.B. Beech, C.W.S. Cheung, C.S.P. Chan, M.A. Hill, R. Franco, and A.R. Lino, Study of Parameters Implicated in the Biodeterioration of Mild Steel in the Presence of Different Species of Sulphate-Reducing Bacteria, Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad., 1994, 34, p 289–303
C.D. Ellwood, W.C. Keevil, D.P. Marsh, M.C. Brown, and N.J. Wardell, Surface-Associated Growth, Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B, 1982, 297, p 517–532
A. Boyd and M.A. Chakrabart, Role of Alginate Lyase in Cell Detachment of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 1994, 60, p 2355–2359
X. Zhang and L.P. Bishop, Biodegradability of Biofilm Extracellular Polymeric Substances, Chemosphere, 2003, 50, p 63–69
J. Wingender, T.R. Neu, and H.C. Flemming, What are Bacterial Extracellular Polymeric Substance, Microbial Extracellular Polymeric Substances: Characterization, Structure and Function, J. Wingender, T.R. Neu, and H.C. Flemming, Ed., Springer, Berlin, 1999, p 1–19
K.-Y. Chan, L.-C. Xu, and H.H.P. Fang, Anaerobic Electrochemical Corrosion of Mild Steel in the Presence of Extracellular Polymeric Substances Produced by a Culture Enriched in Sulfate-Reducing Bacteria, Environ. Sci. Technol., 2002, 36, p 1720–1727
V. Zinkevich, I. Bogdarina, H. Kang, W.A.M. Hil, R. Tapper, I.B. Beech, K.-Y. Chan, L.-C. Xu, and H.H.P. Fang, Anaerobic Electrochemical Corrosion of Mild Steel in the Presence of Extracellular Polymeric Substances Produced by a Culture Enriched in Sulfate-Reducing Bacteria, Environ. Sci. Technol., 1996, 36, p 1720–1727
V.W. Kueher and I.S.V.D. Vlugt, Graphitization of Cast Iron an Electrochemical Process in Anaerobic Soil, Water, 1934, 18, p 147–165
R.S. Poulsion, S.J.P. Colberg, and I.J. Drever, Toxicity of Heavy Metals (Ni, Zn) to Desulfovibrio desulfuricans, Geomicrobiol J., 1997, 14, p 41–49
C. Sun, J. Xu, F.H. Wang, and C.K. Yu, Effect of Sulfate Reducing Bacteria on Corrosion of Stainless Steel 1Cr18Ni9Ti in Soils Containing Chloride Ions, Mater. Chem. Phys., 2011, 126, p 330–336
A.K. Singh and A. Pourbaix, Rapports Techniques CEBELCOR 166, 1997, RT.318
G. Schmitt, Effect of Elemental Sulfur on Corrosion in Sour Gas Systems, Corrosion, 1991, 47, p 285–307
S.J. Yuan and S.O. Pehkonen, AFM Study of Microbial Colonization and its Deleterious Effect on 304 Stainless Steel by Pseudomonas NCIMB 2021 and Desulfovibrio desulfuricans in Simulated Seawater, Corros. Sci., 2009, 51, p 1372–1385
T.E. Ford, J.S. Maki, and R. Mitchell, Involvement of Bacterial Exopolymers in Biodeterioration of Metals, Biodeterioration, Vol 7, D.R. Houghton, R.N. Sith, and H.O.W. Eggins, Ed., Elsevier, London, New York, 1988, p 378–384
T.E. Ford and R. Mitchell, The Ecology of Microbial Corrosion, Adv. Microb. Ecol., 1990, 11, p 231–262
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lata, S., Sharma, C. & Singh, A.K. Effect of Host Media on Microbial Influenced Corrosion due to Desulfotomaculum nigrificans . J. of Materi Eng and Perform 22, 1120–1128 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-012-0384-z
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-012-0384-z