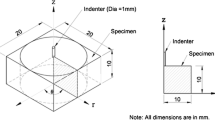
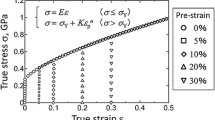
Abstract
Impression creep tests have been carried out at 923 K on 316LN SS containing 0.07, 0.14, and 0.22 wt.% nitrogen, under different applied stress levels. It was observed that the impression creep depth versus time curves were similar to the creep curves obtained from conventional uniaxial creep tests. The impression creep curves were characterized by a loading strain and primary and secondary creep stages similar to uniaxial creep curves. The tertiary stage observed in uniaxial creep curves was absent. The steady-state impression velocity was found to increase with increasing applied stress. The equivalent steady-state creep rates calculated from impression velocities were found to be in good agreement with the steady-state creep rates obtained from conventional uniaxial creep tests. Equivalence between applied stress and steady-state impression velocity with uniaxial creep stress and steady-state creep rate, respectively, has been established based on the laws of mechanics for time-dependent plasticity. It was found that impression velocity was sensitive to the variation in nitrogen content in the steel; impression velocity decreased with increasing nitrogen content, and the results obtained in this study were in agreement with those obtained from uniaxial creep tests.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
O.D. Sherby and P.E. Armstrong, Prediction of Activation Energies for Creep and Self-Diffusion from Hot Hardness Data, Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 1971, 2(12), p 3479–3484
H.D. Merchant, G.S. Murty, S.N. Bahadur, L.T. Dwivedi, and Y. Mehrotra, Hardness-Temperature Relationships in Metals, J. Mater. Sci., 1973, 8, p 437–442
P.M. Sargent and M.F. Ashby, Indentation Creep, Mater. Sci. Technol., 1992, 8(7), p 594–601
U.K. Viswanathan, T.R.G. Kutty, R. Keswani, and C. Ganguly, Evaluation of Hot Hardness and Creep of a 350 Grade Commercial Maraging Steel, J. Mater. Sci., 1996, 31, p 2705–2709
J.C.M. Li and S.N. Chu, Impression Creep: A New Creep Test, J. Mater. Sci., 1977, 12, p 2200–2208
J. Larsen-Badse, ORNL-TM-1862 Report, 1967
S.H. Wang, Impression Creep Behaviour in Weldments, J. Mar. Sci. Technol., 1994, 2(1), p 17–24
S.N.G. Chu and J.C.M. Li, Impression Creep of β-Tin Single Crystals, J. Mater. Sci. Eng., 1979, 39, p 1–10
D. Chiang and J.C.M. Li, Impression Creep of Lead, J. Mater. Res., 1994, 9(4), p 903–908
G.S. Murty and D.H. Sastry, Impression Creep of Zinc and the Rate-Controlling Dislocation Mechanism of Plastic Flow at High Temperatures, Phys. Stat. Sol. A, 1982, 70, p 63–71
G.S. Murty and D.H. Sastry, Impression Creep and High Temperature Deformation Mechanism in Cadmium, Trans. Indian Inst. Met., 1981, 34, p 195–201
R. Mahmudi and F. Kabirian, Impression Creep Behaviour of Cast AZ91 Magnesium Alloy, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2009, 40A, p 116–127
R. Mahmudi, Impression Creep Behaviour of Cast Pb-Sn Alloys, J. Alloys Compd., 2007, 427, p 124–129
D.H. Sastry, Impression Creep Technique—An Overview, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2005, 409, p 67–75
H.Y. Yu, M.A. Imam, and B.B. Rath, An Impression Test Method for Characterization of the Flow Behaviour of Superplastic Material, Mater. Sci. Eng., 1986, 79, p 125–132
T.H. Hyde, W. Sun, and J.A. Williams, Creep Behaviour of Parent, Weld and HAZ Materials of New, Service-aged and Repaired 1/2Cr1/2Mo1/4V:2 1/4Cr1Mo Pipe Welds at 640 °C, Mat. High Temp., 1991, 16, p 117–129
N.Q. Chinh, P. Tasnadi, A. Juhasz, P. Szommer, E. Szep-Kiss, and I. Kovacs, Investigation of the High Temperature Plasticity of Materials by Indentation Measurements, Key Eng. Mater., 1994, 97–98, p 159–168
K.M. Fox, J.R. Hellmann, E.C. Dickey, J.D. Green, and D.L. Shellmann, Impression and Compression Creep of SiAlON Ceramics, J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2006, 89(8), p 2555–2563
M.A. Azeem, A.K. Mondal, and S. Kumar, Creep Behaviour of Short Fibre Reinforced QE22 Magnesium Alloy Using Impression Creep Test, Trans. Indian Inst. Met., 2005, 58(2–3), p 489–492
A.K. Mondal and S. Kumar, Creep Behaviour of AE42 Magnesium Alloy and Its Composites Using Impression Creep Technique, Mater. Sci. Forum, 2010, 638–642, p 1552–1557
F. Yang and J.C.M. Li, Impression Creep of Thin Film by Vacancy Diffusion. 1. Straight Punch, J. Appl. Phys., 1993, 74, p 4382–4389
H.Y. Yu and J.C.M. Li, Computer Simulation of Impression Creep by the Finite Element Method, J. Mater. Sci., 1977, 12, p 2214–2222
E.C. Yu and J.C.M. Li, Impression Creep of LiF Single Crystals, Philos. Mag., 1977, 36(4), p 811–825
D. Dorner, K. Roller, B. Skrotzki, B. Stockhert, and G. Eggeler, Creep of a TiAl Alloy: A Comparison of Indentation and Tensile Testing, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2003, 357A, p 346–354
L. Peng, F. Yang, J.-F. Nie, and J.C.M. Li, Impression Creep of a Mg-8Zn-4Al-0.5Ca Alloy, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2005, 410–411, p 42–47
P.S. Gondavarti and K. Linga Murty, Creep Anisotropy of Zinc Using Impression Tests, J. Mater. Sci. Lett., 1987, 6, p 456–458
G. Nayyeri and R. Mahmudi, The Microstructure and Impression Creep Behaviour of Cast Mg-5Sn-xCa Alloys, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2010, 527, p 2087–2098
T.H. Hyde, K.A. Yehia, and A.A. Becker, Interpretation of Impression Creep Data Using a Reference Stress Approach, Int. J. Mech. Sci., 1993, 35(6), p 451–462
T.H. Hyde, K.A. Yehia, and A.A. Becker, Application of the Reference Stress Method for Interpreting Impression Creep Test Data, Mat. High Temp., 1995, 13(3), p 133–138
V. Ganesan, M.D. Mathew, P. Parameswaran, and K. Bhanu Sankara Rao, Creep Strengthening of Low Carbon Grade Type 316LN Stainless Steel by Nitrogen, Trans. Indian Inst. Met., 2010, 63(2–3), p 417–421
M.D. Mathew, Evolution of Creep Resistant 316 Stainless Steel for Sodium Cooled Fast Reactor Applications, Trans. Indian Inst. Met., 2010, 63(2–3), p 151–158
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Mr. N.S. Thampi for the technical support in carrying out the experiments. The support and encouragement received from Dr. T. Jayakumar, Director, the Metallurgy and Materials Group and from Dr. Baldev Raj, Director, the Indira Gandhi Centre for Atomic Research are gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mathew, M.D., Naveena & Vijayanand, D. Impression Creep Behavior of 316LN Stainless Steel. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 22, 492–497 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-012-0290-4
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-012-0290-4