Abstract
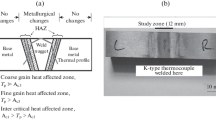
Different regions of heat-affected zone (HAZ) were simulated by heat treatment to investigate the mechanisms of the Type IV fracture of P92 (9Cr-2W) steel weldments. Creep deformation of simulated HAZ specimens with uniform microstructures was investigated and compared with those of the base metal (BM) and the weld metal (WM) specimens. The results show that the creep strain rate of the fine-grained HAZ (FGHAZ) is much higher than that of the BM, WM, the coarse-grained HAZ (CGHAZ), and the inter-critical HAZ (ICHAZ). According to the metallurgical investigation of stress-rupture, the FGHAZ and the ICHAZ have the most severely cavitated zones. During creep process, carbides become coarser, and form on grain boundaries again, leading to the deterioration of creep property and the decline of creep strength. In addition, the crack grows along the FGHAZ adjacent to the BM in the creep crack growth test (CCG) of HAZ.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. Blum and R.W. Vanstone, Materials Development for Boilers and Steam Turbines Operating at 700 °C, Proceedings of the Sixth International Charles Parsons Turbine Conference, September 16–18, 2003 (Dublin, Ireland), 2003, p 489–510
R. Viswanathan, J.F. Henry, J. Tanzosh, G. Stanko, J. Shingledecker, and B. Vitalis, US Program on Materials Technology for USC Power Plants, Proceedings of the Fourth International Conference on Advances in Materials Technology for Fossil Power Plants, 25–28 October 2004 (Hilton Head Island, South Carolina, USA), 2004, p 3–19
F. Abe, H. Okada, S. Wanikawa, M. Tabuchi, T. Itagaki, K. Kimura, K. Yamaguchi, and M. Igarashi, Guiding Principles for Development of advanced Ferritic Steels for 650 1C USC Boilers, Proceedings of the Seventh Liege Conference on Materials for Advanced Power Engineering 2002, 30 September–2 October, 2002 (Liege, Belgium), 2002, p 1397–1406
M.E. Kassner and T.A. Hayes, Creep Cavitation in Metals, Int. J. Plast., 2003, 19(10), p 1715–1748
J.H. Kim, Y.J. Oh, I.S. Hwang, D.J. Kim, and J.T. Kim, Fracture Behavior of Heat-Affected Zone in Low Alloy Steels, J. Nucl. Mater., 2001, 299(2), p 132–139
D.M. Rodrigues, L.F. Menezes, and A. Loureiro, The Influence of the HAZ Softening on the Mechanical Behaviour of Welded Joints Containing Cracks in the Weld Metal, Eng. Fract. Mech., 2004, 71(13–14), p 2053–2064
F. Abe and M. Tabuchi, Microstructural and Creep Strength of Welds in Advanced Ferritic Power Plant Steels, Sci. Technol. Weld. Join., 2004, 9, p 22–30
E. Letofsky and H. Cerjak, Metallography of 9Cr Steel Power Plant Weld Microstructures, Sci. Technol. Weld. Join., 2004, 9, p 31–36
Y. Hasegawa, M. Ohgami, and Y. Okamura, Creep Properties of Heat Affected Zone of Weld in W Containing 9-12% Chromium Creep Resistant Martensitic Steels at Elevated Temperature. Advanced Heat Resistant Steels for Power Generation, IOM Communications, The University Press, Cambridge, 1999, p 655–667
M. Tabuchi, T. Watanabe, K. Kubo, M. Matsui, J. Kinugawa, and F. Abe, Microstructure and Creep Strength of Welded Joints for W Strengthened High Cr Ferritic Steel, J. Soc. Mater. Sci., 2001, 50, p 116–121 (in Japanese)
M. Tabuchi, T. Watanabe, K. Kubo, M. Matsui, J. Kinugawa, and F. Abe, Creep Crack Growth Behavior in the HAZ of Weldments of W Containing High Cr Steel, Int. J. Pres. Ves. Pip., 2001, 78, p 779–784
M. Matsui, M. Tabuchi, T. Watanabe, K. Kubo, J. Kinugawa, and F. Abe, Degradation of Creep Strength in Welded Joint of 9-12%Cr Steels, ISIJ Int., 2001, 41, p S126–S130
M. Tabuchi, M. Matsui, T. Watanabe, H. Hongo, K. Kubo, and F. Abe, Creep Fracture Analysis of W Strengthened High Cr Steel Weldment, Mater. Sci. Res. Int., 2003, 9, p 23–28
T. Watanabe, M. Yamazaki, H. Hongo, M. Tabuchi, and T. Tanabe, Effect of Stress on Microstructural Change Due to Aging at 823 K in Multilayer Welded Joint of 2.25Cr-1Mo Steel, Int. J. Pres. Ves. Pip., 2004, 81, p 279–284
T. Watanabe, Relationship Between Type IV Fracture and Microstructure on 9Cr-1Mo-V-Nb Steel Welded Joint Creep-Ruptured After Long Term, Tetsu-to-Hagane, 2004, 90, p 206–212 (in Japanese)
ASTM E1457-00, Standard Test Method for Measurement of Creep Crack Growth Rates in Metals, Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 3 (No. 1), 2001, p 936–950
S.K. Albert, M. Matsui, H. Hongo, T. Watanabe, K. Kubo, and M. Tabuchi, Creep Rupture Properties of HAZs of a High Cr Ferritic Steel Simulated by a Weld Simulator, Int. J. Pres. Ves. Pip., 2004, 81(3), p 221–234
H.H. Johnson, Calibrating the Electric Potential Method for Studying Slow Crack Growth, Mater. Res. Stand., 1965, 5, p 442–445
K.H. Schwalbe and D. Hellmann, Application of the Electrical Potential Method to Crack Length Measurements Using Johnson’s Formula, J. Test. Eval., 1980, 9(4), p 218–220
P.J. Ennis, A. Zielinska-Lipiec, O. Wachter, and A. Czyrska-Filemonowicz, Microstructural Stability and Creep Rupture Strength of the Martensitic Steel P92 for Advanced Power Plant, Acta Mater., 1997, 45, p 4901
H. Riedel and J.R. Rice, Tensile Cracks in Creeping Solids Fracture Mechanics, Fracture Mechanics: Twelfth Conference, ASTM STP 700, American Society for Testing and Materials, 1980, p 112–130
B. Dogan and B. Petrovski, Creep Crack Growth oh High Temperature Weldments, Int. J. Pres. Ves. Pip., 2001, 78, p 795–805
L. Allais, J.P. Dessalas, T. Forgeron et al., Creep Behaviour of Full-Size Welded Joints: Defect Acceptance Criteria, Fatig. Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct., 1998, 21, p 791–803
Acknowledgment
The authors acknowledge the research funding and support by National Natural Science Foundation for Youth of China (Grant No. 50805103), Tianjin Nature Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 08JCZDJC18100) , Tianjin Nature Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 08JCYBJC09100) and New Teacher Project in Doctor sites Foundation of China Ministry of Education (Grant No. 20070056096).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
An, J., Jing, H., Xiao, G. et al. Analysis of the Creep Behavior of P92 Steel Welded Joint. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 20, 1474–1480 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-010-9779-x
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-010-9779-x