Abstract
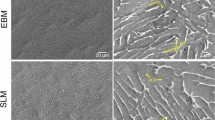
W-Ni-Fe alloys are important materials for many practical applications; however, at present, they are usually fabricated by conventional powder metallurgy techniques, which is difficult in fabrication with complex shapes. In this work, a selective laser melting (SLM) processing method was developed for fabricating W-Ni-Fe alloys parts. A process map was obtained for selection of proper laser parameters by optimizing processing conditions. Microstructures of laser fabricated samples in different laser energy inputs were investigated. There are two coexisting forming mechanisms in the SLM process: (i) liquid phase sintering (LPS) with full melting of Ni and Fe powders but non-melting of W powders and (ii) melting/solidification with full melting of W powders. Moreover, with increasing laser energy, a transition trend of forming mechanism from LPS to full melting/solidification can be observed.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
F. Abe, K. Osakada, M. Shiomi, K. Uematsu, and M. Matsumoto, The Manufacturing of Hard Tools from Metallic Powders by Selective Laser Melting, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2001, 111(1–3), p 210–213
E.C. Santos, M. Shiomi, K. Osakada, and T. Laoui, Rapid Manufacturing of Metal Components by Laser Forming, Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf., 2006, 46(12–13), p 1459–1468
A. Simchi, F. Petzoldt, and H. Pohl, On the Development of Direct Metal Laser Sintering for Rapid Tooling, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2003, 141(3), p 319–328
X. Wu and J. Mei, Near Net Shape Manufacturing of Components Using Direct Laser Fabrication Technology, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2003, 135(2–3), p 266–270
P. Fischer, V. Romano, H.P. Weber, N.P. Karapatis, E. Boillat, and R. Glardon, Sintering of Commercially Pure Titanium Powder with a Nd: YAG Laser Source, Acta Mater., 2003, 51(6), p 1651–1662
A. Simchi and H. Pohl, Direct Laser Sintering of Iron-Graphite Powder Mixture, Mater. Sci. Eng. A Struct. Mater. Prop. Microstruct. Process., 2004, 383(2), p 191–200
A. Simchi, Direct Laser Sintering of Metal Powders: Mechanism, Kinetics and Microstructural Features, Mater. Sci. Eng. A Struct. Mater. Prop. Microstruct. Process., 2006, 428(1–2), p 148–158
J.P. Kruth, L. Froyen, J. Van Vaerenbergh, P. Mercelis, M. Rombouts, and B. Lauwers, Selective Laser Melting of Iron-Based Powder, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2004, 149(1–3), p 616–622
Y. Wang, J. Bergstrom, and C. Burman, Characterization of an Iron-Based Laser Sintered Material, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2006, 172(1), p 77–87
A. Simchi and H. Pohl, Effects of Laser Sintering Processing Parameters on the Microstructure and Densification of Iron Powder, Mater. Sci. Eng. A Struct. Mater. Prop. Microstruct. Process., 2003, 359(1–2), p 119–128
M.L. Sun, L. Lu, and J.Y.H. Fuh, Microstructure and Properties of Fe-Base Alloy Fabricated Using Selective Laser Melting, 2nd International Symposium on Laser Precision Microfabrication, I. Miyamoto, Y.F. Lu, K. Sugioka, and J.J. Dubowski, Ed., Singapore, 2001, p 139–142
K.A. Mumtaz, P. Erasenthiran, and N. Hopkinson, High Density Selective Laser Melting of Waspaloy (R), J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2008, 195(1–3), p 77–87
C.P. Paul, P. Ganesh, S.K. Mishra, P. Bhargava, J. Negi, and A.K. Nath, Investigating Laser Rapid Manufacturing for Inconel-625 Components, Opt. Laser Technol., 2007, 39(4), p 800–805
K. Mumtaz and N. Hopkinson, Top Surface and Side Roughness of Inconel 625 Parts Processed Using Selective Laser Melting, Rapid Prototyping J., 2009, 15(2), p 96–103
H.H. Zhu, L. Lu, and J.Y.H. Fuh, Development and Characterisation of Direct Laser Sintering Cu-Based Metal Powder, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2003, 140, p 314–317
D.D. Gu and Y.F. Shen, Development and Characterisation of Direct Laser Sintering Multicomponent Cu Based Metal Powder, Powder Metall., 2006, 49(3), p 258–264
S.R. Pogson, P. Fox, C.J. Sutcliffe, and W. O’Neill, The Production of Copper Parts Using DMLR, Rapid Prototyping J., 2003, 9(5), p 334–343
W.H. Wu, Y.Q. Yang, and Y.L. Huang, Direct Manufacturing of Cu-Based Alloy Parts by Selective Laser Melting, Chin. Opt. Lett., 2007, 5(1), p 37–40
D.A. Hollander, M. von Walter, T. Wirtz, R. Sellei, B. Schmidt-Rohlfing, O. Paar, and H.J. Erli, Structural, Mechanical and In Vitro Characterization of Individually Structured Ti-6Al-4V Produced by Direct Laser Forming, Biomaterials, 2006, 27(7), p 955–963
K. Osakada and M. Shiomi, Flexible Manufacturing of Metallic Products by Selective Laser Melting of Powder, Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf., 2006, 46(11), p 1188–1193
D.D. Gu and Y.F. Shen, WC-Co Particulate Reinforcing Cu Matrix Composites Produced by Direct Laser Sintering, Mater. Lett., 2006, 60(29–30), p 3664–3668
D.D. Gu, Z.Y. Wang, Y.F. Shen, Q. Li, and Y.F. Li, In Situ TiC Particle Reinforced Ti-Al Matrix Composites: Powder Preparation by Mechanical Alloying and Selective Laser Melting Behavior, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2009, 255(22), p 9230–9240
H.H. Soon and H.J. Ryu, Combination of Mechanical Alloying and Two-Stage Sintering of a 93W-5.6Ni-1.4Fe Tungsten Heavy Alloy, Mater. Sci. Eng. A Struct. Mater. Prop. Microstruct. Process., 2003, 344(1–2), p 253–260
A. Upadhyaya, S.K. Tiwari, and P. Mishra, Microwave Sintering of W-Ni-Fe Alloy, Scr. Mater., 2007, 56(1), p 5–8
J. Shen, L. Campbell, P. Suri, and R.M. German, Quantitative Microstructure Analysis of Tungsten Heavy Alloys (W-Ni-Cu) During Initial Stage Liquid Phase Sintering, Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater., 2005, 23, p 99–108
S. Das, Physical Aspects of Processing Control in Selective Laser Sintering of Metals, Adv. Eng. Mater., 2003, 5, p 701–711
A. Simchi, F. Petzoldt, and H. Pohl, Direct Metal Laser Sintering: Material Considerations and Mechanisms of Particle Bonding, Int. J. Powder Metall., 2001, 37(2), p 49–61
P. Wang, Powder Metallurgy, Beijing Technology University, Metallurgy Industry Publishing Company, Beijing, 2000 (in Chinese)
T.B. Massalski, Binary Alloy Phase, ASM International, Material Park, OH, 1996
D.D. Gu, Y.F. Shen, J.L. Yang, and Y. Wang, Effects of Processing Parameters on Direct Laser Sintering of Multicomponent Cu Based Metal Powder, Mater. Sci. Technol., 2006, 22(12), p 1449–1455
D.D. Gu, Y.F. Shen, and X.J. Wu, Formation of a Novel W-Rim/Cu-Core Structure During Direct Laser Sintering of W-Cu Composite System, Mater. Lett., 2008, 62(12–13), p 1765–1768
K. Lai, Y. Yang, and L. Zhang, Fiber Laser and its Applications in Rapid Prototyping of Selective Laser Melting, Laser Optoelectron. Prog., 2006, 43, p 32–36 (in Chinese)
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the Open fund of State Key Laboratory of Powder Metallurgy of Central South University of China (2008112022). The authors also thank the Analytic and Testing Centre of Huazhong University of Science and Technology for their assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, D., Cai, Q., Liu, J. et al. Research on Process and Microstructure Formation of W-Ni-Fe Alloy Fabricated by Selective Laser Melting. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 20, 1049–1054 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-010-9720-3
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-010-9720-3