Abstract
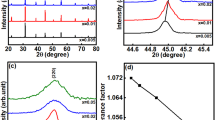
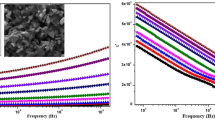
Li-doped La2/3Cu3Ti4O12 ceramics and the Li0.5La0.5Cu3Ti4O12 ceramic samples were prepared by the sol–gel technique. The influence of sintering conditions on structures and dielectric properties of Li0.5La0.5Cu3Ti4O12 ceramic samples were systematically researched. The results indicated that the Li0.5La0.5Cu3Ti4O12 ceramic samples sintered at 1070°C for 10 h exhibited low porosity structure, larger grain sizes (ca 8 μm and 4 μm) with bimodal distribution, higher permittivity (ca 0.70–1.0 × 104), especially lower dielectric loss (ca 0.030) and better stability of frequency and temperature. The internal barrier layer capacitor effect could well explain the giant permittivity phenomenon of the Li0.5La0.5Cu3Ti4O12 ceramics. Additionally, the grain boundary conduction of the Li0.5La0.5Cu3Ti4O12 ceramic samples displayed two different characteristics, thus two kinds of conductivity activation energy values were obtained in the grain boundary. Simultaneously, it was found that the temperature among 190–230°C seemed to be an important temperature region. The permittivity, dielectric loss and conductivity characteristics in the critical temperature region of 190–230°C showed abnormal change. It was concluded that in the critical temperature region, the oxygen vacancy forms, concentration and extra electrons concentration might vary significantly. The second-ionized oxygen vacancies (\( V_{\rm{O}}^{ \cdot \cdot } \)) might play a dominating role below about 190°C for the electrical properties of ceramic samples, while the first-ionized oxygen vacancies (\( V_{\rm{O}}^{ \cdot } \)) might be principal above about 230°C.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
X.J. Cheng, Z.W. Li, and J.G. Wu, J. Mater. Chem. A 3, 5805 (2015).
Z.W. Li, J.G. Wu, D.Q. Xiao, and J.G. Zhu, Acta Mater. 103, 243 (2016).
Z.W. Li, X. Luo, W.J. Wu, and J.G. Wu, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 100, 3004 (2017).
C.L. Zhao and J.G. Wu, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 10, 3680 (2018).
X.H. Zhu, L.H. Yang, J.L. Li, L. Jin, and F. Li, Ceram. Int. 43, 640 (2017).
J.L. Li, F. Li, X.H. Zhu, D.B. Lin, and Z. Xu, J. Alloys Compd. 692, 375 (2017).
M.A. Subramanian, D. Li, N. Duan, B.A. Reisner, and A.W. Sleight, J. Solid State Chem. 151, 323 (2000).
P.B. Shri and K.B.R. Varma, Phys. B 403, 2246 (2008).
Y.Q. Tana, J.L. Zhanga, W.T. Haoa, and G. Chena, Mater. Chem. Phys. 124, 1100 (2010).
P.F. Liang, Z.P. Yang, X.L. Chao, and Z.H. Liu, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 95, 2218 (2012).
H.M. Ren, P.F. Liang, and Z.P. Yang, Mater. Res. Bull. 45, 1608 (2010).
P. Thongbai, T. Yamwong, and S. Maensiri, Mater. Res. Bull. 47, 432 (2012).
X. Wang, P.F. Liang, Z.H. Peng, H. Peng, and Z.P. Yang, J. Alloys Compd. 778, 391 (2019).
Z.Q. Liu and Z.P. Yang, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 46, 6175 (2017).
L.H. Yang, X.L. Chao, Z. Yang, N. Zhao, L.L. Wei, and Z.P. Yang, Ceram. Int. 42, 2526 (2016).
J.J. Liu, R.W. Smith, and W.N. Mei, Chem. Mater. 19, 6020 (2007).
D.L. Sun, A.Y. Wu, and S.T. Yiny, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 91, 169 (2008).
Z.Q. Liu, X.L. Chao, and Z.P. Yang, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 27, 8980 (2014).
Z.Q. Liu, X.L. Chao, and Z.P. Yang, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 97, 2154 (2014).
B. Xu, J. Zhang, and Z.M. Tian, Mater. Lett. 75, 87 (2012).
B.A. Bender and M.J. Pan, Mater. Sci. Eng. B 117, 339 (2005).
P. Zheng, J.L. Zhang, S.F. Shao, Y.Q. Tan, and C.L. Wang, Appl. Phys. Lett. 94, 032902 (2009).
Q.L. Zhang, T. Li, Z.P. Chen, R.Z. Xue, and Y.Q. Wang, Mater. Sci. Eng. B 177, 168 (2012).
W.T. Hao, J.L. Zhang, Y.Q. Tan, and W.B. Su, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 92, 2937 (2009).
W.T. Hao, J.L. Zhang, Y.Q. Tan, M.L. Zhao, and C.L. Wang, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 94, 1067 (2011).
S.M. Moussa and B.J. Kennedy, Mater. Res. Bull. 36, 2525 (2001).
Y.H. Lin, J.N. Cai, M. Li, C.W. Nan, and J.L. He, J. Appl. Phys. 103, 074111 (2008).
M.A. Siddiqui, V.S. Chandel, and A. Azam, Appl. Surf. Sci. 258, 7354 (2012).
W.Z. Yang, C.L. Song, and X.Q. Liu, J. Electron. Mater. 43, 1645 (2014).
H. Hong and D.Y. Kjm, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 90, 2118 (2007).
H.Y. Zhu and X.M. Chen, J. Mater. Sci. 46, 6339 (2011).
L. Zhang and Z.J. Tang, Phys. Rev. B 70, 17436 (2004).
C.K. Suman, K. Prasad, and R.N.P. Choudhary, Mater. Chem. Phys. 97, 425 (2006).
T.Y. Li, H.Q. Fan, C.B. Long, and G.Z. Dong, J. Alloys Compd. 609, 60 (2014).
Z.Q. Liu, X.L. Chao, and Z.P. Yang, Mate. Res. Bull. 48, 4877 (2013).
J.G. Wu and J. Wang, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 93, 2795 (2010).
P.F. Liang, X.L. Chao, F. Wang, Z.Q. Liu, and Z.P. Yang, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 96, 3883 (2013).
J.G. Wu, J. Wang, D.Q. Xiao, and J.G. Zhu, J. Appl. Phys. 110, 064104 (2011).
J.Y. Li, X.T. Zhao, and F. Gu, Appl. Phys. Lett. 100, 202905 (2012).
F. Moura, A.Z. Simoes, and R.C. Deus, Ceram. Int. 39, 3499 (2013).
J.K. Gill, O.P. Pandey, and K. Singh, Solid State Sci. 13, 1960 (2011).
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Science Foundation of China (No. 51172136), the Science Foundation of Shaanxi Province (No. 2017JM2037), the Scientific Research Funds of Shaanxi Provincial Education Department (17JK0277) and the Scientific Research Funds of Weinan Normal University (Nos. 18ZRRC16, 2018JYKX013).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Z., Yang, Z. High Permittivity, Low Dielectric Loss and Impedance Characteristics of Li0.5La0.5Cu3Ti4O12 Ceramics by a Sol–Gel Technique. J. Electron. Mater. 48, 5333–5341 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-019-07344-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-019-07344-x