Abstract
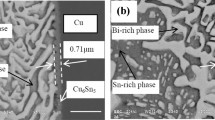
The interfacial reaction in soldering is a crucial subject for the solder-joint integrity and reliability in electronic packaging technology. However, electronic industries are moving toward lead-free alloys because of environmental concerns. This drive has highlighted the fact that the industry has not yet arrived at a decision for lead-free solders. Among the lead-free alloys, Sn-3.5Ag and Sn-3.5Ag-0.5Cu are the two potential candidates. Here, detailed microstructural studies were carried out to compare the interfacial reaction of Sn-3.5Ag and Sn-3.5Ag-0.5Cu solder with a ball grid array (BGA) Cu substrate for different reflow times. The Cu dissolution from the substrate was observed for different soldering temperatures ranging from 230°C to 250°C, and the dissolution was found to increase with time and temperature. Dissolution of Cu in the Sn-3.5Ag solder is so fast that, at 240°C, 12 µm of the Cu substrate is fully consumed within 5 min. Much less dissolution is observed for the Sn-3.5Ag-0.5Cu solder. In respect to such high dissolution, there is no significant difference observed in the intermetallic compound (IMC) thickness at the interface for both solder alloys. A simplistic theoretical approach is carried out to find out the amount of Cu6Sn5 IMCs in the bulk of the solder by the measurement of the Cu consumption from the substrate and the thickness of the IMCs that form on the interface.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Sriyarunya, Proc. Int. IEEE Conf. on the Business of Electronic Product Reliability and Liability (Hong Kong, China, 2003), p. 192.
C.M. Miller, I.E. Anderson, and J.F. Smith, J. Electron. Mater. 23, 595 (1994).
R.J. Klein Wassink, Soldering in Electronics, 1st ed. (Ayr, Scotland: Electrochemical Publications Ltd., 1984), pp. 93–118.
M. Scaefer, W. Laub, R.A. Fournelle, and J. Liang, Design and Reliability of Solders and Solder Interconnects, ed. R.K. Mahidhara (Warrendale, PA: TMS, 1997), pp. 247–258.
D. Grivas, D. Fear, L. Quan, and J.W. Morris, J. Electron. Mater. 15, 355 (1986).
J.O.G. Parent, D.D.L. Chung, and I.M. Bernstein, J. Mater. Sci. 23, 2564 (1988).
S. Bader, W. Gust, and H. Hieber, Acta Metall. Mater. 43, 329 (1995).
H.K. Kim, H.K. Liou, and K.N. Tu, Appl. Phys. Lett. 66, 2337 (1995).
R.W. Barnard, Plating 6, 452 (1974).
R. Roy and S.K. Sen, J. Mater. Res. 7, 1377 (1992).
H.K. Kim and K.N. Tu, Appl. Phys. Lett. 67, 2002 (1995).
H.K. Kim and K.N. Tu, Phys. Rev. B 53, 16027 (1996).
A.G. Ward and J.W. Taylor, J. Inst. Met. 86, 36 (1957).
T. Ishida, Trans. JIM 14, 37 (1973).
L.H. Su, Y.W. Yen, C.C. Lin, and S.W. Chen, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 28B, 927 (1997).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sharif, A., Chan, Y.C. Comparative study of interfacial reactions of Sn-Ag-Cu and Sn-Ag solders on Cu pads during reflow soldering. J. Electron. Mater. 34, 46–52 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-005-0179-1
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-005-0179-1