Abstract
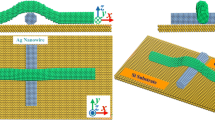
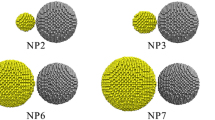
Molecular dynamics (MD) simulation was conducted to investigate the coalescence of Ag nanoparticles and their deposition on a gold substrate at various temperatures from 400 K to 1,000 K using the embedded atom method (EAM). Density distribution function, x-z plane projection, spreading index, and coalescence index were analyzed to gain more insight into the sintering and diffusion process. Simulation results showed that Ag and Au atoms can diffuse into each other significantly at a temperature of 1,000 K and reform the lattice structure after the temperature is cooled back to 400 K. Simulation data also demonstrated that even at a low temperature of 400 K, silver spheres can be collapsed and deposited on the substrate. Yet higher temperatures were helpful in enhancing the degree of collapsing and deposition.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.C. Jagt, IEEE Trans. Comp. Packaging Manufacturing Technol. Part A 21, 215 (1998).
A.J. Lovinger, J. Adhes. 10, 1 (1979).
S. Asai, U. Saruta, M. Tobita, M. Takano, and Y. Miyashita, J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 56, 769 (1995).
A.O. Ogunjimi, O. Boyle, D.C. Whalley, and D.J. Williams, J. Electron. Manuf. 2, 109 (1992).
K. Gilleo, Solder. Surf. Mount Technol. 19, 12 (1995).
P.G. Harris, Solder. Surf. Mount Technol. 20, 19 (1995).
J. Liu, ed., Conductive Adhesives for Electronics Packaging (Bristol, U.K.: Electrochemical Publications, 1999).
J. Lin, J. Drye, W. Lytle, T. Scharr, R. Subrahmanyan, and R. Sharma, IEEE Proc. 46th Electronic Components and Technology Conf. (Piscataway, NJ: IEEE, 1996), pp. 1059–1068.
J.C. Jagt, P.J.M. Beric, and G.F.C.M. Lijten, IEEE Trans. Components Packaging Manufacturing Technol. Part B 18, 292 (1995).
M.A. Gaynes, R.H. Lewis, R.F. Saraf, and J.M. Roldan, IEEE Trans. Comp. Packaging Manufacturing Technol. Part B 18, 299 (1995).
R. Dudek, H. Berek, T. Fritsch, and B. Michel, IEEE Trans. Comp. Packaging Manufacturing Technol. Part A 23, 462 (2000).
D. Klosterman, L. Li, and J.E. Morris, IEEE Trans. Comp. Packaging Manufacturing Technol. Part A 21, 23 (1998).
D. Lu, Q.K. Tong, and C.P. Wong, IEEE Trans. Comp. Packaging Manufacturing Technol. Part C 22, 228 (1999).
D. Lu, Q.K. Tong, and C.P. Wong, IEEE Trans. Comp. Packaging Manufacturing Technol. 23, 620 (2000).
Q.K. Tong, G. Fredrickson, R. Kuder, and D. Lu, IEEE Proc. 49th Electronic Components and Technology Conf. (Piscataway, NJ: IEEE, 1999), pp. 347–352.
G.R. Ruschau, S. Yoshikawa, and R.E. Newnhan, J. Appl. Phys. 72, 953 (1992).
I. Dietrich, Z. Phys. 132, 231 (1952).
C.P. Wong, K.S. Moon, and Y. Li, Georgia Tech. Corp. Invention Disclosure 2003, U.S. patent pending.
P. Pawlow, Z. Phys. Chem. 65, 545 (1909).
H. Reiss and I.B. Wilson, J. Coll. Sci. 3, 551 (1948).
K.M. Unruh, T.E. Huber, and C.A. Huber, Phys. Rev. B 48, 9022 (1993).
M. Oda et al., Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. 704, 3 (2002).
L.J. Lewis, P. Jensen, and J.-L. Barrat, Phys. Rev. B 56, 2248 (1997).
R. Ge, P.C. Clapp, and J.A. Rifkin, Surf. Sci. 426, L413 (1999).
S.J. Zhao, S.Q. Wang, Z.Q. Yang, and H.Q. Ye, J. Phys.: Cond. Matter 13, 8061 (2001).
H. Dong, K.S. Moon, and C.P. Wong, J. Electron. Mater. 33, 1326 (2004).
M.S. Daw and M.I. Baskes, Phys. Rev. B 29, 6443 (1984).
S.M. Foiles, M.I. Baskes, and M.S. Daw, Phys. Rev. Lett. 50, 1285 (1983).
S.J. Plimpton and B.A. Hendrickson, MRS Proc. 291, 37 (1993).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dong, H., Moon, KS. & Wong, C.P. Molecular dynamics study of nanosilver particles for low-temperature lead-free interconnect applications. J. Electron. Mater. 34, 40–45 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-005-0178-2
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-005-0178-2