Abstract
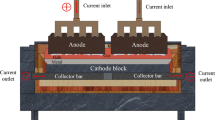
In the aluminum reduction cells, gas bubbles are generated at the bottom of the anode which eventually reduces the effective current contact area and the system efficiency. To encourage the removal of gas bubbles, slotted anode has been proposed and increasingly adopted by some industrial aluminum reduction cells. Nonetheless, the exact gas bubble removal mechanisms are yet to be fully understood. A three-dimensional (3D) transient, multiphase flow mathematical model coupled with magnetohydrodynamics has been developed to investigate the effect of slotted anode on the gas bubble movement. The Eulerian volume of fluid approach is applied to track the electrolyte (bath)–molten aluminum (metal) interface. Meanwhile, the Lagrangian discrete particle model is employed to handle the dynamics of gas bubbles with considerations of the buoyancy force, drag force, virtual mass force, and pressure gradient force. The gas bubble coalescence process is also taken into account based on the O’Rourke’s algorithm. The two-way coupling between discrete bubbles and fluids is achieved by the inter-phase momentum exchange. Numerical predictions are validated against the anode current variation in an industrial test. Comparing the results using slotted anode with the traditional one, the time-averaged gas bubble removal rate increases from 36 to 63 pct; confirming that the slotted anode provides more escaping ways and shortens the trajectories for gas bubbles. Furthermore, the slotted anode also reduces gas bubble’s residence time and the probability of coalescence. Moreover, the bubble layer thickness in aluminum cell with slotted anode is reduced about 3.5 mm (17.4 pct), so the resistance can be cut down for the sake of energy saving and the metal surface fluctuation amplitude is significantly reduced for the stable operation due to the slighter perturbation with smaller bubbles.
















Similar content being viewed by others

References
J. Thonstad, H. D. Kleinschrodt, H. Vogt: Light Metals, TMS, Warrendale, PA, 1997, pp. 427-432.
T. M. Hyde, B. J. Welch: Light Metals, TMS, Warrendale, PA, 1997, pp. 333-340.
Q. Wang, B. K. Li, Z. He, N. X. Feng: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2014, vol. 45, pp. 272-294.
J. P. Peng, Y. F. Tian, N. X. Feng, Y. W. Wang, Z. Q. Wang: J. Mater. Metall., 2009, vol. 8, pp. 165-171.
N.X. Feng: Low energy consumption aluminum reduction cell with novel cathode, China, ZL 200710010523.4, 2008.
G. Bearne, D. Gadd, S. Lix: Light Metals, TMS, Warrendale, PA, 2007, pp. 305-310.
W. E. Haupin: JOM, 1971, vol. 23, pp. 46-49.
S. Fortin, M. Gerhardt, A. J. Gesing: Light Metals, TMS, Warrendale, PA, 1984, pp. 721-741.
X. W. Wang, G. Tarcy, S. Whelan, S. Porto: Light Metals, TMS, Warrendale, PA, 2007, pp. 299-304.
W. Yang, M. A. Cooksey: Light Metals, TMS, Warrendale, PA, 2007, pp. 451-456.
Y. F. Wang, L. F. Zhang, X. J. Zuo: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2011, vol. 42, pp. 1051-1064.
S. Yang, H. L. Zhang, Y. J. Xu, H. H. Zhang, Z. Zou, J. Li, Y. Q. Lai: J. Cent. South Univ., 2012, vol. 43, pp. 4617-4625.
S.Q. Zhan, M. Li, J. M. Zhou: J. Cent. South Univ., 2015, vol. 22, pp. 2482-2492.
Y. L. Wang, J. Tie, G. F. Tu, S. C. Sun, R. T. Zhao, and Z. F. Zhang: Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China, 2015, 25, pp. 335-344.
L. I. Kiss, S. Ponesak, J. Antille: Light Metals, TMS, Warrendale, PA, 2005, pp. 559-564.
M. Alam, W. Yang, K. Mohanarangam, G. Brooks, and Y. S. Morsi: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2013, vol. 44, pp. 1155-1165.
Y. Feng, M. P. Schwarz, W. Yang, and M. Cooksey: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2015, vol. 46, pp. 1959-81.
K. Vekony and L. I. Kiss: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2012, vol. 43B, pp. 1086-1097.
A. L. Perron, L. K. Kiss, and S. Poncsak: J. appl. Electrochem., 2006, vol. 36, pp. 1381-1389.
A. L. Perron, L. K. Kiss, and S. Poncsak: J. appl. Electrochem., 2007, vol. 37, pp. 303-310.
T.M. Hyde and B.J. Welch: Royal Australian Chemical Institute, 1992, pp. 161–168.
Z.B. Zhao, Z.W. Wang, B.L. Gao, Y.Q. Feng, Z.N. Shi, and X.W. Hu: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2016, vol. 47, pp. 1-14.
J. U. Brackbill, D. B. Kothe, and C. Zemach: J. Comput. Phys., 1992, vol. 100, pp. 335-354.
S. A. Morsi and A. J. Alexander: J. Fluid Mech., 1972, vol. 55, pp. 193–208.
P.J. O’rourke: PhD Thesis. Princeton University, Princeton, New Jersey, 1981.
L. M. Li, and B. K. Li: JOM, 2016, vol. 68, pp. 2160-2169.
J. Li, Y. J. Xu, and H. L. Zhang, Y. Q. Lai: Int. J. Multiphase Flow, 2011, vol. 37, pp. 46-54.
A. Solheim, S. T. Johansen, and S. Rolseth: J. Appl. Electrochem., 1989, vol. 19, pp. 703-712.
M. Alam, Y. Morsi, and W. Yang: Light metals, TMS, Warrendale, PA, 2013, pp. 591-596.
S. Poncsak, L.K. Kiss, and D. Toulouse: Light Metals, 2006, pp. 457-462.
H. L. Zhang, T. S. Li, and J. Li: JOM, 2017, 69, pp. 292-300.
D. S. Severo, A. F. Schneider, and E. C. Pinto: Light Metals, TMS, Warrendale, PA, 2005.
O. Zikanov, A. Thess, and P. A. Davidson: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2000, vol. 31, pp. 1541-1550.
H.S. Li, X. Cao, and Y.F. Tian: Nonferrous metals industry conference on low carbon development, 2010, pp. 22–27.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51434005) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 50934005).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted January 17, 2017.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, M., Li, B., Li, L. et al. Effect of Slotted Anode on Gas Bubble Behaviors in Aluminum Reduction Cell. Metall Mater Trans B 48, 3161–3173 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-017-1065-y
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-017-1065-y