Abstract
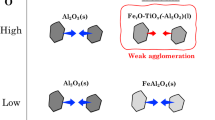
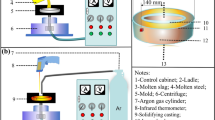
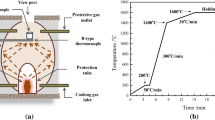
An innovative approach of super gravity was proposed to separate fine Al2O3 inclusions from liquid steel in this study. To investigate the removal behaviors of inclusions, the effects of different gravity coefficients and time on separating the inclusions were studied. The results show that a large amount of Al2O3 inclusions gathered at the top of the sample obtained by super gravity, whereas there were almost no inclusions appearing at the bottom. The volume fraction and number density of inclusions presented a gradient distribution along the direction of the super gravity, which became steeper with increasing gravity coefficient and separating time. As a result of the collision between inclusions, a large amount of inclusions aggregated and grew during the moving process, which further decreased the removal time. The experimental required removal time of inclusions is close to the theoretical values calculated by Stokes law under gravity coefficient G ≤ 80, t ≤ 15 minutes, and the small deviation may be because the inclusion particles are not truly spherical. Under the condition of gravity coefficient G = 80, t = 15 minutes, the total oxygen content at the bottom of the sample (position of 5 cm) is only 8.4 ppm, and the removal rate is up to 95.6 pct compared with that under normal gravity.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Liu, Q. Huang, C. Li, and B. Huang: Fusion Eng. Des., 2009, vol. 84, pp. 1214-8.
K. Shiozawa, Y. Morii, S. Nishino, and L. Lu: J. Soc. Mater. Sci. Jpn., 2003, vol. 52, pp. 1311-7.
Z.G. Yang, J.M. Zhang, S.X. Li, G.Y. Li, Q.Y. Wang, W.J. Hui, and Y.Q. Weng: Mater. Sci. Eng.: A, 2006, vol. 427, pp. 167-74.
G. Qian, Y. Hong, and C. Zhou: Eng. Fail. Anal., 2010, vol. 17, pp. 1517-25.
L.T. Wang, Q.Y. Zhang, S.H. Peng, and Z.B. Li: ISIJ Int., 2005, vol. 45, pp. 331-7.
Z. Taslicukur, C. Balaban, and N. Kuskonmaz: J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 2007, vol. 27, pp. 637-40.
L. Zhang and S. Taniguchi: Int. Mater. Rev., 2000, vol. 45, pp. 59-82.
Y. Miki, H. Kitaoka, T. Sakuraya, and T. Fujii: ISIJ Int., 1992, vol. 32, pp. 142-9.
Y. Miki, S. Ogura, and T. Fujii: Kawasaki Steel Technical Report-English Edition, 1996, pp. 67–73.
C. Ramshaw and R.H. Mallinson: Patent 0002568, 1979.
A. Das, A. Bhowal, and S. Datta: Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2008, vol. 47, pp. 4230-5.
C.C. Lin and K.S. Chien: Separ. Purif. Tech., 2008, vol. 63, pp. 138-44.
Y.S. Chen, F.Y. Lin, C.C. Lin, C.Y.D. Tai, and H.S. Liu: Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2006, vol. 45, pp. 6846-53.
T. Liu, Z.C. Guo, Z. Wang, and M.Y. Wang: Appl. Surf. Sci., 2010, vol. 256, pp. 6634-40.
M.Y. Wang, Z. Wang, Z.C. Guo, and Z.J. Li: Int. J. Hydro. Energ., 2011, vol. 36, pp. 3305-12.
C. Li, J.T. Gao, and Z.C. Guo: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2016, vol. 47, pp. 1516-9.
J.T. Gao, Y.W. Zhong, and Z.C. Guo: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2016, vol. 47, pp. 2459-67.
J.T. Gao, Y.W. Zhong, L. Guo, and Z.C. Guo: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2016, vol. 47, pp. 1080-92.
J.T. Gao, Y.W. Zhong, and Z.C. Guo: ISIJ Int., 2016, vol. 56, pp. 1352-7.
J.T. Gao, L. Guo, and Z.C. Guo: ISIJ Int., 2015, vol. 55, pp. 2535-42.
L.X. Zhao, Z.C. Guo, Z. Wang, and M.Y. Wang: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2010, vol. 41, pp. 505-8.
G.Y. Song, B. Song, Y.H. Yang, Z.B. Yang, and W.B. Xin: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2015, vol. 46, pp. 2190-7.
Y. Watanabe, A. Kawamoto, and K. Matsuda: Compos. Sci. Tech., 2002, vol. 62, pp. 881-8.
Y. Watanabe, Y. Inaguma, H. Sato, and E. Miura-Fujiwara: Materials, 2009, vol. 2, pp. 2510-25.
J.C. Li, Z.C. Guo, and J.T. Gao: ISIJ Int., 2014, vol. 54, pp. 743-9.
S.G. Shabestari and J.E. Gruzleski: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1995, vol. 26, pp. 999-1006.
Acknowledgment
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundations of China (Nos. 51234001 and 51404025) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (FRF-TP-15-009A2), which is acknowledged with thanks.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted August 19, 2016.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, C., Gao, J., Wang, Z. et al. Separation of Fine Al2O3 Inclusion from Liquid Steel with Super Gravity. Metall Mater Trans B 48, 900–907 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-016-0905-5
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-016-0905-5