Abstract
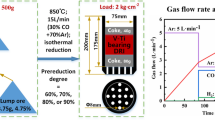
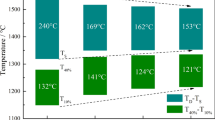
The effect of TiO2 on the crushing strength for high-Cr V-Ti magnetite pellets was studied in this paper. On one hand, the crushing strength obviously decreased with the increasing TiO2 contents. On the other hand, the crushing strength had an obvious increase after grinding treatment for the high-Cr V-Ti magnetite and titanium concentrate. It is found that the crushing strength has great relations with the mineral phase and microstructure. The effect of TiO2 on the smelting mechanism for high-Cr V-Ti magnetite pellets was also studied in this paper. With the increasing TiO2 contents in the range of 2.47 to 12.14 pct, the softening start temperature and softening temperature gradually increased, and the softening zone gradually narrowed down; the melting start temperature and the dripping temperature increased, and the melting–dripping temperature zone also increased. The permeability index increased with the increasing TiO2 contents as a whole. In the process of slag–iron’s dripping and separating, it is proposed that amounts of Cr and V moving to the melted iron are obviously more than those moving to the slag, while amount of Ti moving to slag is much greater than that moving to the melted iron. It is demonstrated that Ti(C,N) generates increasingly with the increasing TiO2 contents and accumulates as especial regular rigid granules on the surface of coke. The size of melted iron decreased with the increasing TiO2 contents, and this is in accordance with the present investigations that the dripping difficulty increased with the increasing TiO2 contents.



















Similar content being viewed by others
References
H.G. Du: Principle of smelting vanadium-titanium magnetite in the blast furnace, 1st ed., p. 1, Science Press, Beijing, China, 1996.
G.-J. Cheng, J.-X. Liu, Z.-G. Liu, M.-S. Chu, X.-X. Xue: Ironmaking and Steelmaking, 2015, vol. 42(1), pp. 17-26.
J.X. Liu, G.J. Cheng, Z.G. Liu, M.S. Chu, X.X. Xue: Steel Res. Int., 2015, vol. 86(7), pp. 808-816.
G.B. Qiu, L. Chen, J.Y. Zhu, X.W. Lv, C.G. Bai: ISIJ Int., 2015, vol. 55(7), pp. 1367-1376.
S.K. Gupta, V. Rajakumar, and P. Grieveson: Metall. Trans. B, 1989, vol 20B, pp. 735-745.
T. Hu, X.W. Lv, C.G. Bai, Z.G. Lun, and G.B. Qiu: Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2013, vol 44B, pp. 252-260.
G.D. McAdam: Ironmaking and Steelmaking, 1974, vol 1(3), pp. 138-150.
J.B. Zhang, Q.S. Zhu, Z.H. Xie, L. Chao, and H.Z. Li: Metall. Mater. Trans. B. 2013, vol 44B, pp. 897-905.
K. Sun, R. Takahashi, J. Yagi: ISIJ Int., 1992, vol 32(4), pp. 496-504.
L. H. Zhou, and F. H. Zeng: Ironmaking and Steelmaking, 2011, vol 38(1), pp. 59-64.
R. Huang, X.W. Lv, C.G. Bai, K. Zhang, and G.B. Qiu: Steel Research Int., 2013, vol 84(9), pp. 892-899.
S.Z. El-Tawil, I.M. Morsi, A. Yehia, and A.A. Francis: Can. Metall. Quart., 1996, vol 35(1), pp. 31-37.
E. Park, and O. Ostrovski: ISIJ Int., 2004, vol 44(6), pp. 999-1005.
J. Dang, X.J. Hu, G.H. Zhang, X.M. Hou, X.B. Yang, and K.C. Chou: High Temperature Materials and Processes, 2013, vol 32(3), pp. 229-236.
K. Sun, T. Akiyama, R. Takahashi, and J. Yagi: ISIJ Int., 1995, vol 35(4), pp. 360-366.
J.-Y. Hwang: Characterization of Minerals, Metals, and Materials 2013, Minerals, Metals and Materials Society, Warrendale, 2013, pp. 363–69.
L.B. Xu: Master’s Thesis, Northeastern University, 2012.
H.Z. Ou: Master’s Thesis, Northeastern University, 2012.
T. Paananen, K. Kinnunen: Steel Research Int., 2009, vol 80(6), pp. 408-414.
M.S. Chu: Raw fuels and auxiliary materials in Ferrous Metallurgy, 1st ed., p. 158, Metallurgical Industry Press, Beijing, China, 2010.
Y.M. Chen, and R. Chen: Microstructure of sinter and pellet, 1st ed., p. 111, Central South University Press, Changsha, China, 2011.
D.Q. Zhu, D. Chen, J. Pan: J Central South Univ. (Sci. Technol.), 2011, vol 42(7), pp. 1825–32.
X.L. Chen, S. Liu, M. Gan, and X.H. Fan: Chin. J. Eng., in press.
S. Hayashi, and Y. Iguchi: Ironmaking and Steelmaking, 2005, vol 32(4), pp. 353-358.
H.T. Wang, and H.Y. Sohn: Ironmaking and Steelmaking, 2011, vol 38(6), pp. 447-452.
G.H. Li, Z.K. Tang, Y.B. Zhang, Z.X. Cui, and T. Jiang: Ironmaking and Steelmaking, 2010, vol 37(6), pp. 393-397.
G.Q. Yang, J.L. Zhang, J.G. Shao, Y.C. Wen, J.T. Rao, and W.G. Fu: Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2012, vol 33(5), pp. 30-34.
M.H. KHEDR: ISIJ Int., 2000, vol 40(4), pp. 309-314.
W.Z. Luo, Y.W. Mao, L. H, and Y.K. Zhu: Iron and Steel, 1987, vol 22(1), pp. 1–4.
G.Y. Wen, Y.Z. Yan, S.J. Zhao, J.J. Huang, G.H. Jiang, and X.M. Yang: Iron and Steel, 1996, vol 31(2), pp. 6-11.
W.Z. Wang, and Y.X. Shi: Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 1989, vol 10(2), pp. 13-15.
N. Saito, N. Hori, K. Nakashima, and K. Mori: Metall. Trans. B, 2003, vol 34B, pp. 509-516.
G.Y. Wen, Y.Z. Yan, P.T. Zhou, Y.C. Zhou, D.H. Liao, and G. Wang: Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 1996, vol 17(3), pp. 24-29.
H.G. Du, and Z.P. Zhang: Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 1994, vol 15(4), pp. 1–3, 27.
P. Liu, and W.Z. Ding: Ferro-Alloys, 2004, vol 2, pp. 8-11.
Acknowledgments
The authors are especially thankful to the Major Program of National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51090384), 863 Program (Grant No. 2012AA062302 and No. 2012AA062304) and Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Grant No. N110202001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted August 23, 2015.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cheng, G., Xue, X., Jiang, T. et al. Effect of TiO2 on the Crushing Strength and Smelting Mechanism of High-Chromium Vanadium-Titanium Magnetite Pellets. Metall Mater Trans B 47, 1713–1726 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-016-0628-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-016-0628-7