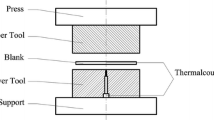
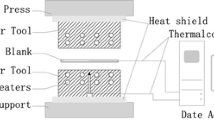
Abstract
An optimization-based numerical procedure was developed to determine the pressure-dependent heat transfer coefficient (HTC) between the blank and tools during the hot stamping of boron steel. During the quenching period, HTC increased with the contact pressure between blank and lower tool. There is no obvious linear relationship between them. The maximum value of 1500 W/m2 K was achieved at contact pressure 18 MPa.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- C p :
-
Specific heat (J/kg K)
- M s :
-
Martensite start temperature (K)
- T :
-
Temperature (K)
- \( {T_{{i,{\text{B}}}}^{\text{Exp}} } \) :
-
Blank experimental temperatures
- \( {T_{{i,{\text{B}}}}^{\text{Sim}} } \) :
-
Blank calculating temperatures
- \( T_{{j,{\text{L}}}}^{\text{Exp}} \) :
-
Lower tool experimental temperatures
- \( {T_{{i,{\text{L}}}}^{\text{Sim}} } \) :
-
Lower tool calculating temperatures
- f M :
-
Martensite fraction (–)
- k :
-
Thermal conductivity (W/m K)
- t :
-
Time (s)
- δ B :
-
Error function of blank temperature
- δ L :
-
Error function of lower tool temperature
- B:
-
Blank
- L:
-
Lower tool
References
T. Altan: Stamp. J., 2006, vol. 12, pp. 40–41.
B. Hochholdinger, P. Hora, H. Grass, and A. Lipp: 8th International Conference and Workshop on Numerical Simulation of 3D Sheet Metal Forming Processes (Numisheet 2011), 21–26 August 2011, Seoul, Korea, K. Chung, N.H. Heung, H. Huh, F. Barlat, and M.-G. Lee, eds., 2011, pp. 618–25.
A. Turetta, S. Bruschi, and A. Ghiotti: J. Mater. Process. Technol.,2006, vol. 177, pp. 396–400.
H. Karbasian and A.E. Tekkaya: J. Mater. Process. Technol.,2010, vol. 210, pp. 2103–118.
M. Merklein, J. Lechler, and T. Stoehr: J. Int. Mater. Form., 2009,vol. 2, pp. 259–62.
M. Eriksson, M. Oldenburg, M.C. Somani, and L.P. Karjalainen: Model. Simul. Mater. Sci. Eng., 2002, vol. 10, pp. 277–94.
M. Merklein and J. Lechler: SAE Int. J. Mater. Manuf., 2009, vol.1, pp. 411–26.
B. AbdulHay, B. Bourouga, and C. Dessain: Int. J. Mater. Form., 2010, vol. 3, pp. 147–63.
B. Abdulhay, B. Bourouga, and C. Dessain: Appl. Therm. Eng., 2011, vol. 31, pp. 674–85.
J.V. Beck, B. Blackwell, and C.R. StClair: Inverse Heat Conduction: III-Posed Problems, Wiley, New York, NY, 1985, pp. 108–61.
C. Fieberg and R. Kneer: Int. J. Heat Mass Transf., 2008, vol. 51,pp. 1017–23.
P. Hu, L. Ying, Y. Li, and Z.W. Liao: J. Mater. Process. Technol.,2013, vol. 213, pp. 1475–83.
D. Lorenz: DYNAmore GmbH, Stuttgart, Germany, Private communication.
G. Bergman: Modelling and Simulation of Simultaneous Forming and Quenching, Dissertation, Luleå University of Technology, 1999.
D.P. Koistinen and R.E. Marburger: Acta Metall., 1959, vol. 7, pp. 59–60.
M. Naderi, A. Saeed-Akbari, and W. Bleck: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2008, vol. 487, pp. 445–55.
M. Geiger, M. Merklein, and C. Hoff: Adv. Mater. Res., 2005, vols. 6–8, pp. 795–804.
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51205162) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (51275203).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted April 6, 2015.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Z., Gao, P., Liu, C. et al. Experimental and Simulation Study for Heat Transfer Coefficient in Hot Stamping of High-Strength Boron Steel. Metall Mater Trans B 46, 2419–2422 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-015-0452-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-015-0452-5