Abstract
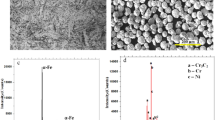
The chromium carbide (Cr3C2)-reinforced Ni-based composite clad on austenitic stainless steel (SS-316) substrate was successfully developed by the microwave cladding route after optimizing process parameters (Power: 900 Watt, Exposure Time: 380 seconds). Clads were developed at 2.45 GHz frequency in a domestic microwave oven. The developed composite clad has been examined for metallurgical and mechanical properties. The investigation was carried out by using scanning electron microscopy (SEM) equipped with a backscatter electron detector, energy dispersive spectroscopy (EDS) for elemental analysis, and X-ray diffractometry (XRD) for phase analysis and their quantification and Vicker’s microhardness tester for microhardness. Clads of thickness 600 µm were successfully developed, which are free from visible pores and all types of cracks (interfacial or solidification cracks). The porosity analysis was carried out by using ASTM B-276 standard, and results reveal that porosity is less than 2 pct. The average microhardness of the developed clad is observed 605 ± 80 HV0.3. The developed clad was three times harder than the substrate (SS-316). The various intermetallic (Ni3Fe, Cr3Si, and Ni2Si) and different carbides (Cr7C3, NiC, Ni3C, SiC, and Cr3Ni2SiC) phases were observed through XRD examination. The distribution of intermetallic and various hard carbide phases in the clad has a direct influence on hardness and increases hardness at great extent.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
B. Bhushan: Introduction to Tribology, Wiley, Chichester 2013.
2 S. Li: Interface Focus, 2015, vol. 5, p. 20150020.
3 X. Escaler, E. Egusquiza, M. Farhat, F. Avellan, and M. Coussirat: Mech. Syst. Signal Process., 2006, vol. 20, pp. 983–1007.
4 L. Ceschini, C. Chiavari, E. Lanzoni, and C. Martini: Mater. Des., 2012, vol. 38, pp. 154–60.
5 M. Kulka, D. Mikolajczak, N. Makuch, P. Dziarski, and A. Miklaszewski: Surf. Coatings Technol., 2016, vol. 291, pp. 292–313.
6 K.G. Budinski: Surface Engineering for Wear Resistance, Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs, N.J, 1988.
7 M. Roy: Surface Engineering for Enhanced Performance against Wear, Springer Vienna, Vienna, 2013.
8 R. Singh, S.K. Tiwari, and S.K. Mishra: J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2012, vol. 21, pp. 1539–51.
9 H. Vasudev, G. Singh, A. Bansal, S. Vardhan, and L. Thakur: Mater. Res. Express, 2019, vol. 6, pp. 1–20.
10 R.R. Mishra and A.K. Sharma: Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf., 2016, vol. 81, pp. 78–97.
11 A. Bekal, A.M. Hebbale, and M.S. Srinath: IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng., 2018, vol. 376, p. 012079.
Patent application 527/Del, India: 2010.
13 D. Gupta, P.M. Bhovi, A.K. Sharma, and S. Dutta: J. Manuf. Process., 2012, vol. 14, pp. 243–9.
14 S. Zafar, A.K. Sharma, and N. Arora: i-manager’s J. Mech. Eng., 2013, vol. 3, pp. 9–16.
15 A.M. Hebbale and M.S. Srinath: Measurement, 2017, vol. 99, pp. 98–107.
16 A. Bansal, S. Zafar, and A.K. Sharma: J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2015, vol. 24, pp. 3708–16.
17 D. Gupta and A.K. Sharma: J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2012, vol. 21, pp. 2165–72.
S. Kaushal, V. Sirohi, D. Gupta, H. Bhowmick, and S. Singh: Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. L, 2018, vol. 232, pp. 80–6.
19 B. Singh, S. Kaushal, D. Gupta, and H. Bhowmick: J. Tribol., 2018, vol. 140, p. 061603.
20 S. Zafar and A.K. Sharma: Wear, 2016, vol. 346–347, pp. 29–45.
21 B. Singh and S. Zafar: Wear, 2019, vol. 426–427, pp. 491–500.
22 S. Kaushal, D. Gupta, and H. Bhowmick: Surf. Eng., 2018, vol. 34, pp. 809–17.
23 A. Babu, H.S. Arora, H. Singh, and H.S. Grewal: Wear, 2019, vol. 422–423, pp. 242–51.
24 R.B. Bhagat: J. Mater. Sci. Lett., 1987, vol. 6, pp. 1473–5.
25 U. Dorji and R. Ghomashchi: Eng. Fail. Anal., 2014, vol. 44, pp. 136–47.
H.O. Pierson: Handbook of Refractory Carbides and Nitrides, Elsevier, Amsterdam, 1996.
27 A. Babu, H.S. Arora, S.N. Behera, M. Sharma, and H.S. Grewal: Surf. Coatings Technol., 2018, vol. 349, pp. 655–66.
28 A. Babbar, P. Singh, and H.S. Farwaha: Indian J. Sci. Technol., 2017, vol. 10, pp. 1–7.
C.Y. Ho and T.K. Chu: in Electrical Resistivity and Thermal Conductivity of Nine Selected AISI Stainless Steels - Center for Information and Numerical Data Analysis and Synthesis, 1977.
30 W.D. Callister: Mater. Des., 1991, vol. 12, p. 59.
31 A.K. Sharma and D. Gupta: Appl. Surf. Sci., 2012, vol. 258, pp. 5583–92.
32 R.W. Powell, R.P. Tye, and M.J. Hickman: Int. J. Heat Mass Transf., 1965, vol. 8, pp. 679–88.
33 A. Mondal, A. Shukla, A. Upadhyaya, and D. Agrawal: Sci. Sinter., 2010, vol. 42, pp. 169–82.
34 S.M. Lingappa, M.S. Srinath, and H.J. Amarendra: Mater. Res. Express, 2017, vol. 4, p. 106521.
35 F.T. Cheng, C.T. Kwok, and H.C. Man: Surf. Coatings Technol., 2001, vol. 139, pp. 14–24.
36 S.N. Aqida, M.I. Ghazali, and J. Hashim: J. Teknol., 2013, vol. 40, pp. 17–32.
37 T. Pramod, R.K. Kumar, S. Seetharamu, and M. Kamaraj: Int. J. Adv. Mech. Eng., 2014, vol. 4, pp. 307–14.
38 J.F. Santa, L.A. Espitia, J.A. Blanco, S.A. Romo, and A. Toro: Wear, 2009, vol. 267, pp. 160–7.
O. Knotek, R. Elsing, and H. R. Heintz: J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 1985, vol. 3, pp. 2490–3.
40 C. Pan, H. Wang, H. Wang, Q. Chang, and H. Wang: J. Wuhan Univ. Technol. Sci. Ed., 2010, vol. 25, pp. 991–5.
41 S. Li, D. Feng, and H. Luo: Surf. Coatings Technol., 2007, vol. 201, pp. 4542–6.
42 D. Bhattacharyya, J. Davis, M. Drew, R.P. Harrison, and L. Edwards: Mater. Charact., 2015, vol. 105, pp. 118–28.
43 S. Kaushal, D. Gupta, and H. Bhowmick: Mater. Res. Express, 2019, vol. 6, pp. 1–10.
N.-T. Nguyen: in Micromixers, Elsevier, Amsterdam, 2012, pp. 113–61.
Acknowledgments
This research is financially supported by the SERB (Science & Engineering research board), India. Under the under project titled “Development of Microwave Processed Cavitation Resistant Cladding” (Grant No. EMR/2016/007964).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Manuscript submitted November 4, 2019.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mago, J., Bansal, S., Gupta, D. et al. Investigation of Microwave Processing Parameters on Development of Ni-40Cr3C2 Composite Clad and Their Characterization. Metall Mater Trans A 51, 4288–4300 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-020-05832-y
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-020-05832-y