Abstract
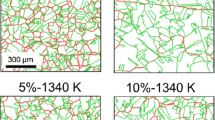
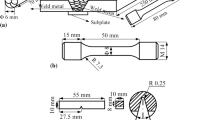
The influence of the chemical composition, especially the niobium content, chromium equivalent Creq, and nickel equivalent Nieq, on the weld solidification cracking susceptibility in the austenite single-phase region in the Schaeffler diagram was investigated. Specimens were fabricated using the hot-wire laser welding process with widely different compositions of Creq, Nieq, and niobium in the region. The distributions of the susceptibility, such as the crack length and brittle temperature range (BTR), in the Schaeffler diagram revealed a region with high susceptibility to solidification cracking. Addition of niobium enhanced the susceptibility and changed the distribution of the susceptibility in the diagram. The BTR distribution was in good agreement with the distribution of the temperature range of solidification (ΔT) calculated by solidification simulation based on Scheil model. ΔT increased with increasing content of alloying elements such as niobium. The distribution of ΔT was dependent on the type of alloying element owing to the change of the partitioning behavior. Thus, the solidification cracking susceptibility in the austenite single-phase region depends on whether the alloy contains elements. The distribution of the susceptibility in the region is controlled by the change in ΔT and the segregation behavior of niobium with the chemical composition.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Kou: Welding Metallurgy, John Wiley & Sons, New Jersey, 2003.
J.C. Lippold and D. J. Kotecki: Welding Metallurgy and Weldability of Stainless Steels, John Wiley & Sons, New Jersey, 2005.
A. L. Schaeffler: Metal Progress, 1949, vol. 56, pp. 680 - 680B.
American Welding Society: Welding Handbook, 9th ed., vol. 4, Materials and Applications, Miami, 2011, pp. 413–22.
K. Saida, H. Matsushita, K. Nishimoto, K. Kikuchi, J. Nakayama: Science Technology of Welding and Joining, 2013, vol. 18, pp. 616-623.
Y. Arata, F. Matsuda, H. Nakagawa, and S. Katayama: Trans. JWRI, 1978, vol. 7 1978, pp. 169–72.
V. P. Kujanpaa, S. A. David and C. L. White: Welding Journal, 1986, vol. 65, pp. 203s-212s.
V. P. Kujanpaa, N. Suutala, T. Takalo, T. Moisio: Welding Research International, 1979, vol. 9, pp. 55-76.
T. Ogawa: Welding International., 1991, vol. 5, pp. 931-935.
T. Ogawa, E. Thsunetomi: Welding Journal, 1982, vol. 63, pp. 82s-93s.
R. Phaoniam, K. Shinozaki, M. Yamamoto, K. Kadoi, S. Tsuchiya, A. Nishijima: Welding in the World, 2013, vol. 57, pp. 607-613.
K. Kadoi, K. Shinozaki, M. Yamamoto, K. Owaki, K. Inose and D. Takayanagi: Quarterly Journal of Japan Welding Society, 2011, vol. 29, pp. 62s-65s.
D. Wang, S. Sakoda, K. Kadoi, K. Shinozaki and M. Yamamoto: Quarterly Journal of Japan Welding Society, 2015, vol. 33, pp. 39s-43s.
F. Matsuda, H. Nakagawa, S. Ogata and S. Katayama: Transactions of JWRI, 1978, vol. 7, pp. 59- 70.
R. A. Patterson, J. O. Milewski: Welding Journal, 1985, vol. 64, pp. 227s-31s.
J. N. Dupont, C. V. Robino, A. R. Marder: Welding Journal, 1998, vol. 77, pp. 417s-31s.
J.N. DuPont, C.V. Robino, and A.R. Marder: Science and Technology of Welding and Joining, 1999, Vol. 4, pp. 1-14.
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by JSPS KAKENHI Grant Number 15K18223 and a grant of Japan welding engineering society.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted April 3, 2017.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kadoi, K., Shinozaki, K. Effect of Chemical Composition on Susceptibility to Weld Solidification Cracking in Austenitic Weld Metal. Metall Mater Trans A 48, 5860–5869 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-017-4340-2
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-017-4340-2