Abstract
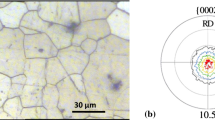
An AZ31 wrought magnesium alloy was processed by employing multipass accumulative back extrusion process. The obtained microstructure, texture, and room temperature tensile properties were characterized and discussed. Ultrafine-grained microstructure including nano-grains were developed, where the obtained mean grain size was decreased from 8 to 0.5 μm by applying consecutive passes. The frequency of both low angle and high angle boundaries increased after processing. Strength of the experimental alloy was decreased after processing, which was attributed to the obtained texture involving the major component lying inclined to the deformation axis. Both the uniform and post-uniform elongations of the processed materials were increased after processing, where a total elongation of 68 pct was obtained after six-pass deformation. The contribution of different twinning and slip mechanisms was described by calculating corresponding Schmid factors. The operation of prismatic slip was considered as the major deformation contributor. The significant increase in post-uniform deformation of the processed material was discussed relying on the occurrence of grain boundary sliding associated with the operation of prismatic slip.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
B. Mordike, T. Ebert: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2001, 302, 37-45.
T. Al-Samman, G. Gottstein: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2008, 488, 406-14.
H. Yan, R. Chen, E. Han: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2010, 527, 3317-22.
S. Agnew, J. Horton, T. Lillo, D. Brown: Scripta Mater., 2004, 50, 377-81.
J. Del Valle, F. Carreno, O. Ruano, Acta Mater., 2006, 54, 4247-59.
J. Koike, T. Kobayashi, T. Mukai, H. Watanabe, M. Suzuki, K. Maruyama, K. Higashi, Acta Mater., 2003, 51, 2055-65.
S. Agnew, P. Mehrotra, T. Lillo, G. Stoica, P. Liaw: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2005, 408, 72-78.
T. Al-Samman, X. Li, S.G. Chowdhury: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2010, 527, 3450-3463.
S. Biswas, S. Singh Dhinwal, S. Suwas: Acta Mater., 2010, 58, 3247-61.
S. Fatemi-Varzaneh, A. Zarei-Hanzaki: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2009, 504, 104-06.
S. Fatemi-Varzaneh, A. Zarei-Hanzaki, J. Cabrera, P. Calvillo: Mater. Chem. Phys., 2015, 149, 339-43.
H. Wang, P. Wu, J. Wang: Comput. Mater. Sci., 2015, 96, 214-18.
J. Wang, D. Zhang, Y. Li, Z. Xiao, J. Fouse, X. Yang: Mater. Des., 2015, 86, 526-35.
H. Fan, S. Aubry, A. Arsenlis, J.A. El-Awady: Scripta Mater., 2015, 97, 25-28.
M. Quadir, M. Ferry, O. Al-Buhamad, P. Munroe: Acta Mater. 2009, 57, 29-40.
J. Del Valle, P. Rey, D. Gesto, D. Verdera, J.A. Jiménez, O.A. Ruano: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2015, 628, 198-206.
M. Gzyl, A. Rosochowski, S. Boczkal, L. Olejnik: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2015, 638, 20-29.
S. Biswas, S. Suwas: Scr. Mater., 2012, 66, 89-92.
R.B. Figueiredo, S. Sabbaghianrad, A. Giwa, J.R. Greer, T.G. Langdon: Acta Mater., 2017, 122, 322-31.
W. Yuan, S. Panigrahi, J.Q. Su, R. Mishra: Scr. Mater., 2011,
J. Xing, X. Yang, H. Miura, T. Sakai: Mater. Trans., 2008, 49, 69-75.
Z. Zuberova, Y. Estrin, T. Lamark, M. Janecek, R. Hellmig, M. Krieger, J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2007, 184: 294-99.
W. Kim, C. An, Y. Kim, S. Hong: Scr. Mater., 2002, 47, 39-44.
H. Miura, G. Yu, and X. Yang: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2011, vol. 528, pp. 6981–92.
Y. Wang and E. Ma: Acta Mater., 2004, vol. 52, pp. 1699–1709.
Q. Yang, A. Ghosh, Acta Mater., 2006, 54, 5159-70.
N. Haghdadi, A. Zarei-Hanzaki, D. Abou-Ras: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2013, 584, 73-81.
B. Bazaz, A. Zarei-Hanzaki, S. Fatemi-Varzaneh: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2013, 559, 595-600.
S. Fatemi-Varzaneh, A. Zarei-Hanzaki: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2011, 528, 1334-39.
S. Fatemi-Varzaneh, A. Zarei-Hanzaki, M. Naderi, and A.A. Roostaei: J. Alloys Compd., 2010, vol. 507, pp. 207–14.
S. Fatemi-Varzaneh, A. Zarei-Hanzaki, J. Cabrera: J. Alloys Compd., 2011, 509, 3806-10.
S. Fatemi-Varzaneh, A. Zarei-Hanzaki, H. Paul: Mater. Charac., 2014, 87, 27-35.
J.W. Cahn, Y. Mishin, and A. Suzuki: Acta Mater., 2006, vol. 54, pp. 4953–75.
Y. Zhao, Y. Guo, Q. Wei, A. Dangelewicz, C. Xu, Y. Zhu, T. Langdon, Y. Zhou, E. Lavernia: Scripta Mater., 2008, 59, 627-30.
W.F. Hosford and R.M. Caddell: Metal Forming: Mechanics and Metallurgy, Cambridge University Press, New York, 2011.
H. Somekawa, T. Mukai: Philos. Mag. Lett., 2010, 90, 883-90.
C. Cepeda-Jiménez, J. Molina-Aldareguia, M. Pérez-Prado: Acta Mater., 2015, 84, 443-56.
M. Dahms, H.J. Bunge: J. Appl. Crystallogr., 1989, 22, 439-47.
J. Koike: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2005, 36, 1689-96.
R. Lapovok, P. Thomson, R. Cottam, Y. Estrin: J. Mater. Sci., 2005, 40, 1699-708.
S. Yin, C. Wang, Y. Diao, S. Wu, S. Li: J. Mater. Sci. Tech., 2011, 27, 29-34.
S. Agnew, Ö. Duygulu: Int. J. Plast., 2005, 21, 1161-93.
I. Saxl and I. Haslinggerová: J. Phys. B, 1974, vol. 24, pp. 1351–61.
S. Kleiner, P. Uggowitzer: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2004, 379, 258-63.
H. Somekawa, T. Mukai: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2015, 46A, 894-902.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted November 19, 2016.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fatemi, S.M., Zarei-Hanzaki, A. & Cabrera, J.M. Microstructure, Texture, and Tensile Properties of Ultrafine/Nano-Grained Magnesium Alloy Processed by Accumulative Back Extrusion. Metall Mater Trans A 48, 2563–2573 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-017-4029-6
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-017-4029-6