Abstract
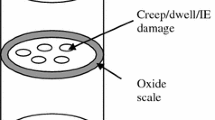
Thermomechanical fatigue (TMF) behaviors of ductile cast iron (DCI) were investigated under out-of-phase (OP), in-phase (IP), and constrained strain-control conditions with temperature hold in various temperature ranges: 573 K to 1073 K, 723 K to 1073 K, and 433 K to 873 K (300 °C to 800 °C, 450 °C to 800 °C, and 160 °C to 600 °C). The integrated creep-fatigue theory (ICFT) model was incorporated into the finite element method to simulate the hysteresis behavior and predict the TMF life of DCI under those test conditions. With the consideration of four deformation/damage mechanisms: (i) plasticity-induced fatigue, (ii) intergranular embrittlement, (iii) creep, and (iv) oxidation, as revealed from the previous study on low cycle fatigue of the material, the model delineates the contributions of these physical mechanisms in the asymmetrical hysteresis behavior and the damage accumulation process leading to final TMF failure. This study shows that the ICFT model can simulate the stress–strain response and life of DCI under complex TMF loading profiles (OP and IP, and constrained with temperature hold).













Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.R. Davis, ed.: ASM Specialty Handbook: Cast Irons, ASM International, Materials Park, OH, 1996.
G.M. Goodrich, Iron Castings Engineering Handbook, American Foundry Society (AFS), Des Plaines, IL, 2003.
R. Elliott, Cast Iron Technology, Butterworths, London, UK, 1988.
D. Li, R. Perrin, G. Burger, D. McFarlan, B. Black, R. Logan, and R. Williams: Advances in Lightweight Automotive Castings and Wrought Aluminum Alloys, 2004 SAE World Congress, Detroit, Michigan, March 8–11, No. 2004-01-0792, 2004.
B. Black, G. Burger, R. Logan, R. Perrin, and R. Gundlach: Microstructure and Dimensional Stability in Si-Mo Ductile Irons for Elevated Temperature Applications, SAE International, No. 2002-01-2115.
D.L. Sponseller, W.G. Scholz, and D.F. Rundle, “Development of Low-Alloy Ductile Irons for Service at 1200-1500 F” AFS Trans. 1968, vol. 76, pp. 353-368.
T. Kobayashi, K. Nishino, Y. Kimoto, Y. Awano, Y. Hibino, and H. Ueno, “673K Embrittlement of Ferritic Spheroidal Graphite Cast Iron by Magnesium”, Casting Engineering, 1998, vol. 70, pp. 273-278.
D. Li and C. Sloss: 2010 SAE World Congress, April 13–15, Detroit, MI, SAE International, No. 2010-01-0654, 2010.
Y.-J. Kim, H. Jang, and Y.-J. Oh, Metall. and Mater. Trans. A, 2009, vol. 40A, pp. 2087-2097.
F. Szmytka, L. Rémy, H. Maitournam, A. Köster, Int. J. Plasticity, 2010, vol. 26, pp. 905-924.
L.Rémy, F.Szmytka, L.Bucher, Int. J. Fatigue, 2013, vol. 53, pp. 2-14.
T. Seifert, H. Riedel, Int. J. Fatigue, 2010, vol. 32, pp. 1358-1367.
T. Seifert, G. Maier, A. Uihlein, K.-H. Lang, H. Riedel, Int. J. Fatigue, 2010, vol. 32, pp. 1368-1377.
X.J. Wu, T. Quan, R. MacNeil, Z. Zhang and C. Sloss, Failure Mechanisms and Damage Model of Ductile Cast Iron under Low-Cycle Fatigue Conditions, Metall. and Mater. Trans. A, 2014, vol. 45A, pp.5088-5097.
ASTM E2368-10: Standard Practice for Strain Controlled Thermomechanical Fatigue Testing, American Society for Testing of Materials, West Conshohocken, PA, 2004.
K. Ishii, M. Nakada, S. Takahashi, M. Enomoto, and Y. Konishi: Evaluation of Thermal Fatigue Life on the Exhaust Manifold by Analyzing Restraint Ratio. FISITA World Automotive Congress, paper # F2000G295, June 12-15, 2000, Seoul, Korea.
T. Seifert, R. Hazime, and S. Dropps: SAE Int. J. Mater. Manuf., 2014, DOI:10.4271/2014-01-0905.
P. von Hartrott, T. Seifert, and S. Dropps: SAE Int. J. Mater. Manuf., 2014, DOI:10.4271/2014-01-0915.
R. W. Neu, H. Sehitoglu, Metall. Trans. 1989, vol. 20 (9), pp. 1755-1767.
R. W. Neu, H. Sehitoglu, Metall. Trans. 1989, vol. 20 (9), pp. 1769-1783.
X.J. Wu: in Gas Turbine, I. Gurrappa, ed., Sciyo, Rijeka, 2010, pp. 215–82.
X.J. Wu: Trans. ASME J. Eng. Gas Turbines Power, 2009, vol. 131, pp. 032101/1–1/6.
Toth Information Systems, Private Communication, 2013.
Acknowledgments
Fractographic micrographs were taken by Weijie Chen (formerly research officer) and Dave Chow (technical officer) of National Research Council Canada.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
©Published with permission of the Crown in Right of Canada pertains to Xijia Wu, Ryan MacNeil, and Zhong Zhang.
Manuscript submitted October 2, 2014.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, X., Quan, G., MacNeil, R. et al. Thermomechanical Fatigue of Ductile Cast Iron and Its Life Prediction. Metall Mater Trans A 46, 2530–2543 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-015-2873-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-015-2873-9