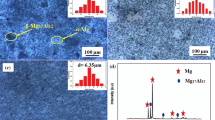
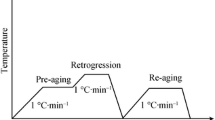
In this study, the effect of thermomechanical treatment on intergranular corrosion (IGC) susceptibility of the Zn-modified Al-5.1 wt pct Mg-0.7 wt pct Mn alloy plates was investigated. The specimens underwent varied amounts of cold work, while final annealing was conducted in the 493 K to 533 K (220 °C to 260 °C) temperature range. It was shown that the extent of cold work, especially at lower temperatures of treatment, had a profound effect on the corrosion resistance of the alloy. Such observation was in direct correlation with the morphology of precipitated ternary grain boundary phase (Al-Mg-Zn). Microstructural characterization showed that, depending on the amount of cold work, different deformation substructures were created, which, in turn, influenced kinetics and the mechanism of precipitation. Wetting of the grain boundaries by the ternary grain boundary phase (Al-Mg-Zn) was a signature of the IGC susceptible state and occurred in the specimens that were subjected to a lower degree of cold work. The specimens that underwent a higher degree of cold work (over 30 pct) showed superior corrosion resistance as a result of ternary grain boundary phase (Al-Mg-Zn) precipitation in the form of discrete particles at the grain boundaries as well as in grain interiors.







Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Foerster Sigmatest 2.069 is a trademark of Foerster Instruments INC, Pittsburgh, PA.
JEOL is a trademark of Japan Electron Optics Ltd., Tokyo.
Philips CM200 is a trademark of Koninklijke Philips, N.V.
References
D.G. Altenpohl: ALUMINUM: Technology, Applications and Environment, 6th ed., The Aluminum Association, Washington DC, and TMS, Warrendale, PA, 1999, pp. 349–79.
K. Buxmann, M. Bertram, and P. Kistler: in Light Metals in Transport Applications, Conf. Proc., M. Pekguleryuz, ed., Canadian Institute of Mining, Metallurgy and Petroleum, Westmount, QC, Canada, 2007, pp. 325–38.
K. Osamura and T. Ogura: Metall. Trans. A, 1984, vol. 15A, pp. 835–42.
M.J. Starink and A.-M. Zahra: Phil. Mag. A, 1997, vol. 76A, pp. 701–14.
M.J. Starink and A.-M. Zahra: Acta Mater., 1998, vol. 46, pp. 3381–97.
J.L. Searles, P.I. Gouma, and R.G. Buchheit: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2001, vol. 32A, pp. 2859–67.
R. Goswami, G. Spanos, P.S. Pao, and R.L. Holtz: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2010, vol. 527A, pp. 1089–95.
A.J. Davenport, Y. Yuan, R. Ambat, B.J. Connolly, M. Strangwood, A. Afseth, and G. Scamans: Mater. Sci. Forum, 2006, vols. 519–521, pp. 641–46.
X.-Y. Liu and J.B. Adams: Acta Mater., 1998, vol. 46, pp. 3467–76.
M. Popović, T. Radetić, and E. Romhanji: in ICAA13: 13th Int. Conf. on Aluminum Alloys, H. Welland, A.D. Rollett, and W.A. Cassada, eds., John Wiley and Sons, Inc., Hoboken, NJ, 2012, pp. 363–68.
A. Haszler: in Proc. Aluminum Technology and Markets for the New Century, W. Hueck and B. Legrand, eds., DMG Business Media Ltd., Surrey, 1997, pp. 2/1–2/9.
S. Ferraris and L.M. Volpone: 5th International Forum on Aluminum Ships, Tokyo, 2005, pp. 1–11.
A. Czechowski: J. Mater. Processing Technol., 2005, vol. 164, pp. 1001–06.
H.-C. Jiang, L.-Y. Ye, and X.-M. Zhang: Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc., 2013, vol. 23, pp. 3553–60.
M.C. Carroll, P.I. Gouma, M.J. Mills, G.S. Daehn, and B.R. Dunbar: Scripta Mater., 2000, vol. 42, pp. 335–40.
R.H. Jones, D.R. Baer, M.J. Danielson, and J.S. Vetrano: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2001, vol. 32A, pp. 1699–1711.
I.N.A. Oguocha, O.J. Adigun, and S. Yannacopoulos: J. Mater. Sci., 2008, vol. 43, pp. 4208–14.
R. Goswami, G. Spanos, P.S. Pao, and R.L. Holtz: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2010, vol. 42A, pp. 348–55.
J. Gao and D.J. Quesnel: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2010, vol. 42A, pp. 356–64.
R.L. Holtz, P.S. Pao, R.A. Bayles, T.M. Longazel, and R. Goswami: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2011, vol. 43A, pp. 2839–49.
N. Bernstein, R. Goswami, and R.L. Holtz: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2012, vol. 43A, pp. 2166–76.
R. Goswami and R.L. Holtz: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2012, vol. 44A, pp. 1279–89.
Y. Zhu, D.A. Cullen, S. Kar, M.L. Free, and L.F. Allard: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2012, vol. 43A, pp. 4933–39.
J.C. Chang and T.H. Chuang: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1999, vol. 30A, pp. 3191–99.
J.C. Chang and T.H. Chuang: J. Mater. Eng. Performance, 2000, vol. 9, pp. 253–60.
L. Tan and T.R. Allen: Corros. Sci., 2010, vol. 52, pp. 548–54.
G.R. Argade, N. Kumar, and R.S. Mishra: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2013, vol. 565A, pp. 80–89.
T. Radetić, A. Halap, M. Popović, and E. Romhanji: in Light Metals 2014: Proc. TMS 2014 Annual Meeting, J. Grandfield, eds., John Wiley and Sons, Hoboken, NJ, 2014, pp. 297–302.
S.I. Vooijs, S.B. Davenport, I. Todd, and S. Van Der Zwaag: Phil. Mag. A, 2001, vol. 81A, pp. 2059–72.
M. Popović and E. Romhanji: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2008, vol. 492A, pp. 460–67.
T.B. Massalski, J.L. Murray, L.H. Bennett, and H. Baker: Binary Alloy Phase Diagrams, ASM International, Metals Park, OH, 1984, vol. 1, pp. 129–31.
Y.K. Yang and T.R. Allen: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2013, vol. 44A, pp. 5226–23.
M.C. Carroll, P.I. Gouma, G.S. Daehn, and M.J. Mills: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2001, vols. A319–A321, pp. 425–28.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technological Development, Republic of Serbia, and Impol-Seval Aluminum Mill, Sevojno, under Contract Grant No. TR 34018.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted September 13, 2013.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Halap, A., Radetić, T., Popović, M. et al. Influence of the Thermomechanical Treatment on the Intergranular Corrosion Susceptibility of Zn-Modified Al-5.1 Wt Pct Mg-0.7 Wt Pct Mn Alloy Sheet. Metall Mater Trans A 45, 4572–4579 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-014-2386-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-014-2386-y