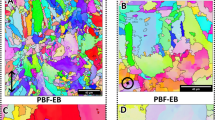
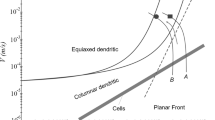
Abstract
Simulative builds, typical of the tip-repair procedure, with matching compositions were deposited on an INCONEL 718 substrate using the laser additive manufacturing process. In the as-processed condition, these builds exhibit spatial heterogeneity in microstructure. Electron backscattering diffraction analyses showed highly misoriented grains in the top region of the builds compared to those of the lower region. Hardness maps indicated a 30 pct hardness increase in build regions close to the substrate over those of the top regions. Detailed multiscale characterizations, through scanning electron microscopy, electron backscattered diffraction imaging, high-resolution transmission electron microscopy, and ChemiSTEM, also showed microstructure heterogeneities within the builds in different length scales including interdendritic and interprecipitate regions. These multiscale heterogeneities were correlated to primary solidification, remelting, and solid-state precipitation kinetics of γ″ induced by solute segregation, as well as multiple heating and cooling cycles induced by the laser additive manufacturing process.













Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
INCONEL 718 and 706 is a trademark of Special Metals Corporation, New Hartford, NY.
LECO is a trademark of LECO Corporation, St. Joseph, MI.
Olympus GX51 is a trademark of Olympus (http://www.olympusims.com/en/microscope/gx51/).
Philips is a trademark of FEI Company, Hillsboro, OR.
TITAN3 is a trademark of FEI Company, Hillsboro, OR.
ChemiSTEM is a trademark of FEI Company, Hillsboro, OR.
It is important to note that the identification of Laves phase is purely based on composition and not on any diffraction evidence. Our attempts to extract these phases consistently for XRD or focused ion-beam extraction were not successful due to the large heterogeneity. Therefore, this identification has to be considered as tentative.
JMATPRO is a trademark of Sun Microsystems, Inc.
References
E.A. Loria: Proc. Superalloy 718, Pittsburgh, 1989, TMS, Warrendale, PA, 1989.
J.F. Barker: Superalloy 718 Metallurgy and Application, TMS, Warrendale, PA, 1989, pp. 269–78.
R.E. Schafrik, D.D Ward, and J.R. Groh: in Superalloys 718, 625, 706, and Various Derivatives, E.A. Loria, ed., TMS, Warrendale, PA, 2001, pp. 1–11.
D.F. Paulonis and J.J. Schirra: in Superalloys 718, 625, 706 and Various Derivatives, E.A. Loria, ed., TMS, Warrendale, PA, 2001, pp. 13–23.
J.P. Collier, S.H. Wong, J.C. Phillips, and J.K. Tien: Metall. Trans. A, 1988, vol. 19A, pp. 657–67.
A. Devaux, L. Nazé, R. Molins, A. Pineau, A. Organista, J.Y. Guédou, J.F. Uginet, and P. Héritier: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2006, vol. A486, pp. 117–22.
X. Xie, Q. Liang, J. Dong, W. Meng, and Z. Xu: in Superalloys 718, 625, 706 and Various Derivatives, E.A. Loria, ed., TMS, Warrendale, PA, 1994, pp. 711–20.
M.K. Miller, S.S. Babu, and M.G. Burke: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 1999, vol. A270, pp. 14–18.
M.K. Miller, S.S. Babu, and M.G. Burke: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2002, vol. A327, pp. 84–88.
R. Cozar and A. Pineau: Metall. Trans., 1973, vol. 4, pp. 47–59.
W.T. Geng, D.H. Ping, Y.F. Gu, C.Y. Cui, and H. Harada: Phys. Rev. B, 2007, vol. 76, pp. 2241021–10.
P.J. Phillips, D. McAllister, Y. Gao, D. Lv, R.E.A. Williams, B. Peterson, Y. Wang, and M.J. Mills: App. Phys. Lett., 2012, vol. 100, pp. 211913-1–211913-3.
J.L. Burger, R.R. Biederman, and W.H. Cuuts: Superalloy 718—Metallurgy and Applications, E.A. Loria, ed., TMS, Warrendale, PA, 1989, pp. 207–17.
T. Alam M. Chaturvedi, S.P. Ringer, and J. Cairney: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2010, vol. 527, pp. 7770–74.
V. Kndrachuk, N. Wanferka, and J. Banhart: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2006, vol. 417, pp. 82–89.
D.D. Gu, W. Meiners, K. Wissenbach, and R. Poprawe: Int. Mater. Rev., 2012, vol. 57, pp. 133–64.
J. Andersson and G.P. Sjöberg: Sci. Technol. Weld. Join., 2012, vol. 7, pp. 49–59.
K. Makiewicz, S.S. Babu, M. Keller, and A. Chaudhary: Unpublished research, 2012.
J.E. Flinkfeldt and T.F. Pedersen: Mater. Sci. Forum, 1994, vols. 163–165, pp. 423–28.
W. König and P.K. Kirner: Proc. Laser Materials Processing: Industrial and Microelectronics Applications, SPIE, Bellingham, WA, 1994, vol. 2207, pp. 44–52.
M. Riabkina-Fishman and J. Zahavi: Lasers Eng., 1996, vol. 5, pp. 31–41.
A. Chaudhary: ASM Handbook, 2010, vol. 22B, pp. 240–52.
C. Zhang, L. Li, and A. Deceuster: J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2011, vol. 211, pp. 1478–87.
J. Ding, P. Colegrove, J. Mehnen, S. Ganguly, P.M. Sequeira Almeida, F. Wang, and S. Williams: Computat. Mater. Sci., 2011, vol. 50, pp. 3315–24.
A. Lundbäck and L.-E. Lindgren: Fin. Elem. Anal. Design, 2001, vol. 47, pp. 1169–77.
M. Chiumenti, M. Cervera, A. Salmi, C. Agelet de Saracibar, N. Dialami, and K. Matsui: Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng., 2010, vol. 199, pp. 2343–59.
“Guide for Verification and Validation in Computation Weld Mechanics,” AWS A9.5: 2013, American Welding Society, Miami, FL, 2013.
K. Makiewicz: Master’s Thesis, The Ohio State University, Columbus, OH, 2013.
H. Qi, M. Azer, and A. Ritter: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2009, vol. 40A, pp. 2410–22.
Xiaoming Zhao, Jing Chen, Xin Lin, and Weidong Huang: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2008, vol. 478, pp. 119–24.
Fencheng Liu, Xin Lin, Chunping Huang, Menghua Song, Gaolin Yang, Jing Chen, and Weidong Huang: J. Alloys Compd., 2011, vol. 509, pp. 4505–09.
K.N. Amato, S.M. Gaytan, L.E. Murr, E. Martinez, P.W. Shindo, J. Hernandez, S. Collins, and F. Medina: Acta Mater., 2012, vol. 60, pp. 2229–39.
Yaocheng Zhang, Zhuguo Li, Pulin Nie, and Yixiong Wu: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2013, vol. 44A, pp. 706–18.
A. Tabernero, S. Lamikiz, E. Martínez, J. Ukar, and J. Figueras: Int. J. Mach. Tools Manufact., 2011, vol. 51, pp. 456–70.
M.J. Cieslak, T.J. Headley, and A.D. Romig: Metall. Trans. A, 1986, vol. 17A, pp. 2035–47.
M.J. Cieslak: Weld J., 1981, vol. 70, pp. 49–56.
G.A. Knorovsky, M.J. Cieslak, T.J. Headley, A.D. Romig, Jr., and W.F. Hammetter: Metall. Trans. A, 1989, vol. 20A, pp. 2149–58.
J.C. Lippold, S.D. Kiser, and J.N. DuPont: Welding Metallurgy and Weldability of Nickel-Base Alloys, John Wiley and Sons Inc., New York, NY, 2009.
AMS 5596 Specification “Nickel Alloy, Corrosion and Heat Resistant, Sheet, Strip, Foil, and Plate 52.5Ni 19Cr 3.0Mo 5.1Cb 0.90Ti 0.50Al 18Fe Consumable Electrode or Vacuum Induction Melted, 1775°F (968 °C) Solution Heat Treated,” AMS, SAE International, Oct. 2012. http://standards.sae.org/ams5596k/.
W. Kurz, C. Bezencon, and M. Gaumann: Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater., 2001, vol. 2, pp. 185–91.
J.M. Vitek: Acta Mater., 2005, vol. 53, pp. 53–67.
J.-W. Park, J.M. Vitek, S.S. Babu, and S.A. David: Sci. Technol. Weld. Join., 2004, vol. 9, pp. 472–82.
T.D. Anderson and J.N. DuPont: Weld. J., 2011, vol. 90, pp. 27s–31s.
C.A. Schneider, W.S. Rasband, and K.W. Eliceiri: Nat. Methods, 2012, vol. 9, pp. 671–75.
R. Rosenthal and D.R.F. West: Mater. Sci. Technol., 1999, vol. 15, pp. 1387–94.
S.S. Babu: Int. Mater. Rev., 2009, vol. 54, pp. 333–67.
R. Nakkalil, N.L. Richards, and M.C. Chaturvedi: Metall. Trans. A, 1993, vol. 24A, pp. 1169–79.
S.M. Seo, J.H. Lee, Y.S. Yoo, C.Y. Jo, H. Miyahara, and K. Ogi: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2011, vol. 42A, pp. 3150–59.
O.A. Ojo, N.L. Richards, and M.C. Chaturvedi: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2006, vol. 37A, pp. 421–33.
B. Radhakrishan and R.G. Thompson: Metall. Trans. A, 1991, vol. 22A, pp. 887–902.
O.A. Ojo and F. Tancret: Computat. Mater. Sci., 2009, vol. 45, pp. 388–89.
Acknowledgments
This research was performed within the Center for Integrative Materials Joining Science for Energy Applications (CIMJSEA), and the authors thank the Rolls Royce Corporation for supporting this project. This material is based upon work supported by the National Science Foundation under Grant No. 1034729. Any opinions, findings, and conclusions or recommendations expressed in this material are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the views of the National Science Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted September 1, 2013.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tian, Y., McAllister, D., Colijn, H. et al. Rationalization of Microstructure Heterogeneity in INCONEL 718 Builds Made by the Direct Laser Additive Manufacturing Process. Metall Mater Trans A 45, 4470–4483 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-014-2370-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-014-2370-6