Abstract
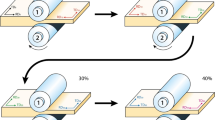
The current study describes the evolution of microstructure and texture in an Al-Zn-Mg-Cu-Zr-based 7010 aluminum alloy during different modes of hot cross-rolling. Processing of materials involves three different types of cross-rolling. The development of texture in the one-step cross-rolled specimen can be described by a typical β-fiber having the maximum intensity near Copper (Cu) component. However, for the multi-step cross-rolled specimens, the as-rolled texture is mainly characterized by a strong rotated-Brass (Bs) component and a very weak rotated-cube component. Subsequent heat treatment leads to sharpening of the major texture component (i.e., rotated-Bs). Furthermore, the main texture components in all the specimens appear to be significantly rotated in a complex manner away from their ideal positions because of non-symmetric deformations in the two rolling directions. Detailed microstructural study indicates that dynamic recovery is the dominant restoration mechanism operating during the hot rolling. During subsequent heat treatment, static recovery dominates, while a combination of particle-stimulated nucleation (PSN) and strain-induced grain boundary migration (SIBM) causes partial recrystallization of the grain structure. The aforementioned restoration mechanisms play an important role in the development of texture components. The textural development in the current study could be attributed to the combined effects of (a) cross-rolling and inter-pass annealing that reduce the intensity of Cu component after each successive pass, (b) recrystallization resistance of Bs-oriented grains, (c) stability of Bs texture under cross-rolling, and (d) Zener pinning by Al3Zr dispersoids.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
K.V. Jata, A.K. Hopkins, and R.J. Rioja: Mater. Sci. Forum, 1996, vols. 217-222, pp. 647-652.
A.K. Vasudevan, M.A. Przystupa, and W.G. Fricke, Jr.: Scripta metall., 1990, vol. 24, pp. 1429-1434.
M.J. Bull and D.J. Lloyd: 3rd Int. Conf. on Al-Li Alloys, C. Baker, P.J. Gregson, S.J. Harris and C.J. Peel, eds., The Institute of Metals, London, 1986, pp. 402–41.
J.R. Hirsch: Int. Conf. on Recrystallization in Metallic Materials (’90), T. Chandra, ed., The Minerals, Metals & Materials Society, 1990, pp. 759–68.
A.K. Singh, G.G. Saha, A.A. Gokhale, and R.K. Ray: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1998, vol. 29A, pp. 665-675.
S. Panchanadeeswaran, and D.P. Field: Acta metall. mater., 1995, vol. 43, pp. 1683-1692.
J. Liu and J.G. Morris: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2003, vol. 34A, pp. 2029-2032.
O. Brun, Th. Chauveau, and B. Bacroix: Mat. Sci. Technol., 1991, vol. 7, pp. 167-175.
O. Engler, E. Sachot, J.C. Ehrström, A. Reeves, and R. Shahani: Mater. Sci. Technol., 1996, vol. 12, pp. 717-729.
P.J. Gregson, and H.M. Flower: Acta metall., 1985, vol. 33, pp. 527-537.
J.C. Ehrström, R. Shahani, A. Reeves, and P. Sainfort: 4th Int Conf. on Aluminium Alloys (ICAA4), T.H. Sanders, Jr. and E.A. Starke, Jr., eds., Atlanta, Geogia Institute of Technology, vol. 2, 1994, pp. 32–39.
X.-H. Zeng, N.-E. Andersson, and S.Johansson: Proc. 11 th Int. Conf. Texture of Materials (ICOTOM 11), Z. Liang, L. Zuo, and Y. Chu, eds., International Academic Publishers, Beijing, 1996, p.1172.
B.D. Cullity, Elements of X-ray Diffraction, Addison-Wesley Publishing Company, Reading, MA (1978).
L.G. Schultz: J. Appl. Phys., 1949, vol. 20, pp. 1030-1033.
H.J. McQueen, E. Evangelista, J. Bowles, and G. Crawford: Met. Sci., 1984, vol. 18, pp. 395-402.
B. Morere, Cl. Maurice, J. Driver, and R. Shahani: Mat. Sci. Forum, 1996, vol. 217-222, pp. 517-522.
F.J. Humphreys and P.N. Kalu: Acta metall., 1987, vol. 35, pp. 2815.
P. Hollinshead and T. Sheppard: Metall. Trans. A, 1989, vol. 20A, pp. 1495-1507.
F. J. Humphreys and M. Hatherly: Recrystallization and Related Phenomena, Pergamon Press, Oxford, United Kingdom, 1995.
B. Ren and J.G. Morris: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1995, vol. 26A, pp. 31-40.
A. Merlini and P.A. Beck: Acta metall., 1953, vol. 1, pp. 598-606.
X.H. Zeng, M. Ahmad, and O. Engler: Mater. Sci. Technol., 1994, vol. 10, pp. 581-591.
W. Liu, X. Li, and X. Meng: Scripta mat., 2009, vol. 60, pp. 768-771.
C. Mondal, A.K. Singh, A.K. Mukhopadhyay, and K. Chattopadhyay: Scripta mat., 2011, vol. 64, pp. 446-449.
Cl. Maurice and J.H. Driver: Mat. Sci. Forum, 1994, vol. 157–162, pp. 807–12.
D. Raabe: Acta metall. mater., 1995, vol. 43, pp. 1023-1028.
T. Leffers: 15th Risø International Symposium on Materials Science, S.I. Anderson, J.B. Bilde-Sørensen, T. Lorentzen, O.B. Pedersen, and N.J. Sørensen, eds., Risø National Library, Roskilde, Denmark, 1994, p. 387.
P.S. Bate, Y. Huang, and F.J. Humphreys: Acta mater., 2004, vol. 52, pp. 4281-4289.
A. Böcker, H. Klein, and H.J. Bunge, Textures and Microstructures, 1990, vol. 12, pp. 155-174.
H. Klein and H.J.Bunge, Steel Research, 1991, vol. 62, pp.548-559.
J. H. Driver: Mat. Sci. Forum, 1994, vol. 157-162, pp. 585–96.
M.Y. Huh, S.Y. Cho, and O. Engler: Mat. Sci. Engg. A, 2001, vol. A315, pp. 35-46.
Y. Zhou, L.S. Toth and K.W. Neale: Acta metall., 1992, vol. 40, pp. 3179-3193.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to acknowledge the financial support by the DRDO, Government of India. The microtexture studies were carried out using the FEG-SEM facility at the Institute Nano-Science Initiative, the Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted January 12, 2012.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mondal, C., Singh, A.K., Mukhopadhyay, A.K. et al. Effects of Different Modes of Hot Cross-Rolling in 7010 Aluminum Alloy: Part I. Evolution of Microstructure and Texture. Metall Mater Trans A 44, 2746–2763 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-013-1626-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-013-1626-x