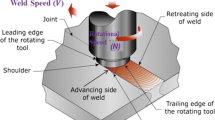
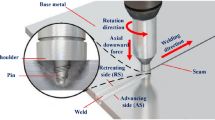
Abstract
In Part II of this series of articles, the transient thermal model, which was introduced in Part I, is used to explore the effects of welding conditions on the heat generation and temperature. FSW of the 6061-T651 aluminum alloy is modeled to demonstrate the model. The following two steps are adopted to study the influence of welding conditions on the heat generation and temperature. First, the thermal model is used to compute the heat generation and temperature for different welding conditions, the calculated results are compared with the reported experimental temperature, and a good agreement is observed. Second, the analytical method is used to explore the approximate functions describing the effect of welding conditions on the heat generation and temperature. Based on the computed results, we discuss the relationship between the welding conditions, heat generation, temperature, and friction coefficient, and propose a relationship map between them for the first time at the end.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
R.S. Mishra and Z.Y. Ma: Mater. Sci. Eng. R, 2005, vol. 50, pp. 1–78.
C.G. Rhodes, M.W. Mahoney, W.H. Bingel, R.A. Spurling, and C.C. Bampton: Scripta. Mater., 1997, vol. 36, pp. 69–75.
M.W. Mahoney, C.G. Rhodes, J.G. Flintoff, R.A. Spurling, and W.H. Bingle: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1998, vol. 29A, pp. 1955–64.
Y.S. Sato, H. Kokawa, M. Enmoto, and S. Jogan: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1999, vol. 30A, pp. 2429–38.
Y.S. Sato, M. Urata, and H. Kokawa: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2002, vol. 33A, pp. 625–35.
P. Cavaliere, G. Campanile, F. Panella, and A. Squillace: J. Mater. Process. Technol., 2006, vol. 5, pp. 263–70.
W.B. Lee, Y.M. Yeon, and S.B. Jung: Mater. Trans., 2004, vol. 45, pp. 1700–05.
S.G. Lim, S.S. Kim, C.G. Lee, and S.J. Kim: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2004, vol. 35A, pp. 2829–35.
S.R. Ren, Z.Y. Ma, and L.Q. Chen: Scripta Mater., 2007, vol. 56, pp. 69–72.
A. Scialpi, L.A.C. De Filippis, and P. Cavaliere: Mater. Des., 2007, vol. 28, pp. 1124–29.
H. Fujii, L. Cui, M. Maeda, and K. Nogi: Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2006, vol. A419, pp. 25–31.
F.C. Liu and Z.Y. Ma: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2008, vol. 39A, pp. 2378–88.
H.B. Schmidt and J.H. Hattel: Scripta Mater., 2008, vol. 58, pp. 332–37.
J.H. Kim, F. Barlat, C. Kim, and K. Chung: Metall. Mater. Int., 2009, vol. 15, pp. 125–32.
S. Xu, X. Deng, and A.P. Reynolds: Sci. Technol. Weld. Join., 2001, vol. 6, pp. 191–93.
H. Schmidt and J. Hattel: Model. Simul. Mater. Sci. Eng., 2005, vol. 13, pp. 77–93.
Q.Z. Zhang, L.W. Zhang, W.W. Liu, X.G. Zhang, W.H. Zhu, and S. Qu: Sci. Technol. Weld. Join., 2006, vol. 11, pp. 737–43.
Z. Zhang and H.W. Zhang: Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 2008, vol. 37, pp. 279–93.
R. Nandan, G.G. Roy, T.J. Lienert, and T. DebRoy: Acta Mater., 2007, vol. 55, pp. 883–95.
A. Arora, R. Nandan, A.P. Reynolds, and T. DebRoy: Scripta Mater., 2009, vol. 60, pp. 13–16.
A.P. Reynolds, W. Tang, Z. Khandkar, J.A. Khan, and K. Lindner: Sci. Technol. Weld. Join., 2005, vol. 10, pp. 190–99.
Y.J. Chao and X. Qi: Proc. 1st Int. Symp. on Friction Stir Welding, TWI, Thousand Oaks, CA, June 1999, pp. 31–38.
Ø. Frigaard, Ø. Grong, and O.T. Midling: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2001, vol. 32A, pp. 1189–98.
M. Song and R. Kovacevic: Int. J. Mach. Tools. Manuf., 2003, vol. 43, pp. 605–15.
M.Z.H. Khandkar, J.A. Khan, and A.P. Reynolds: Sci. Technol. Weld. Join., 2003, vol. 8, pp. 165–74.
H. Schmidt, J. Hattel, and J. Wert: Model. Simul. Mater. Sci. Eng., 2004, vol. 12, pp. 143–57.
H. Schmidt and J. Hattel: Sci. Technol. Weld. Join., 2005, vol. 10, pp. 176–86.
M.J. Peel, A. Steuwer, P.J. Withers, T. Dickerson, Q. Shi, and H. Shercliff: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2006, vol. 37A, pp. 2183–93.
X.X. Zhang, B.L. Xiao, and Z.Y. Ma: Metall. Mater. Trans. A. DOI: 10.1007/s11661-011-0729-5.
P. Colegrove, M. Pinter, D. Graham, and T. Miller: Proc. 2nd Int. Symp. on Friction Stir Welding, TWI, Gothenburg, Sweden, June 2000, pp. 26–28.
Q. Shi, T. Dickerson, and H.R. Shercliff: Proc. 4th Int. Symp. on Friction Stir Welding, TWI, Park City, UT, May 2003, pp. 14–16.
Recommended Values of Thermophysical Properties for Selected Commercial Alloys, C.M. Kenneth, ed., Woodhead Publishing Ltd., Cambridge, England, 2002.
J.H. Yan, M.A. Sutton, and A.P. Reynolds: Sci. Technol. Weld Join., 2005, vol. 10, pp. 725–36.
T. Long, W. Tang, and A.P. Reynolds: Sci. Technol. Weld. Join., 2007, vol. 12, pp. 311–17.
K. Mundra, T. DebRoy, and K.M. Kelkar: Numer. Heat Transfer A, 1996, vol. 29, pp. 115–29.
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the support of (a) the National Outstanding Young Scientist Foundation of China under Grant No. 50525103 and (b) the Hundred Talents Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted October 18, 2010.
Nomenclature
Nomenclature
- D p , D s :
-
pin, shoulder diameter (mm)
- E :
-
weld heat input (J/mm)
- h p :
-
pin length (mm)
- K :
-
curve fitting slope
- L :
-
characteristic length (mm)
- M :
-
torque (Nm)
- P :
-
pressure (Pa)
- q :
-
heat generation rate (J mm−3)
- Q P , Q s , Q total :
-
pin, shoulder and total heat generation (W)
- R p , R s :
-
pin, shoulder radius (mm)
- r :
-
radius (mm)
- T :
-
temperature (K)
- T melt :
-
melting point (K)
- T p :
-
temperature in pin/matrix interface (K)
- \( \overline{{T_{p} }} \) :
-
temperature (K), \( T_{{p, { \max }}} < \overline{{T_{p} }} < T_{{p, { \min }}} \)
- T s :
-
temperature in shoulder/matrix interface (K)
- \( \overline{{T_{s} }} \) :
-
temperature (K), \( T_{{s, { \max }}} < \overline{{T_{s} }} < T_{{s, { \min }}} \)
- \( T_{\text{center}}^{s} \) :
-
temperature at the SC (K)
- \( T_{\text{center}}^{p} \) :
-
temperature at the PC (K)
- t d :
-
dissolution time (s)
- v :
-
advancing speed (mm min−1)
- x,y,z :
-
coordinate axes
- β :
-
pin contact coefficient for treaded pin
- μ 0 :
-
curve fitting intercept
- μ :
-
comprehensive friction coefficient
- \( \theta \) :
-
angle (rad)
- \( \omega \) :
-
rotation rate (rpm)
- \( \pi \) :
-
Pi
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, X.X., Xiao, B.L. & Ma, Z.Y. A Transient Thermal Model for Friction Stir Weld. Part II: Effects of Weld Conditions. Metall Mater Trans A 42, 3229–3239 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-011-0730-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-011-0730-z