Abstract
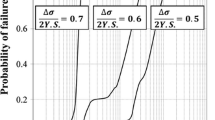
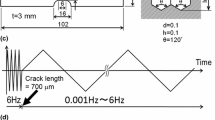
The micromechanism of fatigue damage in an interstitial-free (IF) steel sheet has been studied using fully reversed stress amplitudes (Δσ/2). The stress-life (S-N) curve of the steel sheet has been generated, together with a series of interrupted fatigue tests at each of the chosen Δσ/2, to study the progress of fatigue damage in terms of the initiation, growth, and coalescence of the fatigue cracks on the surfaces of the sheet specimens using scanning electron microscopy. The steel sheet possesses a higher endurance limit (0.98 times its yield strength (YS)), as compared to conventional low-carbon steel sheets. This is attributed to (1) the occurrence of nonpropagating microcracks initiating primarily at the inclusions below the endurance limit and (2) a significant delay in the spread of plastic deformation, until Δσ/2 is close to YS. Above the endurance limit, widespread plastic deformation through slip bands promotes the formation of fatigue cracks at the ferrite grain boundaries and occasionally within a ferrite grain body, as well as at inclusions. Fatigue failure is preceded by the significant growth of grain-boundary cracks over and above those at inclusions and the ferrite grain body. A series of grain-boundary cracks link up to form mesocracks, one of which grows to cause the final failure. The predominance of grain-boundary cracks in the process of fatigue failure is attributed to the lesser cohesive strength of the grain boundaries caused by the depletion of interstitials.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
I. Gupta, D. Bhattacharya: in Metallurgy of Vacuum Degassed Steel Products, R. Pradhan, ed., TMS, Warrendale, PA, 1990, pp. 43–72
Y. Tokunaga: in Metallurgy of Vacuum Degassed Steel Products, R. Pradhan, ed., TMS, Warrendale, PA, 1990, pp. 91–108
M.T. Milan, D. Spinelli, W.W. Bose Filho: Int. J. Fatigue, 2001, vol. 23, pp. 129–33
G.E. Dieter: Mechanical Metallurgy, SI Metric ed., McGraw Hill Publishing Co., London, 1988, pp. 394–98
ASM Handbook, vol. 19, Fatigue and Fracture, 9th ed., ASM INTERNATIONAL, Metals Park, OH, 1996, pp. 96–98
C. Holzapfel, W. Schaf, M. Marx, H. Vehoff, F. Mucklich: Scripta Mater., 2007, vol. 56, pp. 697–700
ASM Handbook, vol. 19, Fatigue and Fracture, 9th ed., ASM INTERNATIONAL, Metals Park, OH, 1996, pp. 153–54
Microscopic Testing Method for the Non-Metallic Inclusions of Steels, Japanese Standard JISG-0555, 1992
S. Majumdar: Tata Search, 2007, vol. 2, pp. 295–98
Standard Test Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Materials (Metric), ASTM Designation E 8M-04, ASTM, Philadelphia, PA, 2004, pp. 86–109
Standard Test Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Materials (Metric), ASTM Designation E 8M-04, ASTM, Philadelphia, PA, 2004, pp. 86–109
H.J. Christ, H. Mughrabi, C. Witting-Link: Basic Mechanism in Fatigue of Metals, 1st ed., Elsevier, Amsterdam, 1988, pp. 83–84
M. Zhang, P. Yang, Y. Tan: Int. J. Fatigue, 1999, vol. 21, pp. 823–30
Y.M. Hu, W. Floer, U. Krupp, H.-J. Christ: Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2000, vol. 278, pp. 170–80
R.E. Hook, J.P. Hirth: Acta Metall., 1967, vol. 15, pp. 1099–110
P. Sittner, V. Paidar: Acta Metall., 1989, vol. 37, pp. 1717–26
N. Narasaiah, P.C. Chakraborti, R. Maiti, K.K. Ray: ISIJ Int., 2005, vol. 45, pp. 127–32
U. Essman, U. Gosele, H. Mughrabi: Philos. Mag, 1981, vol. 44, pp. 405–26
A. Hunche, P. Neuman: Acta Metall., 1986, vol. 34, pp. 207–17
M. Long, R. Crooks, H.J. Rack: Acta Mater., 1999, vol. 47, pp. 661–69
H.O. Fuchs, R.I. Stephens: Metal Fatigue in Engineering, John Wiley & Sons, New York, NY, 1980, pp. 296–98
G.E. Dieter: Mechanical Metallurgy, SI Metric ed., McGraw Hill Publishing Co. Place, London, 1988, pp. 418–19
L. Nian, D. Bai-ping, Z. Hui-jiu: Int. J. Fatigue, 1984, vol. 6 (2), pp. 89–94
P. Lukas, M. Klesnil: Mater. Sci. Eng., 1978, vol. 34, pp. 61–66
G. Oates, D.V. Wilsons: Acta Metall., 1964, vol. 12, pp. 21–33
G.E. Dieter: Mechanical Metallurgy, SI Metric Edition, McGraw Hill Publishing Co. Place, London, 1988, pp. 197–98
P.G. Forrest: Fatigue of Metals, 2nd ed., Addison Wesley Publishing Company, Inc., London, 1962, pp. 146–47
J.C. Suits, B. Chalmers: Acta Metall., 1961, vol. 9, pp. 854–60
R.W. Hertzberg: Deformation and Fracture Mechanics of Engineering Materials, 4th ed., John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York, NY, 1995, pp. 529–30
B. Yan: Proc. 37th MWSP Conf., The Iron and Steel Society Inc., Warrendale, PA, 1996, vol. XXXIII, pp. 101–14
F.B. Pickering: Physical Metallurgy and the Design of Steel, Applied Science Publishers Ltd., London, 1978, pp. 18–20
J.W. Cahn: Acta Metall., 1962, vol.10, pp. 789–99
W.H. Kim, C. Laird: Acta Metall., 1978, vol. 26, pp. 777–87
J.C. Figueroa, C. Laird: Mater. Sci. Eng., 1983, vol. 60, pp. 45–58
F. Guiu, R. Dubniak, R.C. Edward: Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct., 1982, vol. 5, pp. 311–21
H. Mugrhabi, K. Herze, X. Stark: Int. J. Fract., 1981, vol. 17, pp. 193–220
K. Tanaka, Y. Akinawa, In Fatigue 87, EMAS, Warley, UK, p.739–49, 1987
Acknowledgments
One of the authors (SM) gratefully acknowledges the sponsorship rendered by Tata Steel, Ltd., for pursuing her doctoral studies program. The authors are grateful to Dr. N. Gope (Head, Product Research Group, R&D Division, Tata Steel, Ltd.), for making the experimental facilities available, and to Mr. Vikram Sharma of the R&D Division, Tata Steel, Ltd., for his help in carrying out the scanning electron microscopy work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted August 21, 2007.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Majumdar, S., Bhattacharjee, D. & Ray, K. On the Micromechanism of Fatigue Damage in an Interstitial-Free Steel Sheet. Metall Mater Trans A 39, 1676–1690 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-008-9537-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-008-9537-y