Abstract
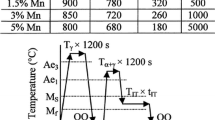
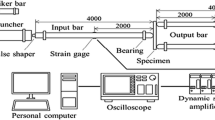
High-strength, low-alloy transformation-induced plasticity (TRIP) steels are advanced multiphase steel grades that combine high-strength levels with an excellent ductility, making them ideally suited for application in crash-relevant parts of automotive car bodies. The enhanced plastic hardening and deformability are due to a complex interaction between the microstructural phases and to the transformation of metastable austenite to martensite during plastic deformation. During high-strain-rate loading, not only the material but also the transformation will be influenced by adiabatic heating. The impact-dynamic properties of CMnAl- and CMnSi-TRIP steels were determined in the range of 500 to 2000 s−1 using a split Hopkinson tensile bar (SHTB) setup. Bake-hardening treatments were applied to study the effect of strain aging. The experiments show that strain-rate hardening is superior to thermal softening: yield stresses, deformation, and energy dissipation increase with the strain rate. Phenomenological material models were investigated to describe the strain-rate and temperature-dependent behavior of TRIP steels. Both the Johnson-Cook model and an extended version of the Ludwig model were found to give good agreement with the experimental data.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A.N. Vasilakos, J. Ohlert, K. Giasla, G.N. Haidemenopoulos, and W. Bleck: Steel Res., 2002, vol. 73 (6–7), pp. 249–52.
V.F. Zackay, E.R. Parker, D. Fahr, and R. Busch: Trans. ASM, 1967, vol. 60, pp. 252–59.
O. Matsumura and O. Sakuma: Trans. Iron Steel Inst. Jpn., 1987, vol. 27, pp. 570–79.
Y. Sakuma, O. Matsumura, and H. Takechi: Metall. Trans. A, 1991, vol. 22A, pp. 489–98.
B.C. De Cooman, L. Samek, J. Mahieu, J. Van Slycken, P. Verleysen, J. Degrieck, L. Lin, L. Wang, X. Cheng Wei, and S. Peng: Proc. 2003 Fall Meeting of TMS and 45th ISS Mechanical Working and Steel Processing Conf., Vancouver, BC, Canada, 2003.
J. Mahieu: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2002, vol. 33A, pp. 2573–80.
E. Girault, A. Mertens, P. Jacques, Y. Houbaert, B. Verlinden, and J. Van Humbeeck: Scripta Mater., 2001, vol. 44, pp. 885–92.
A.K. Pickett, T. Pyttel, F. Payen, F. Lauro, N. Petrinic, H. Werner, and J. Christlein: Int. J. Impact Eng., 2004, vol. 30, pp. 853–72.
P.J. Jacques, J. Ladriere, and F. Delannay: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2001, vol. 32, pp. 2759–68.
A. Itami, M. Takahashi, and K. Ushioda: Iron Steel Inst. Jpn. Int., 1995, vol. 35, pp. 1121–27.
L. Zhao, N.H. van Dijk, E. Brück, J. Sietsma, and S. van der Zwaag: Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2001, vol. 313, pp. 145–52.
E. Girault, P. Jacques, P. Harlet, K. Mols, J. Van Humbeeck, E. Aernoudt, and F. Delannay: Mater. Characterization, 1998, vol. 40, pp. 111–18.
H. Kolsky: Proc. Phys. Soc. London Sect. B, 1949, vol. 62, pp. 676–700.
P. Verleysen and J. Degrieck: Int. J. Impact Eng., 2004, vol. 30, pp. 239–53.
K.P. Staudhammer and L.E. Murr: Mater. Sci. Eng., 1980, vol. 44, pp. 97–113.
L.E. Murr: in Materials at High Strain Rates, T.Z. Blazynski, ed., Elsevier Applied Science Publishers Ltd., New York, NY, 1987, pp. 1–46.
W.S. Lee and C.F. Lin: Mater. Sci. Technol., 2002, vol. 18, pp. 869–76.
A.S. Khan and R. Liang: Int. J. Plast., 1999, vol. 15, pp. 1089–109.
J. Mahieu: Ph.D. Thesis, Ghent University, Ghent, 2004.
A. Mark, D. Boyd, and E. Essadiqi: Int. Conf. on Advanced High Strength Sheet Steels for Automotive Applications Proc., Winterpark, CO, 2004, pp. 307–13.
G.R. Johnson and W.H. Cook: Proc. 7th Int. Symp. Ballistics, The Hague, 1983, pp. 541–47.
H. Zhao: Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 1997, vol. 230, pp. 95–99.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Van Slycken, J., Verleysen, P., Degrieck, J. et al. High-strain-rate behavior of low-alloy multiphase aluminum- and silicon-based transformation-induced plasticity steels. Metall Mater Trans A 37, 1527–1539 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-006-0097-8
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-006-0097-8