Abstract
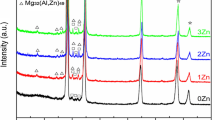
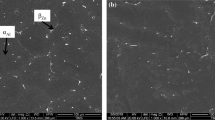
In the present research, Al-Zn-Mg alloys were vacuum induction melted and gravity cast into steel molds. Ingots were microstructurally and electrochemically characterized to evaluate their performance as Al-sacrificial anodes for cathodic protection of structures exposed to marine environments. The microstructure observed in as-cast ingots consisted mainly of α-Al dendrites with 0.68 to 2.25 vol pct of τ phase in α-Al matrix and eutectic in interdendritic regions. After heat treatment, the presence of the τ phase increased up to 5 vol pct. Electrochemical efficiencies obtained in Al alloys showed maximum values of 73 and 87 pct in as-cast ingots and heat-treated ingots, respectively. In order to contribute to the development of Al-Zn-Mg anodes, the Al-5.3 at. pct Zn-6.2 at. pct Mg (Al-12 wt pct Zn-5.4 wt pct Mg) alloy was monitored to identify the temperature changes as it cools through phase transformation intervals. Growth temperatures of the phases present in this alloy were employed to predict the structure growing at fixed growth velocity. Predictions of variation of solute concentration with growth velocity in α-Al dendrites were included, too. The results of these analyses help to select alloy composition and to control microstructure in order to develop a new generation of Al-sacrificial anodes free of In and Hg.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- C :
-
total current charge (amp-h)
- C 1, C 2 :
-
constants for a given system (Ks1/2 m−1/2)
- C eq max :
-
the maximum concentration of solute at equilibrium
- C* L :
-
liquidus tip concentration (wt pct or at. pct)
- C 0 :
-
concentration (wt pct or at. pct)
- C* s :
-
solidus tip concentration (wt pct or at. pct)
- D :
-
diffusion coefficient in the liquid (m2s−1)
- G :
-
temperature gradient (Km)
- Iv(P):
-
is the Ivantsov function
- k :
-
partition coefficient
- k 1 :
-
constant
- K 1 :
-
a constant (= π/P2 D 2)
- K 2 :
-
a constant (= mC o pξ c/D[1 − pIv(P)])
- m :
-
liquidus slope (°C/wt pct or °C/at. pct)
- n :
-
a constant that depends on growth morphology and regime
- p :
-
complementary partition coefficient.
- P:
-
solute Peclet number
- T G :
-
growth temperature of dendrites, intermetallic or eutectics (°C or K)
- T :
-
equilibrium liquidus, intermetallic or eutectic temperature (°C or K)
- V :
-
solidification front velocity (ms−1)
- W :
-
specimen weight loss (kg)
- ξ c :
-
a constant (= 1 − 2k/{[1 + (2π/P)2]1/2})
- Γ :
-
Gibbs-Thompson coefficient (Km)
- Δf p :
-
fraction of precipitates that form during aging
- C m :
-
mean solute concentration in the matrix (wt pct or at. pct)
- C m 0 :
-
matrix solute content in stabilized base material (wt pct or at. pct)
References
G. Bruzzone, A. Barbucci, and G. Cerisola: J. Alloys Compounds, 1997, vol. 247, pp. 210–16.
S. Valdes, J. Genesca, B. Mena, and J.A. Juarez-Islas: J. Mater. Eng. Performance, 2000, vol. 10 (5), pp. 596–601.
K. Ravidran and A.G. Gopalakrishna: Fishery Technol., 1987, vol. 24, pp. 1–4.
D.R. Salinas, S.G. Garcia, and J.B. Bessone: J. Appl. Electrochem., 1999, vol. 29 (9), pp. 1063–71.
D.R. Salinas and J.B. Bessone: Corrosion, 1991, vol. 47 (9), pp. 665–74.
I. Gurrappa: Corr. Prevention Control, 1997, June, pp. 69–80.
A. Barbucci, G. Cerisola, G. Bruzzone, and A. Saccone: Electrochemica Acta, 1997, vol. 42 (15), pp. 2369–80.
H. Liang, S.-L. Chen, and Y.A. Chang: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1997, vol. 28A, pp. 1725–34.
G. Eger: Int. Z. Metallogr., 1993, vol. 4, pp. 50–128.
D.A. Petrov: in Ternary Alloys, G. Petzow and G. Effenberg, eds., ASM INTERNATIONAL, Materials Park, OH, 1993, vol. 7, pp. 57–71.
C. Labrecque and M. Gagné: AFS Trans., 1998, vol. 106, pp. 83–90.
J.A. Juarez-Islas and H. Jones: Inst. Met., 1988, vol. 421, pp. 492–95.
W. Kurz, B. Giovanola, and R. Trivedi: Acta Metall., 1986, vol. 34 (5), pp. 823–30.
G.M. Kuznetsov, A.D. Barsukov, G.B. Krivosheeva, and E.G. Dieva: Izv. Akad. Nauk, SSSR Metall., 1986, vol. 4, pp. 198–200.
P.E. Droeneb and N. Ryum: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1994, vol. 25A, pp. 521–30.
J.A. Juarez-Islas: J. Mater. Sci., 1994, vol. 26, pp. 5004–09.
K.A. Jackson and D. Hunt: TMS-AIME, (1966), vol. 236, p. 1129.
W. Kurz and D.J. Fisher: Int. Mater. Rev., 1979, vol. 24, p. 177.
A. Moore and R. Elliot: The Solidification of Metals, The Iron and Steel Institute, London, 1968, p. 167.
M. Tasa and J.D. Hunt: J. Cryst. Growth, 1976, vol. 34, p. 38.
B.J. Bjorneklett, O. Grong, O.R. Myhr, and A.O. Klñuken: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1999, vol. 30A, pp. 2667–77.
A.M. Samuel, P. Ouellet, F.H. Samuel, and H.W. Doty: AFS Trans., 1977, vol. 156, pp. 951–62.
A. Juarez-Hernandez and H. Jones: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2000, vol. 31A, pp. 327–28.
H.D. Brody and M.C. Flemings: Metall. Trans. A, 1981, vol. 12A, p. 965.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gonzalez, C., Genesca, J., Alvarez, O. et al. Solidification of chill-cast Al-Zn-Mg alloys to be used as sacrificial anodes. Metall Mater Trans A 34, 2991–2997 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-003-0198-6
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-003-0198-6