Abstract
Objective
To study the angiogenesis modulation mechanism of Xuefu Zhuyu Decoction (血府逐瘀汤) on the endothelial cell line ECV304.
Methods
ECV304 cells were treated with 2.5% Xuefu Zhuyu Decoctioncontaining serum (XFZYD-CS) for 24 h, 48 h or 72 h. Thiazolyl blue tetrazolium bromide (MTT), fluorescence activating cell sorter (FACS), migration, adhesion and in vitro tube formation assays were conducted to confirm an angiogenesis effect of XFZYD at 3 time points. An analysis of angiogenesis regulator profiles was performed at 3 times with real-time polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) superarray.
Results
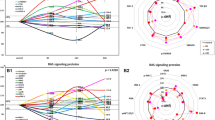
At 48 h, XFZYD-CS induced ECV304 significantly improved cell viability, number in S phase, migration, adhesion and tube formation. At 24 h and 72 h, only cell migration was elevated. Microarray results showed that the expression of 27 angiogenesis-related genes was changed.
Conclusion
XFZYD-CS treatment induced angiogenesis on ECV304 cells with significant cellcular changes occurring at 48 h and genetic changes as early as 24 h.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gao D, Song J, Hu J, Lin JM, Zheng LP, Cai J, et al. Angiogenesis promoting effects of Chinese herbal medicine for activating blood circulation to remove stasis on chick embryo chorio-allantoic membrane. Chin J Integr Tradit West Med (Chin) 2005;25:912–915.
Gao D, Lin W, Zhen LP, Lin JM, Chen XZ, Song J, et al. Effect of Xuefu Zhuyu Decoction on endothelial progenitor cells migrating from rat marrow. Chin J Integr Med Cardio-/ Cerebrovasc Dis (Chin) 2007;5:829–831.
Gao D, Wu LY, Jiao YH, Chen WY, Zheng LP, Song J, et al. The experimental analysis of Xuefu Zhuyu Decoction on EPC mobilization factor. J Tradit Chin Med (Chin) 2010;51:457–459.
Gao D, Wu LY, Jiao YH, Chen WY, Song J, Chen KJ. The experimental study of effect on EPCs differentiation function by Xuefu Zhuyu Decoction. Chin J Basic Med Tradit Chin Med (Chin) 2009;15:917–919.
Gao D, Wu LY, Jiao YH, Chen WY, Chen Y, Kaptchuk TJ, et al. The effect of Xuefu Zhuyu Decoction on in vitro endothelial progenitor cell tube formation. Chin J Integr Med 2010;16:50–53.
Gao D, Chen WY, Wu LY, Zheng LP, Lin W, Song J. The study on angiogenesis regulation gene profile of ECV304 by Xuefu Zhuyu Decoction. Chin J Integr Tradit West Med (Chin) 2010;30:153–156.
Wang PL, Lei Y, Chen KJ. Angiogenesis-a novel therapeutic strategy for cardiovascular diseases. Chin J Integr Tradit West Med (Chin) 2006;26:173–176.
Brantley-Sieders DM, Chen J. Eph receptor tyrosine kinases in angiogenesis: from development to disease. Angiogenesis 2004;7:17–28.
Zhang J, Hughes SE. Role of the ephrin and Eph receptor tyrosine kinase families in angiogenesis and development of the cardiovascular system. J Pathol 2006;208:453–461.
Pandey A, Shao H, Marks RM, Polverini PJ, Dixit VM. Role of B61, the ligand for the Eck receptor tyrosine kinase, in TNF-alpha induced angiogenesis. Science 1995;268:567–569.
Daniel TO, Stein E, Cerretti DP, St John PL, Robert B, Abrahamson DR. ELK and LERK-2 in developing kidney and microvascular endothelial assembly. Kidney Int Suppl 1996;57:S73–S81.
Stein E, Lane AA, Cerretti DP, Schoecklmann HO, Schroff AD, Van Etten RL, et al. Eph receptors discriminate specific ligand oligomers to determine alternative signalling complexes, attachment, and assembly responses. Genes Dev 1998;12:667–678.
Wang HU, Chen ZF, Anderson DJ. Molecular distinction and angiogenic interaction between embryonic arteries and veins revealed by ephrin-B2 and its receptor EphB4. Cell 1998;93:741–753.
Gerety SS, Anderson DJ. Cardiovascular ephrinB2 function is essential for embryonic angiogenesis. Development 2002;129:1397–1410.
Hayashi S, Asahara T, Masuda H, Isner JM, Losordo DW. Functional ephrin-B2 expression for promotive interaction between arterial and venous vessels in postnatal neovascularization. Circulation 2005;111:2210–2218.
Zamora DO, Davies MH, Planck SR, Rosenbaum JT, Powers MR. Soluble forms of ephrinB2 and EphB4 reduce retinal neovascularization in model of proliferative retinopathy. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2005;46:2175–2182.
Sakamaki K. Regulation of endothelial cell death and its role in angiogenesis and vascular regression. Curr Neurovasc Res 2004;1:305–315.
Sato Y. Update on endogenous inhibitors of angiogenesis. Endothelium 2006;13:147–155.
Li X, Jiang L, Wang Y, Xiao Y, Huang Y, Yao Q, et al. Inhibition of angiogenesis by a novel small peptide consisting of the active fragments of platelet factor-4 and vasostatin. Cancer Lett 2007;256:29–32.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81072933 and No. 81173431); Fujian Natural Science Foundation (No. 2007J0101); Fujian Academy of Integrative Medicine Foundation (No. CKJ2008001); National Institutes of Health—The National Center for Complementary and Alternative Medicine Foundation of US (NIH-NCCAM No. K24 AT004095)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, J., Chen, Wy., Wu, Ly. et al. A microarray analysis of angiogenesis modulation effect of Xuefu Zhuyu Decoction (血府逐瘀汤) on endothelial cells. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 18, 502–506 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-012-1143-6
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-012-1143-6