Abstract
Objective
To investigate the role of the TLR4-NFκB-TNFα inflammation pathway on: lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced neonatal rat cardiomyocyte injury and the possible protective effects of salvianolic acid B (Sal B).
Methods
Wistar rat (1–2 days old) cardiomyocytes were isolated and cultured. Sal B 10−5mol/L, 10−6mol/L and 10−7mol/L were pre-treated for 6 h in the culture medium. LPS (1 μg/mL) was added to mol/the culture medium and kept for 6 h to induce inflammation injury. The concentration of lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) in the supernatant was detected by spectrophotometry. The concentrations of tumor necrosis factor α (TNFα) and heat shock protein 70 (HSP70) in the supernatant were detected by enzyme linked immunosorbent assay. The protein expressions of toll, such as receptor 4 (TLR4) and nuclear factor kappa B (NFκB) were detected by immunohistochemistry. The mRNA expressions of TLR4 and NFκB were detected by real-realtime reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR).
Results
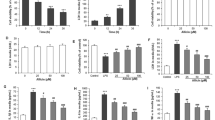
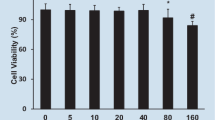
(1) The concentrations of LDH and: TNFα in the LPS control group were significantly higher than those in the control group (561.41±67.39 U/L and 77.94±15.08 pg/mL, versus 292.13±26.02 U/L and 25.39±16.53 pg/mL, respectively, P<0.01, P<0.05). Compared with the LPS control group, the concentrations of LDH and TNFα were significantly decreased in the Sal B 10−5mol/L pre-treated group (451.76±83.96 U/L and 34.00±10.38 pg/mL, respectively, P<0.05). (2) The TLR4 and NFκB protein expression area in the LPS control group were significantly higher than those in the control group (1712.41±410.12 μm2 and 2378.15±175.29 μm2, versus 418.62±24.42 μm2 and 1721.74±202.87 μm2, respectively, P<0.01). The TLR4 and NFκB protein expression internal optical density (IOD) values in the LPS control group were also significantly higher than those in the control group (3.06±0.33 and 7.20±1.04, versus 0.91±0.21 and 4.24±0.48, respectively, P<0.05 and P<0.01). Compared with the LPS control group, the TLR4 and NFκB protein expression areas were significantly decreased in the Sal B 10−5mol/L pre-treated group (1251.54±133.82 μm2 and 1996.37±256.67 μm2, respectively, P<0.05), the TLR4 and NFκB protein expression IOD values were also significantly decreased in the Sal B 10−5mol/L pre- mol/pretreated group (1.92±0.28 and 5.17±0.77, respectively, treated P<0.05). (3) The TLR4 and NFκB mRNA expressions (2−ΔΔCT value) in the LPS control group were significantly higher than those in the control group (3.16±0.38 and 5.03±0.43 versus 1.04±0.19 and 1.08±0.21, respectively, P<0.01). Compared with the LPS control group, the TLR4 and NFκB mRNA expressions (2−ΔΔ -CT value) were significantly decreased in the Sal B 10−5mol/L pre- mol/pretreated group (1.34±0.22 and 1.74±0.26, respectively, treated P<0.05). The concentration of HSP70 did not show any <statistical differences in all groups (P>0.05).
Conclusions
The TLR4-NFκB-TNFα pathway was quickly activated: and was independent of HSP70 in the early phase of neonatal cardiomyocyte injury induced by LPS. The protective effects of Sal B may be through inhibiting the TLR4-NFκB-TNFα pathway and are dose-dependent.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li X, Li Y, Shan L, Chen R, Peng T. Over-expression of calpastatin inhibits calpain activation and attenuates myocardial dysfunction during endotoxaemia. Cardiovasc Res 2009;83:72–79.
da Silveira Cruz-Machado S, Carvalho-Sousa CE, Tamura EK, Pinato L, Cecon E, Fernandes PA, de Avellar MC, et al. TLR4 and CD14 receptors expressed in rat pineal gland trigger NFκB pathway. J Pineal Res 2010;49:183–192.
Mong PY, Petrulio C, Kaufman HL, Wang Q. Activation of Rho kinase by TNF-alpha is required for JNK activation in human pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells. J Immunol 2008;180:550–558.
Wu HL, Li YH, Lin YH, Wang R, Li YB, Tie L, et al. Salvianolic acid B protects human endothelial cells from oxidative stress damage: a possible protective role of glucose-regulated protein 78 induction. Cardiovasc Res 2009;81:148–158.
Chen YH, Lin SJ, Chen YL, Liu PL, Chen JW. Anti- inflammatory effects of different drugs/agents with antioxidant property on endothelial expression of adhesion molecules. Cardiovasc Hematological Disord Drug Targets 2006;6:279–304.
Wang SX, Hu LM, Gao XM, Guo H, Fan GW. Anti-inflammatory activity of salvianolic acid B in microglia contributes to its neuroprotective effect. Neurochem Res 2010;35:1029–1037.
Luo P, Tan Z, Zhang Z, Li H, Mo Z. Inhibitory effects of salvianolic acid B on the high glucose-induced mesangial proliferation via NF-κB-dependent pathway. Biol Pharm Bull 2008;31:1381–1386.
Xie LX, Durairajan SS, Lu JH, Liu CL, Kum WF, Wang Y, et al. The effect of salvianolic acid B combined with laminar shear stress on TNF-α-stimulated adhesion molecule expression in human aortic endothelial cells. Clin Hemorheol Microcirc 2010;44:245–258.
Maass AH, Buvoli M. Cardiomyocyte preparation, culture, and gene transfer. Methods Mol Biol 2007;366:321–330.
Liu X, Ren Z, Zhan R, Wang X, Wang X, Zhang Z, et al. Prohibitin protects against oxidative stress-induced cell injury in cultured neonatal cardiomyocyte. Cell Stress Chaperones 2009;14:311–319.
de Jong PR, Schadenberg AW, Jansen NJ, Prakken BJ. HSP70 and cardiac surgery: molecular chaperone and inflammatory regulator with compartmentalized effects. Cell Stress Chaperones 2009;14:117–131.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the Foundation of Guang’anmen Hospital, China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences (No. 81359)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J., Zhang, Y., Guo, Ll. et al. Salvianolic acid B inhibits the TLR4-NFκB-TNFα pathway and attenuates neonatal rat cardiomyocyte injury induced by lipopolysaccharide. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 17, 775–779 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-011-0877-x
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-011-0877-x