Abstract
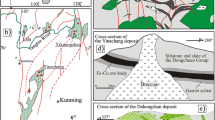
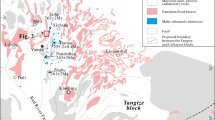
The Xinqiao deposit is one of several polymetallic deposits in the Tongling ore district. There are two types of mineralization in the Xinqiao: skarn-type and stratiform-type. The skarn-type mineralization is characterized by iron oxides such as magnetite and hematite, whereas stratiform-type mineralization is characterized by massive sulfides with small amounts of magnetite and hematite. We defined three types of ores within the stratiform-type mineralization by the mineral assemblages and ore structures. Type I ore is represented by magnetite crosscut by minor calcite veins. Type II is a network ore composed of magnetite and crosscutting pyrite. Type III is a massive ore containing calcite and hematite. Type I magnetite is characterized by highly variable trace element content, whereas Type II magnetite has consistently higher Si, Ti, V, and Nb. Type III magnetite contains more In, Sn, and As than the other two types. Fluid–rock interaction, oxygen fugacity (fO2), and temperature (T) are the main factors controlling element variation between the different magnetite types. Type I magnetite was formed by more extensive fluid–rock interaction than the other two types at moderate fO2 and T conditions. Type II magnetite is thought to have formed in relatively low fO2 and high-T environments, and Type III in relatively high fO2 and moderate-T environments. Ca + Al + Mn and Ti + V discrimination diagrams show that magnetite in the Xinqiao deposit is hydrothermal in origin and is possibly linked with skarn.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acosta-Góngora P, Gleeson SA, Samson IM et al (2014) Trace element geochemistry of magnetite and its relationship to Cu–Bi–Co–Au–Ag–UW mineralization in the Great Bear magmatic zone, NWT, Canada. Econ Geol 109:1901–1928
Angerer T, Hagemann SG, Danyushevsky LV (2012) Geochemical evolution of the banded iron formation-hosted high-grade iron ore system in the Koolyanobbing greenstone belt, Western Australia. Econ Geol 107:599–644
Bajwah ZU, Seccombe PK, Offler R (1987) Trace element distribution Co:Ni ratios and genesis of the big cadia iron–copper deposit, new South Wales, Australia. Miner Depos 22:292–300
Boutroy E, Dare SA, Beaudoin G, Barnes S-J, Lightfoot PC (2014) Magnetite composition in Ni–Cu–PGE deposits worldwide: application to mineral exploration. J Geochem Explor 145:64–81
Canil D, Grondahl C, Lacourse T, Pisiak LK (2016) Trace elements in magnetite from porphyry Cu–Mo–Au deposits in British Columbia, Canada. Ore Geol Rev 72:1116–1128
Carew MJ (2004) Controls on Cu–Au mineralisation and Fe oxide metasomatism in the Eastern Fold Belt, NW Queensland. James Cook University, Australia
Chang YF, Liu YZ (1983) Layer control type skarn type deposit—some deposits in the Middle–Lower Yangtze Depression in Anhui Province as an example. Mineral. Depos 2:11–20 (in Chinese)
Chang Y, Liu X, Wu Y-C (1991) The copper–iron belt of the lower and middle reaches of the Changjiang River. Geology Publication House, Beijing
Chen WT, Zhou MF, Gao JF, Hu R (2015a) Geochemistry of magnetite from Proterozoic Fe–Cu deposits in the Kangdian metallogenic province, SW China. Miner Deposita 50:795–809
Chen WT, Zhou MF, Li X, Gao JF, Hou K (2015b) In-situ LA–ICP-MS trace elemental analyses of magnetite: Cu–(Au, Fe) deposits in the Khetri copper belt in Rajasthan Province, NW India. Ore Geol Rev 65:929–939
Chen C, Chen B, Li Z, Wang Z (2016) Important role of magma mixing in generating the Mesozoic monzodioritic-granodioritic intrusions related to Cu mineralization, Tongling, East China: evidence from petrological and in-situ Sr–Hf isotopic data. Lithos 248:80–93
Chung D, Zhou MF, Gao JF, Chen WT (2015) In-situ LA–ICP-MS trace elemental analyses of magnetite: the late Palaeoproterozoic Sokoman iron formation in the Labrador trough, Canada. Ore Geol Rev 6:917–928
Dare SAS, Barnes S-J, Beaudoin G (2012) Variation in trace element content of magnetite crystallized from a fractionating sulfide liquid, Sudbury, Canada: implications for provenance discrimination. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 88:27–50
Dare SAS, Barnes S-J, Beaudoin G, Méric J, Boutroy E, Potvin-Doucet C (2014) Trace elements in magnetite as petrogenetic indicators. Miner Depos 49:785–796
Dare SAS, Barnes S-J, Beaudoin G (2015) Did the massive magnetite “lava flows” of El Laco (Chile) form by magmatic or hydrothermal processes? New constraints from magnetite composition by LA–ICP–MS. Miner Depos 50:607–617
Dupuis C, Beaudoin G (2011) Discriminant diagrams for iron oxide trace element fingerprinting of mineral deposit types. Miner Deposita 46:319–335
Duran CJ, Barnes S-J, Corkery JT (2016) Trace element distribution in primary sulfides and Fe–Ti oxides from the sulfide-rich pods of the Lac des Iles Pd deposits, Western Ontario, Canada: constraints on processes controlling the composition of the ore and the use of pentlandite compositions in exploration. J Geochem Explor 166:45–63
Einaudi MT (1981) Skarn deposits. Econ Geol 75:317–391
Figueiredo E, Silva RC, Hagemann SG, Lobato LM, Danyushevsky L (2009) Laser-ablation ICP-MS analyses on oxides of hypogene iron ore from the giant Serra Norte jaspilite-hosted iron ore deposits, Carajás mineral province, Brazil, In: The 10th Biennial SGA meeting of the Society For Geology Applied to Mineral Deposits Townsville Australia, pp 570–572
Floyd P, Winchester J (1978) Identification and discrimination of altered and metamorphosed volcanic rocks using immobile elements. Chem Geol 21:291–306
Frost B, Lindsley DH (1991) Occurrence of iron-titanium oxides in igneous rocks. Rev Mineral Geochem 25:433–468
Ganguo W, Da Z, Dongxu L, Xiangxin Z, Yongjun S, Wenshuan Z, Qunfeng W (2004) Study of the emplacement mechanism of the Fenghuangshan granite pluton and related Cu-Au mineralization in Tongling, Anhui Province. Acta Geol Sin 78:492–502 (English edition)
Gao JF, Zhou MF, Lightfoot PC, Wang CY, Qi L, Sun M (2013) Sulfide saturation and magma emplacement in the formation of the Permian Huangshandong Ni-Cu sulfide deposit, Xinjiang, Northwestern China. Econ Geol 108:1833–1848
Gu L, Xu K (1986) On the Carboniferous submarine massive sulphide deposits in the lower reaches of the Changjiang (Yangzi) River. Acta Geol Sin 2:64–106 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Gu L, Hu W, Ni P, He J, Xu Y, Lu J, Lin C (2003) New discussion on the South China-type massive sulphide deposits formed on continental crust. Geol J China Univ 9:592–608 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Guo W, Lu J, Jiang S, Zhang R, Qi L (2011) Re–Os isotope dating of pyrite from the footwall mineralization zone of the Xinqiao deposit, Tongling, Anhui Province: geochronological evidence for submarine exhalative sedimentation. Chin Sci Bull 56:3860–3865
Huang XW, Zhou MF, Qi L, Gao JF, Wang YW (2013) Re–Os isotopic ages of pyrite and chemical composition of magnetite from the Cihai magmatic-hydrothermal Fe deposit, NW China. Miner Depos 48:925–946
Huang X, Qi L, Meng Y (2014) Trace element geochemistry of magnetite from the Fe (–Cu) deposits in the Hami Region, Eastern Tianshan Orogenic Belt, NW China. Acta Geol Sin 88:176–195 (English Edition)
Huang XW, Gao JF, Qi L, Zhou MF (2015a) In-situ LA–ICP–MS trace elemental analyses of magnetite and Re–Os dating of pyrite: the Tianhu hydrothermally remobilized sedimentary Fe deposit, NW China. Ore Geol Rev 65:900–916
Huang XW, Zhou MF, Qiu YZ, Qi L (2015b) In-situ LA–ICP–MS trace elemental analyses of magnetite: the Bayan Obo Fe–REE–Nb deposit, North China. Ore Geol Rev 65:884–899
Huang X, Gao JF, Qi L, Meng YM, Wang YC, Dai ZH (2016) In-situ LA–ICP–MS trace elements analysis of magnetite: the Fenghuangshan Cu–Fe–Au deposit, Tongling, Eastern China. Ore Geol Rev 72:746–759
Huang XW, Zhou MF, Beaudoin G, Gao JF, Qi L, Lyu C (2018) Origin of the volcanic-hosted Yamansu Fe deposit, Eastern Tianshan, NW China: constraints from pyrite Re–Os isotopes, stable isotopes, and in-situ magnetite trace elements. Mineral Depos. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00126-018-0794-4
Ilton ES, Eugster HP (1989) Base metal exchange between magnetite and a chloride-rich hydrothermal fluid. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 53:291–301
Knipping JL, Bilenker LD, Simon AC, Reich M, Barra F, Deditius AP, Lundstrom C, Bindeman I, Munizaga R (2015a) Giant Kiruna-type deposits form by efficient flotation of magmatic magnetite suspensions. Geology 43:591–594
Knipping JL, Bilenker LD, Simon AC, Reich M, Barra F, Deditius AP, Wälle M, Heinrich CA, Holtz F, Munizaga R (2015b) Trace elements in magnetite from massive iron oxide-apatite deposits indicate a combined formation by igneous and magmatic-hydrothermal processes. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 171:15–38
Li H, Yang Z, Meng Y, Zeng P, Xu W (2004) Geological characteristics of massive sulfide deposits in Tongling ore concentration area, Anhui Province. Miner Depos 23:327–333 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Li Y, Li JW, Li XH, Selby D, Huang GH, Chen LJ, Zheng K (2016) A carbonate replacement origin for the Xinqiao stratabound massive sulfide deposit, Middle–Lower Yangtze metallogenic belt, China. Ore Geol Rev 80:985–1003
Li Y, Selby D, Li XH, Ottley CJ (2018) Multisourced metals enriched by magmatic-hydrothermal fluids in stratabound deposits of the Middle-Lower Yangtze River metallogenic belt, China. Geology
Liu Y, Liu Z (1991) Isotope geochemical research of blanket Cu (–Fe–S) deposit in Tongling region. Geological Publishing House, Beijing
Liu Y, Hu Z, Gao S, Günther D, Xu J, Gao C, Chen H (2008) In-situ analysis of major and trace elements of anhydrous minerals by LA–ICP–MS without applying an internal standard. Chem Geol 257:34–43
Liu PP, Zhou MF, Chen WT, Gao JF, Huang XW (2015) In-situ LA–ICP–MS trace elemental analyses of magnetite: Fe–Ti–V) oxide-bearing mafic-ultramafic layered intrusions of the Emeishan Large Igneous Province, SW China. Ore Geol Rev 65:853–871
Lu J (2008) A metallogenic model for the Dongguashan Cu-Au deposit of Tongling. Anhui Province Acta Pet Sin 24:1857–1864
Makvandi S, Ghasemzadeh-Barvarz M, Beaudoin G, Grunsky EC, McClenaghan MB, Duchesne C (2016) Principal component analysis of magnetite composition from volcanogenic massive sulfide deposits: case studies from the Izok Lake (Nunavut, Canada) and Halfmile Lake (New Brunswick, Canada) deposits. Ore Geol Rev 72:60–85
Mao J, Wang Y, Lehmann B, Yu J, Du A, Mei Y, Li Y, Zang W, Stein HJ, Zhou T (2006) Molybdenite Re–Os and albite 40Ar/39Ar dating of Cu–Au–Mo and magnetite porphyry systems in the Yangtze River valley and metallogenic implications. Ore Geol Rev 29:307–324
Mao J, Shao Y, Xie G, Zhang J, Chen Y (2009) Mineral deposit model for porphyry–skarn polymetallic copper deposits in Tongling ore dense district of Middle–Lower Yangtze Valley metallogenic belt. Miner Depos 28:109–119 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Mao J, Xie G, Duan C, Pirajno F, Ishiyama D, Chen Y (2011) A tectono-genetic model for porphyry–skarn–stratabound Cu–Au–Mo–Fe and magnetite-apatite deposits along the Middle-Lower Yangtze River Valley, Eastern China. Ore Geol Rev 43:294–314
McIntire WL (1963) Trace element partition coefficients—a review of theory and applications to geology. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 27:1209–1264
Meinert LD (1992) Skarns and skarn deposits. Geosci Can 19:145–162
Meng YM, Huang XW, Gao JF, Dai ZH, Liang QI (2016) Determination of trace elements in magnetite by laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma–mass spectrometry using multiple external standards without an internal standard calibration. Rock Miner Anal 35:585–594
Middelburg JJ, van der Weijden CH, Woittiez JR (1988) Chemical processes affecting the mobility of major, minor and trace elements during weathering of granitic rocks. Chem Geol 68:253–273
Milani L, Bolhar R, Cawthorn RG, Frei D (2017) In-situ LA–ICP–MS and EPMA trace element characterization of Fe–Ti oxides from the phoscorite-carbonatite association at Phalaborwa, South Africa. Miner Depos 52:747–768
Nadoll P, Koenig AE (2011) LA–ICP–MS of magnetite: methods and reference materials. J Anal At Spectrom 26:1872–1877
Nadoll P, Angerer T, Mauk JL, French D, Walshe J (2014) The chemistry of hydrothermal magnetite: a review. Ore Geol Rev 61:1–32
Nadoll P, Mauk JL, Leveille RA, Koenig AE (2015) Geochemistry of magnetite from porphyry Cu and skarn deposits in the southwestern United States. Miner Depos 50:493–515
Pan Y, Dong P (1999) The lower Changjiang (Yangzi/Yangtze River) metallogenic belt, east—central China: intrusion-and wall rock-hosted Cu–Fe–Au, Mo, Zn, Pb, Ag deposits. Ore Geol Rev 15:177–242
Pearce JA, Cann J (1973) Tectonic setting of basic volcanic rocks determined using trace element analyses. Earth Planet Sci Lett 19:290–300
Pisiak L, Canil D, Lacourse T, Plouffe A, Ferbey T (2017) Magnetite as an indicator mineral in the exploration of porphyry deposits: a case study in till near the Mount Polley Cu–Au deposit, British Columbia, Canada. Econ Geol 112:919–940
Rudnick RL, Gao S (2003) Composition of the continental crust. Treatise Geochem 3:659
Sun X, Zhu X, Tang H, Luan Y (2018) In-situ LA–ICP–MS trace element analysis of magnetite from the late Neoarchean Gongchangling BIFs NE China: constraints on the genesis of high-grade iron ore. Geol J 53:8–20. https://doi.org/10.1002/gj.3004
Tang Y, Wu Y, Cu G, Xing F, Wang Y, Cao F, Chang Y (1998) Copper gold polymetallic ore deposit geology in the region along Yangtze River in Anhui Province. Geological Publishing House, Beijing, pp 1–351
Toplis MJ, Corgne A (2002) An experimental study of element partitioning between magnetite, clinopyroxene and iron-bearing silicate liquids with particular emphasis on vanadium. Contrib Miner Petrol 144:22–37
Tosdal RM, Dilles JH, Cooke DR (2009) From source to sinks in auriferous magmatic-Hydrothermal porphyry and epithermal deposits. Elements 5:289–295
Wang Y-B, Liu D, Meng Y-F, Zeng P-S, Yang Z-S, Tian S-H (2004) SHRIMP U-Pb geochronology of the Xinqiao Cu–S–Fe–Au deposit in the Tongling ore district, Anhui. Chin Geol 2:169–173
Wang X, Peng S, Lai J, Yang B, Shao Y (2008) Relations between granite and mineralization in the Fenghuangshan copper-polymetallic deposit at Tongling, Anhui province. Geol Prospect 44:49–55
Wang S-W, Zhou T-F, Yuan F, Fan Y, Zhang L-J, Song Y-L (2015) Petrogenesis of Dongguashan skarn-porphyry Cu–Au deposit related intrusion in the Tongling district, eastern China: geochronological, mineralogical, geochemical and Hf isotopic evidence. Ore Geol Rev 64:53–70
Wang M, Wang W, Liu K, Michalak PP, Wei K, Hu M (2017) In-situ LA–ICP–MS trace elemental analyzes of magnetite: the Tieshan skarn Fe–Cu deposit, Eastern China. Chem Erde 77:169–181
Xiao X, Ni P (2000) Discussion of comparison of metallogeny for Sedex and sedimentary-rework base metal deposit. Contrib Geol Miner Resour Res 15:238–245 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Xie H, Wang W (1995) The metallogenic epoch and ore-forming materials source in the Xinqiao Cu–S deposit, Anhui province. Volcanol Miner Res 16:101–107 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Xie J, Yang X, Sun W, Du J, Xu W, Wu L, Wang K, Du X (2009) Geochronological and geochemical constraints on formation of the Tongling metal deposits, middle Yangtze metallogenic belt, east-central China. Int Geol Rev 51:388–421
Xu X (2004) U-Pb dating of zircons from quartz diorite and its enclaves at Tongguanshan in Anhui and its petrogenetic implication. Chin Sci Bull 49:2073
Xu G, Zhou J (2001) The Xinqiao Cu–S–Fe–Au deposit in the Tongling mineral district, China: synorogenic remobilization of a stratiform sulfide deposit. Ore Geol Rev 18:77–94
Xu W, Yang Z, Meng Y, Zeng P, Shi D, Tian S, Li H (2004) Genetic model and dynamic migration of ore-forming fluids in carboniferous exhalation-sedimentary massive sulfide deposits of Tongling district, Anhui Province. Miner Depos 23:353–363 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Yang B, Wang ZT (1985) The new type ore body found and deposit genetic model in Tongguanshan Cu deposit. Miner Depos 4:1–13 (in Chinese)
Yang D, Fu D, Wu N (1982) Genesis of pyrite type copper in Xinqiao and its neighboring region according to ore composition and structure. Issue Nanjing Inst Geol Miner Res Chin Acad Geol Sci 3:59–68 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zang W, Wu G, Zhang D, Liu A (2004) Xinqiao iron-deposit field in Tongling, Anhui: geologic and geochemical characteristics and genesis. Geotecton Metallog 28:187–193 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zang WS, Wu G, Zhang D, Zhang XX, Li J, Liu AH, Zhang ZY (2007) A preliminary discussion on genesis of Xinqiao S–Fe orefield. Miner Depos 26:464–474 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zeng P, Yang Z, Meng Y, Pei R, Wang Y, Wang X, Xu W, Tian S, Yao X (2004) Temporal-spatial configuration and mineralization of Yanshanian magmatic fluid systems in Tongling Ore concentration area, Anhui Province. Miner Depos 23:298–309 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zengqian H, Zhusen Y, Yifeng M, Pusheng Z, Hongyang L, Wenyi X (2007) Geological Fluid mapping in the Tongling Area: implications for the Paleozoic Submarine hydrothermal system in the Middle–Lower Yangtze metallogenic belt, East China. Acta Geol Sin 81:833–860 (English Edition)
Zhai Y, Yao S, Lin X, Jin F, Zhou X, Wan T, Zhou Z (1992) Metallogenic regularity of iron and copper deposits in the middle and lower valley of the Yangtze River. Miner Depos 11:1–12 (in Chinese)
Zhang Y, Shao Y-J, Wu C-D, Chen H-Y (2017a) LA–ICP–MS trace element geochemistry of garnets: constraints on hydrothermal fluid evolution and genesis of the Xinqiao Cu–S–Fe–Au deposit, Eastern China. Ore Geol Rev 86:426–439
Zhang Y, Shao Y-J, Li H-B, Liu Z-F (2017b) Genesis of the Xinqiao Cu–S–Fe–Au deposit in the Middle–Lower Yangtze River Valley metallogenic belt, Eastern China: constraints from U–Pb–Hf, Rb–Sr, S, and Pb isotopes. Ore Geol Rev 86:100–116
Zhang Y, Shao YJ, Chen HY, Liu ZF, Li DF (2017c) A hydrothermal origin for the large Xinqiao Cu–S–Fe deposit, Eastern China: evidence from sulfide geochemistry and sulfur isotopes. Ore Geol Rev 88:534–549
Zhang Y, Shao Y, Zhang R, Li D, Liu Z, Chen H (2018) Dating ore deposit using garnet U–Pb geochronology: example from the Xinqiao Cu–S–Fe–Au deposit, East China. Miner 8:31
Zhao WW, Zhou MF (2015) In-situ LA–ICP–MS trace elemental analyses of magnetite: the Mesozoic Tengtie skarn Fe deposit in the Nanling range, South China. Ore Geol Rev 65:872–883
Zhou T-F, Zhang L-J, Yuan F, Fan Y, Cooke D (2010) LA–ICP–MS in-situ trace element analysis of pyrite from the Xinqiao Cu–Au–S deposit in Tongling, Anhui, and its constraints on the ore genesis. Earth Sci Front 17:306–319 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by grants from the National Key R&D Program of China (2016YFC0600207), the Chinese 973 project (2012CB416804), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41503039), and the “CAS Hundred Talents” Project to J.F. Gao (Y5CJ038000). Zhihui Dai and Shaohua Dong are thanked for their LA–ICP–MS and SEM analyses. We also appreciate the field assistance of geologists from the Xinqiao deposit, especially Yixia Wang and Bobo Guo.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Gao, J., Huang, X. et al. Trace element composition of magnetite from the Xinqiao Fe–S(–Cu–Au) deposit, Tongling, Eastern China: constraints on fluid evolution and ore genesis. Acta Geochim 37, 639–654 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11631-018-0286-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11631-018-0286-3