Abstract
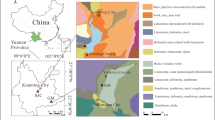
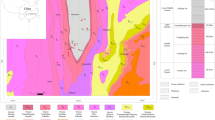
Major, trace and organic elements of a laterite profile developed on Neogene basalt on Hainan Island, South China were reported to investigate elements mobilization and redistribution in tropical regions. The results indicate that strong acid environment and organic matter (OM) can remarkably improve the transfer of insoluble elements. Among all the elements, Th is the least mobile. As for the general conservative elements during incipient chemical weathering, such as Ti, Zr, Hf and Nb, the removals are up to 30%–40% in the upper profile. And for Fe, Al, Cu and Ni, that tend to be combined with secondary minerals and to be retained in temperate zone, they are removed from the upper profile, transferred downwards, and then precipitated in the lower profile. In addition, atmospheric inputs, including sea salt aerosols and dust, have a profound effect on the budgets of elements that are susceptible to leaching losses (e.g. K, Na and Sr). Excluding the possibilities of groundwater and erosion, the remarkable increase of K, Na and Sr concentrations in the upper profile, together with dramatically upward increasing trends of the percentage changes of Sr/Th, K/Th and Na/Th ratios, show that atmospheric inputs, especially sea salt aerosols, contribute much extraneous seawater derived elements, such as K, Na and Sr to the soils. The overall elemental behaviors in this profile suggest that organic matter and atmospheric inputs play a very important role in the mobilization and redistribution of elements during extreme weathering in tropical regions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berner R.A. and Berner E.K. (1997) Silicate weathering and climate. In Tectonic Uplift and Climate Change (eds. Ruddiman W.F.) [M]. pp.353–365. Plenum Press, New York.
Braun J.J., Ngoupayou J.R.N., Viers J., Dupre B., Bedimo J.P.B., Boeglin J.L., Robain H., Nyeck B., Freydier R., and Nkamdjou L.S. (2005) Present weathering rates in a humid tropical watershed, Nsimi, South Cameroon [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta. 69, 357–387.
Braun J.J., Pagel M., Herbillon A., and Rosoin C. (1993) Mobilization and redistribution of Rees and Thorium in a syenitic lateritic profile a mass balance study [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta. 57, 4419–4434.
Chadwick O.A., Derry L.A., Vitousek P.M., Huebert B.J., and Hedin L.O. (1999) Changing sources of nutrients during four million years of ecosystem development [J]. Nature. 397, 491–497.
Chesworth W., Dejou J., and Larroque P. (1981) The weathering of basalt and relative mobilities of the major elements at Belbex, France [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta. 45, 1235–1243.
Chinese Soil Taxonomy Research Group (CST) (2001) Chinese Soil Taxonomy [M]. Science Press, Beijing, New York.
Cornu S., Lucas Y., Lebon E., Ambrosid J.P, Luizãoe F, Rouillerf J, Bonnayg M, and Nealh C. (1999) Evidence of titanium mobility in soil profiles, Manaus, central Amazonia [J]. Geoderma. 91, 281–295.
Cotton J., Le Dez A., Bau M., Caroff M., Maury R.C., Dulski P., Fourcade S., Bohn M., and Brousse R. (1995) Origin of anomalous rare-earth element and yttrium enrichments in subaerially exposed basalts: Evidence from French Polynesia [J]. Chemical Geology. 119, 115–138.
Dequincey O., Chabaux F., Clauer N., Sigmarsson O., Liewig N., and Leprun J.C. (2002) Chemical mobilizations in laterites: Evidence from trace elements and U-238-U-234-Th-230 disequilibria [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta. 66, 1197–1210.
Derry L.A. and Chadwick O.A. (2007) Contributions from earth’s atmosphere to soil [J]. Elements. 3, 333–338.
Dia A., Chauvel C., Bulourde M., and Gérard M. (2006) Eolian contribution to soils on Mount Cameroon: Isotopic and trace element records [J]. Chemical Geology. 226, 232–252.
Dupre B., Viers J., Dandurand J.L., Polve M., Bénézeth P., Vervier P., and Braun J.J. (1999) Major and trace elements associated with colloids in organic-rich river waters: Ultrafiltration of natural and spiked solutions [J]. Chemical Geology. 160, 63–80.
Gardner L.R. (1980) Mobilization of Al and Ti during rock weathering-isovolumetric geochemical evidence [J]. Chemical Geology. 30, 151–165.
Gardner L.R. (2000) Isovolumetric evidence for zirconium mobility during saprolite formation. Southeast [J]. Geology. 39, 117–128.
Gardner L.R., Kheoruenromme I., and Chen H.S. (1978) Isovolume-tric geochemical investigation of a buried granite saprolite near Columbia, SC, U.S.A [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta. 42, 417–424.
Gardner L.R., Kheoruenromme I., and Chen H.S. (1981) Geochemistry and mineralogy of an unusual diabase saprolite near Columbia, South Carolina [J]. Clays and Clay Minerals. 29, 184–190.
Ge Tongming, Chen Wenqi, Xu Xing, Li Daming, Fan Liming, Li Qi, Wen Siyu, and Wang Xi (1989) The geomagnetic polarity time scale of quaternary for Leizhou-Hainan region the K-Ar dating and palaomagnetic evidences from igneous rocks [J]. Acta Geophysical Sinica. 32, 550–558 (in Chinese).
Harnois L. (1988) The CIW index: a new chemical index of weathering [J]. Sediment Geology. 55, 319–322.
Hill I.G., Worden R.H., and Meighan I.G. (2000) Yttrium: the immobility-mobility transition during basaltic weathering [J]. Geology. 28, 923–926.
Huang Chengmin, Gong Zitong, and He Yurong (2004) Elemental geochemistry of a soil chronosequence on basalt on northern Hainan island, China [J]. Chinese Journal of Geochemistry. 23, 245–254.
Huang Zhenguo, Cai Fuxiang, and Han Zhongyuan (1993) Quaternary Volcano in Leizhou Peninsula and Hainan Island [M]. Science Press, Beijing (in Chinese).
Institute of Soil Science, Chinese Academy of Science (ISSCAS) (1978) Soil Physical and Chemical Analysis [M]. pp.143–150. Shanghai Science and Technology Press, Shanghai (in Chinese).
Kennedy M.J., Chadwick O.A., Vitousek P.M., Derry L.A., and Hendricks D.M. (1998) Changing sources of base cations during ecosystem development, Hawaiian Islands [J]. Geology. 26, 1015–1018.
Koppi A.J., Edis R., Field D.J., Geering H.R., Klessa D.A., and Cockayne D.J.H. (1996) Rare-earth element trends and cerium-uranium-manganese associations in weathered rock from Koongarra, northern territory, Australia [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta. 60, 1695–1707.
Kurtz A.C., Derry L.A., and Chadwick O.A. (2000) Refractory element mobility in volcanic soils [J]. Geology. 28, 683–686.
Kurtz A.C., Derry L.A., and Chadwick O.A. (2001) Accretion of Asian dust to Hawaiian soils: Isotopic, elemental, and mineral mass balances [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta. 65, 1971–1983.
Little M.G. and Aeolus Lee C.T. (2006) On the formation of an inverted weathering profile on Mount Kilimanjaro, Tanzania: buried paleosol or groundwater weathering [J]. Chemical Geology. 235, 205–221.
Ma Jinlong, Wei Gangjian, Xu Yigang, and Long Wenguo (2010) Variations of Sr-Nd-Hf isotopic systematics in basalt during intensive weathering [J]. Chemical Geology. 269, 376–385.
Melfi A.J., Subies F., Nahon D., and Formoso M.L.L. (1996) Zirconium mobility in bauxites of southern Brazil [J]. Journal of South American Earth Sciences. 9, 161–170.
Moore C.L. (1996) Processes of Chemical Weathering of Selected Cainozoic Eastern Australian Basalts [D]. Ph.D. Dissertation Thesis, Australian National University. pp.445. Canberra, A.C.T., Australia.
Nahon D. (2003) Weathering in tropical zone. Significance through ancient and still active mechanisms [J]. Comptes Rendus Geoscience. 335, 1109–1119.
Nahon D. and Merino E. (1996) Pseudomorphic replacement versus dilation in laterites: Petrographic evidence, mechanisms, and consequences for modelling [J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration. 57, 217–225.
Nesbitt H.W. (1979) Mobility and fractionation of rare-earth elements during weathering of granodiorite [J]. Nature. 279, 206–210.
Nesbitt H.W. and Markovics G. (1997) Weathering of granodioritic crust, long-term storage of elements in weathering profiles, and petrogenesis of siliciclastic sediments [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta. 61, 1653–1670.
Nesbitt H.W., Markovics G., and Price R.C. (1980) Chemical processes affecting alkalis and alkaline earths during continental weathering [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta. 44, 1659–1666.
Nesbitt H.W. and Wilson R.E. (1992) Recent chemical weathering of basalts [J]. American Journal of Science. 292, 740–777.
Nesbitt Y.W. and Young G.M. (1982) Early Proterozoic climates and plate motions inferred from major element chemistry of lutites [J]. Nature. 299, 715–717.
Nesbitt H.W., Young G.M., McLennan S.M., and Keays R.R. (1996) Effects of chemical weathering and sorting on the petrogenesis of siliciclastic sediments, with implications for provenance studies [J]. Journal of Geology. 104, 525–542.
Oliva P., Viers J., Dupre B., Fortune J.P, Martin F., Braun J.J., Nahon D., and Robain H. (1999) The effect of organic matter on chemical weathering: Study of a small tropical watershed: Nsimi-Zoetele site, Cameroon [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta. 63, 4013–4035.
Parker A. (1970) An index of weathering for silicate rocks [J]. Geology Magzine. 107, 501–504.
Patino L.C., Velbel M.A., Price J.R., and Wade J.A. (2003) Trace element mobility during spheroidal weathering of basalts and andesites in Hawaii and Guatemala [J]. Chemical Geology. 202, 343–364.
Price R.C., Gray C.M., Wilson R.E., Frey F.A., and Taylor S.R. (1991) The effects of weathering on rare-earth element, Y and Ba abundances in tertiary basalts from southeastern Australia [J]. Chemical Geology. 93, 245–265.
Quantin P., Balesdent J., Bouleau A., Delaune M., and Feller C. (1991) Premiers stades d’altération de ponces volcaniques en climat tropical humide (Montagne Pelée, Martinique) [J]. Geoderma. 50, 125–148.
Soil Survey Staff (1996) Soil survey laboratory methods manual. In Soil Survey Investigation Report No. 42 (version 3.0) [M]. pp.15–18. National Soil Survey Center, Lincoln, NE.
Soil Survey Staff (1999) Soil Taxonomy (second edition) [M]. pp.37–43. United States Department of Agriculture Handbook, Washington, DC.
Soil Survey Staff (2003) Keys to Soil Taxonomy (9th edition) [M]. United States Department of Agriculture, Natural Resources Conservation Service, Washington DC.
Stewart B.W., Capo R.C., and Chadwick O.A. (2001) Effects of rainfall on weathering rate, base cation provenance, and Sr isotope composition of Hawaiian soils [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta. 65, 1087–1099.
Viers J., Dupre B., Braun J.J., Deberdt S., Angeletti B., Ngoupayou J.N., and Michard A. (2000) Major and trace-element abundances, and strontium isotopes in the Nyong Basin rivers (Cameroon): Constraints on chemical weathering processes and elements transport mechanisms in humid tropical environments [J]. Chemical Geology. 169, 211–241.
Viers J., Dupre B., Polve M., Schott J., Dandurand J.L., and Braun J.J. (1997) Chemical weathering in the drainage basin of a tropical watershed (Nsimi-Zoetele site, Cameroon): Comparison between organic-poor and organic-rich waters [J]. Chemical Geology. 140(3–4), 181–206.
Wei Gangjian, Liu Ying, Li Xianhua, Shao Lei, and Fang Dianyong (2004) Major and trace element variations of the sediments at ODP Site 1144, South China Sea, during the last 230 ka and their paleoclimate implications [J]. Palaeogeogr. Palaeocl. 212, 331–342.
Windom H.L. (1976) Lithogeneous materials in marine sediments. In Chemical Oceanograpgy, vol. 5 (eds. Riley J.P. and Chester R.) [M]. pp.103–135. Academic Press, London, New York.
Young G.M. and Nesbitt H.W. (1998) Processes controlling the distribution of Ti and Al in weathering profiles, siliciclastic sediments and sedimentary rocks [J]. J. Sediment. Res. 68, 448–455.
Zabel M., Schneider R.R., Wagner T., Adegbie A.T., Vries U.D., and Kolonic S. (2001) Late Quaternary climate changes in central Africa as inferred from terrigenous input to the Niger fan [J]. Quaternary Research. 56, 207–217.
Zhang Ganlin, Pan Jihua, Huang Chengmin, and Gong Zitong (2007) Geochemical features of a soil chronosequence developed on basalt in Hainan Island, China [J]. Revista Mexicana de Ciencias Geologicas. 24, 261–269.
Zhu Weihuang, Yang Yuangen, Wu Fengchang, Bi Hua, and Liu Qiang (2006) Total concentrations and bioavailability of rare-earth elements in latesol in Hainan Province, China [J]. Chinese Journal of Geochemistry. 25, 76.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, J., Zhang, G. & Gong, Z. Mobilization and redistribution of elements in soils developed from extreme weathering basalt on Hainan Island. Chin. J. Geochem. 33, 262–271 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11631-014-0686-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11631-014-0686-y