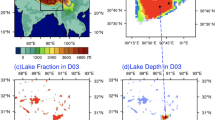
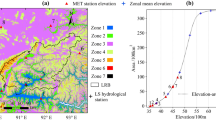
Abstract
There are numerous lakes on the Tibetan Plateau (TP), but the role of lake temperature in precipitation over the TP remains unclear. Here the Weather Research and Forecasting (WRF) model was used to detect the impact of lakes on summer rainfall. Three test cases were used to evaluate the effect of lakes surface temperature (LSTs) on precipitation variability. The three cases used different methods to determine initial LSTs, including using sea surface temperature data (SST), the WRF inland water module (avg_tsfc), and a lake model. Results show that when precipitation was stimulated over the TP, LSTs cannot be initialized using SST, which led to large discrepancies of precipitation. Compared with the simulations, the simulated precipitation were improved obviously with LSTs using avg_tsfc, indicating that LSTs have an considerable influence on determining precipitation over the TP. Due to a lack of observational data, the lake scheme does not improve on rainfall simulation, but does effectively simulate precipitation pattern over lakes, such as rainfall over the lakes was dominated by convection during the nighttime. Though the simulated precipitation using SST to initialize LSTs caused large discrepancies, it suggested that precipitation increase especially convective precipitation with increase in LSTs, which confirmed that the moisture from lakes cannot be neglected over the TP. Generally, it was necessary to monitor the LSTs for accurate weather and climate prediction over the TP.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bartunkova K, Sokol Z, Pop L (2014) Simulations of the influence of lake area on local temperature with the COSMO NWP model. Atmospheric Research 147: 51–67. DOI: 10.1016/j.atmosres.2014.05.003
Burnett AW, Kirby ME, Mullins HT, et al. (2003) Increasing Great Lake-effect snowfall during the twentieth century: A regional response to global warming? Journal of Climate 16: 3535–3542. DOI: 10.1175/1520-0442(2003)016
Che T, Li X, Jin R (2009) Monitoring the frozen duration of Qinghai Lake using satellite passive microwave remote sensing low frequency data. Chinese Science Bulletin 54: 2294–2299. DOI: 10.1007/s11434-009-0044-3
Chen F, Dudhia J (2001) Coupling an advanced land surfacehydrology model with the Penn State-NCAR MM5 modeling system. Part I: Model implementation and sensitivity. Monthly Weather Review 129: 569–585. DOI: 10.1175/1520-0493(2001)129
Chen W, Jiang Z, Li L (2011). Probabilistic Projections of Climate Change over China under the SRES A1B Scenario Using 28 AOGCMs. Journal of Climate 24: 4741–4756. DOI: 10.1175/2011jcli4102.1
Dudhia J (1989) Numerical study of convection observed during the winter monsoon experiment using a mesoscale twodimensional model. Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences 46: 3077–3107. DOI: 10.1175/1520-0469(1989)046
Fu G, Yu J, Yu X, et al. (2013) Temporal variation of extreme rainfall events in China, 1961-2009. Journal of Hydrology 487: 48–59. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2013.02.021
Gerken T, Biermann T, Babel W, et al. (2014) A modelling investigation into lake-breeze development and convection triggering in the Nam Co Lake basin, Tibetan Plateau. Theoretical and Applied Climatology 117: 149–167. DOI: 10.1007/s00704-013-0987-9
Gu H, Jin J, Wu Y, et al. (2015) Calibration and validation of lake surface temperature simulations with the coupled WRFlake model. Climatic Change 129: 471–483.
Gu H, Shen X, Jin J, et al. (2013) An application of a 1-D thermal diffusion lake model to Lake Taihu. Acta Meteorologica Sinica 71: 719–730.
Haginoya S, Fujii H, Kuwagata T, et al. (2009) Air-Lake Interaction Features Found in Heat and Water Exchanges over Nam Co on the Tibetan Plateau. Sola 5: 172–175. DOI: 10.2151/sola.2009-044
Hong SY, Lim J (2006) The WRF Single-Moment 6-Class Microphysics Scheme (WSM6). Asia-Pacific Journal of Atmospheric Sciences 42: 129–151.
Hong SY, Noh Y, Dudhia J (2006) A new vertical diffusion package with an explicit treatment of entrainment processes. Monthly Weather Review 134: 2318–2341. DOI: 10.1175/mwr3199.1
Kourzeneva E, Asensio H, Martin E, et al. (2012) Global gridded dataset of lake coverage and lake depth for use in numerical weather prediction and climate modelling. Tellus Series a-Dynamic Meteorology and Oceanography 64. DOI: 10.3402/tellusa.v64i0.15640
Li M, Ma Y, Hu Z, et al. (2009) Snow distribution over the Namco lake area of the Tibetan Plateau. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences 13: 2023–2030.
Li Z, Lyu S, Ao Y, et al. (2015) Long-term energy flux and radiation balance observations over Lake Ngoring, Tibetan Plateau. Atmospheric Research 155: 13–25. DOI: 10.1016/j.atmosres.2014.11.019
Liu M, Xu X, Sun AY, et al. (2015) Evaluation of high-resolution satellite rainfall products using rain gauge data over complex terrain in southwest China. Theoretical and Applied Climatology 119: 203–219. DOI: 10.1007/s00704-014-1092-4
Ma R, Yang G, Duan H, et al. (2011) China’s lakes at present: Number, area and spatial distribution. Science China-Earth Sciences 54: 283–289. DOI: 10.1007/s11430-010-4052-6
Mallard MS, Nolte CG, Bullock OR, et al. (2014) Using a coupled lake model with WRF for dynamical downscaling. Journal of Geophysical Research-Atmospheres 119: 7193–7208. DOI: 10.1002/2014jd021785
Maussion F, Scherer D, Finkelnburg R, et al. (2011) WRF simulation of a precipitation event over the Tibetan Plateau, China-an assessment using remote sensing and ground observations. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences 15: 1795–1817. DOI: 10.5194/hess-15-1795-2011
Maussion F, Scherer D, Moelg T, et al. (2014) Precipitation Seasonality and Variability over the Tibetan Plateau as Resolved by the High Asia Reanalysis. Journal of Climate 27: 1910–1927. DOI: 10.1175/jcli-d-13-00282.1
Mlawer EJ, Taubman SJ, Brown PD, et al. (1997) Radiative transfer for inhomogeneous atmospheres: RRTM, a validated correlated-k model for the longwave. Journal of Geophysical Research-Atmospheres 102: 16663–16682. DOI: 10.1029/97jd00237
Norton DC, Bolsenga SJ (1993) Spatiotemporal trends in lake effect and continental snowfall in the laurentian great-lakes, 1951-1980. Journal of Climate 6: 1943–1956. DOI: 10.1175/1520-0442(1993)006
Notaro M, Holman K, Zarrin A, et al. (2013) Influence of the Laurentian Great Lakes on Regional Climate. Journal of Climate 26: 789–804. DOI: 10.1175/jcli-d-12-00140.1
Onton DJ, Steenburgh WJA (2001) Diagnostic and sensitivity studies of the 7 December 1998 Great Salt Lake-effect snowstorm. Monthly Weather Review 129: 1318–1338. DOI: 10.1175/1520-0493(2001)129
Subin ZM, Riley WJ, Mironov D (2012) An improved lake model for climate simulations: Model structure, evaluation, and sensitivity analyses in CESM1. Journal of Advances in Modeling Earth Systems 4. DOI: 10.1029/2011ms000072
Tian L, Masson-Delmotte V, Stievenard M, et al. (2001) Tibetan Plateau summer monsoon northward extent revealed by measurements of water stable isotopes. Journal of Geophysical Research-Atmospheres 106: 28081–28088. DOI: 10.1029/2001jd900186
Tong K, Su F, Yang D, et al. (2014) Evaluation of satellite precipitation retrievals and their potential utilities in hydrologic modeling over the Tibetan Plateau. Journal of Hydrology 519: 423–437. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2014.07.044
Wang C, Shi H, Hu H, et al. (2015) Properties of cloud and precipitation over the Tibetan Plateau. Advances in Atmospheric Sciences 32: 1504–1516. DOI: 10.1007/s00376-015-4254-0
Xu Y, Kang S, Zhang Y, et al. (2011) A method for estimating the contribution of evaporative vapor from Nam Co to local atmospheric vapor based on stable isotopes of water bodies. Chinese Science Bulletin 56: 1511–1517. DOI: 10.1007/s11434-011-4467-2
Yang K, Wu H, Qin J, et al. (2014) Recent climate changes over the Tibetan Plateau and their impacts on energy and water cycle: A review. Global and Planetary Change 112: 79–91. DOI: 10.1016/j.gloplacha.2013.12.001
You QL, Min JZ, Zhang W, et al. (2015) Comparison of multiple datasets with gridded precipitation observations over the Tibetan Plateau. Climate Dynamics 45: 791–806. DOI: 10.1007/s00382-014-2310-6
Zhang C, Wang Y, Hamilton K (2011) Improved Representation of Boundary Layer Clouds over the Southeast Pacific in ARWWRF Using a Modified Tiedtke Cumulus Parameterization Scheme. Monthly Weather Review 139: 3489–3513. DOI: 10.1175/mwr-d-10-05091.1
Zhao L, Jin J, Wang SY, et al. (2012) Integration of remotesensing data with WRF to improve lake-effect precipitation simulations over the Great Lakes region. Journal of Geophysical Research-Atmospheres 117. DOI: 10.1029/2011jd016979
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
http://orcid.org/0000-0001-6501-5105
http://orcid.org/0000-0002-3040-2073
http://orcid.org/0000-0003-2031-2370
http://orcid.org/0000-0002-6175-3036
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, X., Duan, Kq., Shi, Ph. et al. Effect of lake surface temperature on the summer precipitation over the Tibetan Plateau. J. Mt. Sci. 13, 802–810 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-015-3743-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-015-3743-z