Abstract
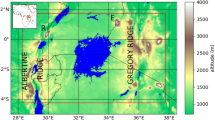
This paper uses the cloud resolving Active Tracer High-resolution Atmospheric Model coupled to the interactive surface model Hybrid in order to investigate the diurnal development of a lake-breeze system at the Nam Co Lake on the Tibetan Plateau. Simulations with several background wind speeds are conducted, and the interaction of the lake breeze with topography and background wind in triggering moist and deep convection is studied. The model is able to adequately simulate the systems most important dynamical features such as turbulent surface fluxes and the development of a lake breeze for the different wind conditions. We identify two different mechanisms for convection triggering that are dependent on the direction of the background wind: triggering over topography, when the background wind and the lake breeze have the same flow direction, and triggering due to convergence between the lake-breeze front and the background wind. Our research also suggests that precipitation measurements at the centre of the basins on the Tibetan Plateau are not representative for the basin as a whole as precipitation is expected to occur mainly in the vicinity of the topography.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antonelli M, Rotunno R (2007) Large-eddy simulation of the onset of the sea breeze. J Atmos Sci 64(12): 4445–4457. doi:10.1175/2007JAS2261.1
Banta RM (1990) The role of mountain flows in making clouds. In: Blumen W (ed) Atmospheric processes over complex terrain, no. 23 in meteorological monographs. American Meteorological Society, Boston, pp 229–283
Banta RM, Barker Schaaf C (1987) Thunderstorm genesis zones in the Colorado Rocky Mountains as determined by traceback of geosynchronous satellite images. Mon Weather Rev 115(2):463–476. doi:10.1175/1520-0493(1987)115<0463:TGZITC>2.0.CO;2
Biermann T, Babel W, Ma W, Chen X, Thiem E, Ma Y, Foken T (2013) Turbulent flux observations and modelling over a shallow lake and a wet grassland in the Nam Co basin, Tibetan Plateau. Theor Appl Climatol. doi:10.1007/s00704-013-0953-6
Chen SH, Lin YL (2005) Effects of moist froude number and CAPE on a conditionally unstable flow over a mesoscale mountain ridge. J Atmos Sci 62(2):331–350. doi:10.1175/JAS-3380.1
Chu CM, Lin YL (2000) Effects of orography on the generation and propagation of mesoscale convective systems in a two-dimensional conditionally unstable flow. J Atmos Sci 57(23):3817–3837. doi:10.1175/1520-0469(2001)057<3817:EOOOTG>2.0.CO;2
Crosman ET, Horel JD (2010) Sea and lake breezes: a review of numerical studies. Bound-Layer Meteorol 137(1):1–29. doi:10.1007/s10546-010-9517-9
Cui X, Graf HF (2009) Recent land cover changes on the Tibetan Plateau: a review. Clim Chang 94(1):47–61. doi:10.1007/s10584-009-9556-8
Cui X, Graf HF, Langmann B, Chen W, Huang R (2006) Climate impacts of anthropogenic land use changes on the Tibetan Plateau. Glob Plan Change 54(1–2):33–56. doi:10.1016/j.gloplacha.2005.07.006
Cui X, Graf HF, Langmann B, Chen W, Huang R (2007a) Hydrological impacts of deforestation on the Southeast Tibetan Plateau. Earth Interact 11(15):1–18. doi:10.1175/EI223.1
Cui X, Langmann B, Graf HF (2007b) Summer monsoonal rainfall simulation on the Tibetan Plateau with a regional climate model using a one-way double-nesting system. SOLA 3:49–52
Emanuel KA (1994) Atmospheric convection. Oxford University Press, New York
Fairall CW, Bradley EF, Godfrey JS, Wick GA, Edson JB, Young GS (1996a) Cool-skin and warm-layer effects on sea surface temperature. J Geophys Res 101(C1):1295–1308
Fairall CW, Bradley EF, Rogers DP, Edson JB, Young GS (1996b) Bulk parameterization of air-sea fluxes for Tropical Ocean-Global Atmosphere Coupled-Ocean Atmosphere Response Experiment. J Geophys Res 101(C2):3747–3764
Foken T (2008a) The energy balance closure problem: an overview. Ecol Appl 18:1351–1367
Foken T (2008b) Micrometeorology. Springer, Heidelberg
Foken T, Aubinet M, Finnigan JJ, Leclerc MY, Mauder M, Paw UKT (2011) Results of a panel discussion about the energy balance closure correction for trace gases. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 92(4): ES13–ES18. doi:10.1175/2011BAMS3130.1
Foken T, Leuning R, Oncley SR, Mauder M, Aubinet M (2012) Corrections and data quality control. In: Aubinet M, Vesala T, Papale D (eds) Eddy covariance: a practical guide to measurement and data analysis. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 85–131
Friend AD, Kiang NY (2005) Land surface model development for the GISS GCM: effects of improved canopy physiology on simulated climate. J Clim 18(15):2883–2902. doi:10.1175/JCLI3425.1
Friend AD, Stevens AK, Knox RG, Cannell MGR (1997) A process-based, terrestrial biosphere model of ecosystem dynamics (Hybrid v3.0). Ecol Model 95(2–3):249–287. doi:10.1016/S0304-3800(96)00034-8
Gao Y, Tang M, Luo S, Shen Z, Li C (1981) Some aspects of recent research on the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau meteorology. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 62(1): 31–35. doi:10.1175/1520-0477(1981)062<0031:SAORRO>2.0.CO;2
Gerken T, Babel W, Hoffmann A, Biermann T, Herzog M, Friend AD, Li M, Ma Y, Foken T, Graf HF (2012) Turbulent flux modelling with a simple 2-layer soil model and extrapolated surface temperature applied at Nam Co Lake basin on the Tibetan Plateau. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 16(4):1095–1110. doi:10.5194/hess-16-1095-2012
Gochis DJ, Jimenez A, Watts CJ, Garatuza-Payan J, Shuttleworth WJ (2004) Analysis of 2002 and 2003 warm-season precipitation from the North American Monsoon Experiment Event Rain Gauge Network. Mon Weather Rev 132(12):2938–2953. doi:10.1175/MWR2838.1
Graf HF, Herzog M, Oberhuber JM, Textor C (1999) Effect of environmental conditions on volcanic plume rise. J Geophys Res 104(D20):24,309–24,320. doi:10.1029/1999JD900498
Guo H, Penner J, Herzog M (2004) Comparison of the vertical velocity used to calculate the cloud droplet number concentration in a cloud-resolving and a global climate model. In: Carrothers D (ed) Fourteenth ARM science team meeting proceedings. Department of Energy, Boston, pp 1–6
Herzog M, Graf HF, Textor C, Oberhuber JM (1998) The effect of phase changes of water on the development of volcanic plumes. J Volcanol Geotherm Res 87(1–4):55–74. doi:10.1016/S0377-0273(98)00100-0
Herzog M, Oberhuber JM, Graf HF (2003) A prognostic turbulence scheme for the nonhydrostatic plume model ATHAM. J Atmos Sci 60(22):2783–2796. doi:10.1175/1520-0469(2003)060<2783:APTSFT>2.0.CO;2
Immerzeel WW, van Beek LPH, Bierkens MFP (2010) Climate change will affect the Asian water towers. Science 328(5984):1382–1385. doi:10.1126/science.1183188
Kirshbaum DJ (2011) Cloud-resolving simulations of deep convection over a heated mountain. J Atmos Sci 68(2):361–378. doi:10.1175/2010JAS3642.1
Kirshbaum DJ, Durran DR (2004) Factors governing cellular convection in orographic precipitation. J Atmos Sci 61(6):682–698. doi:10.1175/1520-0469(2004)061<0682:FGCCIO>2.0.CO;2
Kurita N, Yamada H (2008) The role of local moisture recycling evaluated using stable isotope data from over the middle of the Tibetan Plateau during the monsoon season. J Hydrometeorol 9(4):760–775. doi:10.1175/2007JHM945.1
Kurosaki Y, Kimura F (2002) Relationship between topography and daytime cloud activity around Tibetan Plateau. J Meteorol Soc Jpn 80(6):1339–1355
Kuwagata T, Kondo J, Sumioka M (1994) Thermal effect of the sea breeze on the structure of the boundary layer and the heat budget over land. Bound-Layer Meteorol 67(1–2):119–144. doi:10.1007/BF00705510
Kuwagata T, Numaguti A, Endo N (2001) Diurnal variation of water vapor over the central Tibetan Plateau during summer. J Meteorol Soc Jpn 79(1B):401–418. doi:10.2151/jmsj.79.401
Langmann B, Herzog M, Graf HF (1998) Radiative forcing of climate by sulfate aerosols as determined by a regional circulation chemistry transport model. Atmos Environ 32(16):2757–2768. doi:10.1016/S1352-2310(98)00028-4
Liu WT, Katsaros KB, Businger JA (1979) Bulk parameterization of air-sea exchanges of heat and water vapor including the molecular constraints at the interface. J Atmos Sci 36(9):1722–1735. doi:10.1175/1520-0469(1979)036<1722:BPOASE>2.0.CO;2
Ma L, Zhang T, Li Q, Frauenfeld OW, Qin D (2008) Evaluation of ERA-40, NCEP-1, and NCEP-2 reanalysis air temperatures with ground-based measurements in China. J Geophys Res 113(D15):115. doi:10.1029/2007JD009549
Ma Y, Wang Y, Wu R, Hu Z, Yang K, Li M, Ma W, Zhong L, Sun F, Chen X, et al (2009) Recent advances on the study of atmosphere-land interaction observations on the Tibetan Plateau. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 13(7):1103–1111. doi:10.5194/hess-13-1103-2009
Mauder M, Foken T (2004) Documentation and instruction manual of the eddy covariance software package TK2. Arbeitsergebnisse 26, University of Bayreuth, Bayreuth. http://opus.ub.uni-bayreuth.de/opus4-ubbayreuth/frontdoor/index/index/docId/639
Mauder M, Foken T (2011) Documentation and instruction manual of the eddy covariance software package TK3, Arbeitsergebnisse 46, University of Bayreuth, Bayreuth. http://opus.ub.uni-bayreuth.de/opus4-ubbayreuth/frontdoor/index/index/docId/681
Maussion F, Scherer D, Finkelnburg R, Richters J, Yang W, Yao T (2011) WRF simulation of a precipitation event over the Tibetan Plateau, China — an assessment using remote sensing and ground observations. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 15(6):1795–1817
Miao JF, Kroon LJM, Vila-Guerau de Arellano J, Holtslag AAM (2003) Impacts of topography and land degradation on the sea breeze over eastern Spain. Meteorol Atmos Phys 84(3–4):157–170. doi:10.1007/s00703-002-0579-1
Miglietta MM, Rotunno R (2009) Numerical simulations of conditionally unstable flows over a mountain ridge. J Atmos Sci 66(7):1865–1885. doi:10.1175/2009JAS2902.1
Miller STK, Keim BD, Talbot RW, Mao H (2003) Sea breeze: structure, forcasting and impacts. Rev Geophys 41(3):1011. doi:10.1029/2003RG000124
Mlawer EJ, Taubman SJ, Brown PD, Iacono MJ, Clough SA (1997) Radiative transfer for inhomogeneous atmospheres: RRTM, a validated correlated-k model for the longwave. J Geophys Res 102(D14):16,663–16,682
Oberhuber JM, Herzog M, Graf HF, Schwanke K (1998) Volcanic plume simulation on large scales. J Volcanol Geotherm Res 87(1–4):29–53. doi:10.1016/S0377-0273(98)00099-7
Ookouchi Y, Uryu M, Sawada R (1978) A numerical study on the effects of a mountain on the land and sea breezes. J Meteorol Soc Jpn 56:368–386
Petch JC (2004) The predictability of deep convection in cloud-resolving simulations over land. QJR Meteorol Soc 130(604):3173–3187. doi:10.1256/qj.03.107
Petch JC (2006) Sensitivity studies of developing convection in a cloud-resolving model. QJR Meteorol Soc 132(615):345–358. doi:10.1256/qj.05.71
Rampanelli G, Zardi D, Rotunno R (2004) Mechanisms of up-valley winds. J Atmos Sci 61(24):3097–3111. doi:10.1175/JAS-3354.1
Rebmann C, Kolle O, Heinesch B, Queck R, Ibrom A, Aubinet M (2012) Data acquisition and flux calculations. In: Aubinet M, Vesala T, Papale D (eds) Eddy covariance: a practical guide to measurement and data analysis. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 59–83
Reeves HD, Lin YL (2007) The effects of a mountain on the propagation of a preexisting convective system for blocked and unblocked flow regimes. J Atmos Sci 64(7):2401–2421. doi:10.1175/JAS3959.1
Tanaka K, Tamagawa I, Ishikawa H, Ma Y, Hu Z (2003) Surface energy budget and closure of the eastern Tibetan Plateau during the GAME-Tibet IOP 1998. J Hydrometeorol 283(1–4):169–183. doi:10.1016/S0022-1694(03)00243-9
Taniguchi K, Koike T (2008) Seasonal variation of cloud activity and atmospheric profiles over the eastern part of the Tibetan Plateau. J Geophys Res 113(D10):104. doi:10.1029/2007JD009321
Tian L, Masson-Delmotte V, Stievenard M, Yao T, Jouzel J (2001a) Tibetan Plateau summer monsoon northward extent revealed by measurements of water stable isotopes. J Geophys Res 106(D22):28,081–28,088.
Tian L, Yao T, Numaguti A, Sun W (2001b) Stable isotope variations in monsoon precipitation on the Tibetan Plateau. J Meteorol Soc Jpn 79(5):959–966. doi:10.2151/jmsj.79.959
Trentmann J, Luderer G, Winterrath T, Fromm MD, Servranckx R, Textor C, Herzog M, Graf HF, Andreae MO (2006) Modeling of biomass smoke injection into the lower stratosphere by a large forest fire (Part I): reference simulation. Atmos Chem Phys 6(12):5247–5260
Twine TE, Kustas WP, Norman JM, Cook DR, Houser PR, Meyers TP, Prueger JH, Starks PJ, Wesely ML (2000) Correcting eddy-covariance flux underestimates over a grassland. Agric Forest Meteorol 103(3):279–300. doi:10.1016/S0168-1923(00)00123-4
Wang J, Zhu L, Daut G, Ju J, Lin X, Wang Y, Zhen X (2009) Investigation of bathymetry and water quality of Lake Nam Co, the largest lake on the central Tibetan Plateau, China. Limnology 10(2):149–158. doi:10.1007/s10201-009-0266-8
Wu CM, Stevens B, Arakawa A (2009) What controls the transition from shallow to deep convection. J Atmos Sci 66(6):1793–1806. doi:10.1175/2008JAS2945.1
Xu ZX, Gong TL, Li JY (2008) Decadal trend of climate in the Tibetan Plateau—regional temperature and precipitation. Hydrol Process 22(16):3056–3065. doi:10.1002/hyp.6892
Yanai M, Li C, Song Z (1992) Seasonal heating of the Tibetan Plateau and its effects on the evolution of the Asian summer monsoon. J Meteorol Soc Jpn 70(1B):319–351
Yang K, Koike T, Fujii H, Tamura T, Xu X, Bian L, Zhou M (2004) The daytime evolution of the atmospheric boundary layer and convection over the Tibetan Plateau: observations and simulations. J Meteorol Soc Jpn 82(6):1777–1792. doi:10.2151/jmsj.82.1777
Yang K, Ye B, Zhou D, Wu B, Foken T, Qin J, Zhou Z (2011) Response of hydrological cycle to recent climate changes in the tibetan plateau. Clim Change 109(3–4):517–534. doi:10.1007/s10584-011-0099-4
Yatagai A (2001) Estimation of precipitable water and relative humidity over the Tibetan Plateau from GMS-5 water vapor channel data. J Meteorol Soc Jpn 79(1B):589–598
Yin ZY, Zhang X, Liu X, Colella M, Chen X (2008) An assessment of the biases of satellite rainfall estimates over the Tibetan Plateau and correction methods based on topographic analysis. J Hydrometeorol 9(3):301–326. doi:10.1175/2007JHM903.1
Acknowledgments
This research was funded by the German Research Foundation (DFG) Priority Programme 1372 “Tibetan Plateau: Formation, Climate, Ecosystems” as part of the Atmosphere–Ecology–Glaciology–Cluster (TiP-AEG): FO 226/18-1,2. The work described in this publication has been supported by the European Commission (Call FP7-ENV-2007-1 grant no. 212921) as part of the CEOP-AEGIS project (http://www.ceop-aegis.org/) coordinated by the University of Strasbourg. The authors wish to acknowledge Esri ArcGIS, the Microsoft Corporation, Harris Corp. and Earthstar Geographics LLC for the provision of map data of the Nam Co Lake. The landcover map was produced by Sophie Biskop and Jan Kropacek within the framework of DFG-TiP. MODIS images were provided through AERONET, and we thank the MODIS team for their work. GFS-FNL data were produced by the National Center for Environmental Prediction.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gerken, T., Biermann, T., Babel, W. et al. A modelling investigation into lake-breeze development and convection triggering in the Nam Co Lake basin, Tibetan Plateau. Theor Appl Climatol 117, 149–167 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-013-0987-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-013-0987-9