Abstract
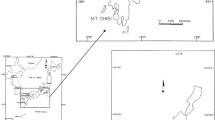
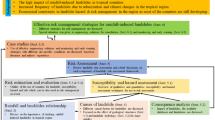
Unsaturated shallow soil deposits may be affected by either superficial soil erosion or shallow landslides in adjacent or overlapping source areas and in different seasons when a different soil suction exists. The triggering analysis of both these processes is a relevant issue for the hazard analysis while the literature mostly provides specific approaches for erosion or for landslides. The paper proposes a large-area analysis for a case study of Southern Italy, consisting of unsaturated shallow deposits of loose pyroclastic (air-fall) volcanic soils that have been repeatedly affected by erosion and landslides in special seasons. For a past catastrophic event, the simulated source areas of shallow landslides are smaller than those observed in the field while the simulated eroded areas with thickness greater than 5 cm are comparable with the in-situ evidences, if the analysis takes into account high rainfall intensity and a spatially variable soil cover use. More in general, the results of the paper are consistent with the previous literature and also provide a methodological contribution about the application of distinct tools over large area. The added value is that the paper shows how the combination of distinct large-area analyses may help with understanding the dominant slope instability mechanisms. Only once this goal is fully achieved, can specific physically-based analyses be confidently performed at detailed scales and for smaller specific areas.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acharya G, Cochrane T, Davies T, Bowman E (2011) Quantifying and modeling postfailure sediment yields from laboratoryscale soil erosion and shallow landslide experiments with silty loess. Geomorphology 129: 49–58. DOI: 10.1016/j.geomorph. 2011.01.012.
Autorità di Bacino Destra Sele (2012) Available online at: http://www.autoritabacinodestrasele.it/Caccessed on 2013-02-05)
Baum RL, Savage WZ, Godt JW (2008) TRIGRS-A Fortran program for transient rainfall infiltration and grid-based regional slope-stability analysis, version 2.0. US Geological Survey Open-File Report 2008-1159. Available online at: http://pubs.usgs.gov/of/2008/1159/(accessed on 2012-01-10)
Bilotta E, Cascini L, Foresta V, et al. (2005) Geotechnical characterization of pyroclastic soils involved in huge flowslides. Geotech Geol Eng 23: 365–402. DOI: 10.1007/ s10706-004-1607-3
Calvello M, Cascini L, Cuomo S, et al. (2012) Applicazione dei metodi di base ed intermedi all’areale delle piroclastiti (Application of basic and intermediate methods to the district of pyroclastic soils). In Criteri di zonazione della suscettibilità e della pericolosità da frane innescate da eventi estremi (piogge e sisma), Composervice S.r.l, Padova, Italy. pp 119–130 (In Italian)
Calvello M, Cascini L, Mastroianni S (2013) Landslide zoning over large areas from a sample inventory by means of scaledependent terrain units. Geomorphology: 33–48. DOI: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2012.10.026
Cascini L, Cuomo S, Guida D (2008) Typical source areas of May 1998 flow-like mass movements in the Campania region, southern Italy. Engineering Geolology 96: 107–125. DOI: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2007.10.003
Cascini L, Cuomo S, Pastor M (2013a) Inception of debris avalanches: remarks on geomechanical modelling. Landslides 10(6): 701–711. DOI: 10.1007/s10346-012-0366-0
Cascini L, Cuomo S, Pastor M, Sacco C (2013b) Modelling the post-failure stage of rainfall-induced landslides of the flowtype. Canadian Geotechnical Journal 50(9): 924–934. DOI: 10.1139/cgj-2012-0375.
Cascini L, Cuomo S, Pastor M, et al. (2010) Modelling of rainfall-induced shallow landslides of the flow-type. ASCE’s Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 136(1): 85–98. DOI: 10.1061/(ASCE)GT.1943-5606.0000182
Cascini L, Sorbino G, Cuomo S, et al. (2014). Seasonal effects of rainfall on the shallow pyroclastic deposits of the Campania region (southern Italy). Landslides 11(5): 779–792. DOI: 10.1007/s10346-013-0395-3
Cascini L, Cuomo S, Ferlisi S, et al. (2009) Detection of mechanisms for destructive landslides in Campania regionsouthern Italy. In: Picarelli L, Tommasi P, Urciuoli G, et al. (Eds.), Rainfall-induced landslides: mechanisms, monitoring techniques and nowcasting models for early warning systems. Proceedings of the first Italian Workshop on Landslides, 8-10 June 2009 Naples, Italy. Studio Editoriale Doppia voce, Naples, Italy. vol 1, pp 43–51.
Chen, HX, Zhang, LM (2014) A physically-based distributed cell model for predicting regional rainfall-induced slope failures. Engineering Geology 176: 79–92. DOI: 10.1016/j.enggeo. 2014.04.011
Corine Land Cover IV livello (2006) Available online at: http://www.sinanet.isprambiente.it/it/sia-ispra/downloadmais/ corine-land-cover. (accessed on 2013-02-05)
Cruden DM, Varnes DJ (1996) Landslide Types and Processes. In: Landslides Investigation and Mitigation, Turner AK and Schuster RL (eds.), Transportation Research Board, Special report no. 247, National Research Council, National Academy Press, Washington DC, USA. pp 36–75.
Cuomo S, Della Sala M (2013) Rainfall-induced infiltration, runoff and failure in steep unsaturated shallow soil deposits. Engineering Geology 162: 118–127. DOI: 10.1016/j.enggeo. 2013.05.010.
Cuomo S, Della Sala M, Novità A (2015) Physically-based modeling of soil erosion induced by rainfall in small mountain basins. Geomorphology 243: 106–115, DOI: 10.1016/j.geomorph. 2015.04.019.
De Falco M (2011) Approcci innovativi per l’identificazione del degrado per erosione idrica in ambienti agro-forestali mediterranei (Innovative approaches for the identification of soil degradation due to erosion in Mediterranean sites). PhD dissertation. University Federico II of Naples, Italy. p 294. (In Italian)
De Luca C, Furcolo P, Rossi F, et al. (2010) Extreme rainfall in the Mediterranean. Proc. Intern. Workshop on "Advances in statistical hydrology", STAHY 2010, Taormina, Italy, May 23-25, 2010. p 11. Available online at: http://www. risorseidriche.dica.unict.it/Sito_STAHY2010_web/proceedin gs.htm(accessed on 2013-03-10)
Della Sala M (2014) Genesis and mechanisms of rainfallinduced hyperconcentrated flows in granular soils. PhD dissertation at the University of Salerno, Fisciano Italy. p 258.
Esposito E, Porfido S, Violante C, et al. (2003) Disaster induced by historical floods in a selected coastal area (Southern Italy). In: Thorndy VR, Benito G, Barr Iendos M, et al. (eds.), Proceedings of the PHEFRA (Palaeofloods, Historical Data and Climatic Variability), International Workshop, Barcelona. CSIC-Centro de CienciasMedioambientales Serrano, Madrid, Spain. pp 143–148.
Fell R, Corominas J, Bonnard C, et al. (2008) Guidelines for landslide susceptibility, hazard and risk zoning for land use planning. Engineering Geolology 102(3-4): 85–98. DOI: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2008.03.022.
Foster GR (1982) Modeling the erosion process. In: Haan CT, Johnson HP, Brakensiek DL (eds.), Hydrologic modeling of small watersheds. American Society of Agricultural Engineers Monograph, pp 297–380.
Fredlund DG, Morgenstern NR, Widger RA (1978) The shear strength of unsaturated soils. Canadian Geotechnical Journal 15(3): 313–321. DOI: 10.1139/t78-029
Frosini P (1955) Il nubifragio di Salerno del 25-26 Ottobre 1954 (The 25th -26th October 1954 rainstorm in Salerno). Giornale Genio Civile (Journal of Civil Engineering) 3-4: 179–188. (In Italian)
Guadagno FM, Forte R, Revellino P, et al. (2005) Some aspects of the initiation of debris avalanches in the Campania Region: the role of morphological slope discontinuities and the development of failure. Geomorphology 66: 237–254. DOI: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2004.09.024
Hessel R, Jetten VG (2007) Suitability of transport equations in modelling soil erosion for a small loess plateau catchment. Engineering Geology 91(1): 56–71. DOI: 10.1016/j.enggeo. 2006.12.013
Hu MJ, Pan HL, Wei HZ, et al. (2013) Landslides & debris flows formation from gravelly soil surface erosion and particle losses in Jiangjia Ravine. Journal of Mountain Science 10(6): 987–995. DOI: 10.1007/s11629-012-2526-z.
Hutchinson JN (1988) In: Bonnard C (ed.), Morphological and geotechnical parameters of landslides in relation to geology and hydrogeology. State of the art report, vol 1. Proceedings of the 5th International Symposium on Landslides, Lausanne, Switzerland. pp 3–35.
Hutchinson JN (2004) Review of flow-like mass movements in granular and fine-grained materials. Proc. of the Int. Workshop "Flows 2003 -Occurrence and Mechanisms of Flows in Natural Slopes and Earthfill". pp 3–16.
Iverson RM (2000) Landslide triggering by rain infiltration. Water Resource Research 36(7): 1897–1910.
Jain M K, Kothyari U C (2000) Estimation of soil erosion and sediment yield using GIS. Hydrological Sciences Journal 45(5): 771–786. DOI: 10.1029/2000WR900090
Li XS, Wu BF, Zhang L (2013) Dynamic monitoring of soil erosion for upper stream of Miyun Reservoir in the last 30 years. Journal of Mountain Science 10(5): 801–811. DOI: 10.1007/s11629-013-2559-y.
Merritt WS, Latcher RA, Jakeman AJ (2003) A review of erosion and sediment transport models. Environmental Modelling and Software 18: 761–799. DOI: 10.1016/S1364-8152(03)00078-1
Moore ID, Burch GJ (1986) Modeling erosion and deposition: Topographics effects. Transaction ASAE 29: 1624–1640. DOI: 10.13031/2013.30363
Rahardjo H, Lee TT, Leong EC, et al. (2004) A flume for assessing flux boundary characteristics in rainfall-induced slope failure studies. Geotechnical Testing Journal 27 (2): 145–153.
Richards LA (1931) Capillary conductions of liquids through porous mediums. Journal of Applied Physics 1: 318–333.
Savage WZ, Godt JW, Baum RL (2004) Modeling timedependent areal slope stability. In: Lacerda WA, 582 Erlich M, Fontoura SAB, Sayao ASF (eds.), Landslides-evaluation and stabilization. Proceedings of 9th International symposium on Landslides. Balkema Editor, Rotterdam, The Netherlands. Vol 1, pp 23–36.
Sorbino G, Foresta V (2002) Unsaturated hydraulic characteristics of pyroclastic soils. In: Jucà JFT, de Campos TMP, Marinho FAM (eds.), Unsaturated soils. Proceedings of the 3rd international conference on unsaturated soils, UNSAT 2002, 10-13 March 2002, Recife (Brazil). Swets & Zeitlinger Publishers, Lisse, The Netherlands. Vol 1, pp 405–410.
Sorbino G, Sica C, Cascini L, Cuomo S (2007) On the forecasting of flowslides triggering areas using physically based models. In: Schaefer VR, Schuster RL, Turner AK (eds.), Proc. First North American Landslide Conference, 3-8 June 2007 Vail, Colorado (USA), AEG Special Publication 23, ISBN: 978-0-975-4295-3-2. pp 305–315.
Sorbino G, Sica C, Cascini L (2010) Susceptibility analysis of shallow landslides source areas using physically based models. Natural hazards 53(2): 313–332. DOI: 10.1007/ s11069-009-9431-y
Tang WJ, Liu HH, Liu BY (2013) Effects of gully erosion and gully filling on soil degradation in the black soil region of Northeast China. Journal of Mountain Science 10(5): 913–922. DOI: 10.1007 11629-013-2560-5.
Terranova O, Antronico L, Coscarelli R, et al. (2009) Soil erosion risk scenarios in the Mediterranean environment using RUSLE and GIS: an application model for Calabria (southern Italy). Geomorphology 112(3): 228–245. DOI: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2009.06.009
Tessitore S, Di Martire D, Martino R, Calcaterra D (2011) Comparison of 2D models for the simulation of the October 1954 debris flow and flood event at Maiori (Campania region, Italy). Italian Journal of Engineering Geology and Environment 1: 513–522. DOI: 10.4408/IJEGE.2011-03.B-057.
Toy TJ, Foster GR, Renard KG (2002) Soil Erosion: Process, Prediction, Measure and Control. John Wiley and Sons, Inc. New York, USA. p 338.
Tranfaglia G, Braca G (2004) Analisi idrologica e meteorologica dell’evento alluvionale del 25-26 Ottobre 1954: confronto con le serie storiche e valutazione del periodo di ritorno di eventi analoghi. (Hydrological analysis of the 25th-26th October 1954 rainstorm: comparison of the hystorical series and the return periods of similar events). Pubblicazione GNDCI n. 2870, ISBN 88-88885-03-X. pp 295–348. (In Italian)
Zhang J, Jiao JJ, Yang J (2000) In situ infiltration studies at a hillside in Hubei Province, China. Engineering Geology 57: 31–38. DOI: 10.1016/S0013-7952(99)00126-X
Wischmeier WH (1959) A rainfall erosion index for a universal soil loss equation. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 23(3): 246–249. DOI: 10.2136/sssaj1959.036159950023000 30027x
Wischmeier WH, Smith DD (1978) Predicting Soil Erosion Losses: A Guide to Conservation Planning. USDA Agricultural Handbook No. 537. p 58.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
http://orcid.org/0000-0001-8024-0319
http://orcid.org/0000-0003-2772-5020
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cuomo, S., Della Sala, M. Large-area analysis of soil erosion and landslides induced by rainfall: A case of unsaturated shallow deposits. J. Mt. Sci. 12, 783–796 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-014-3242-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-014-3242-7