Summary
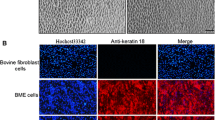
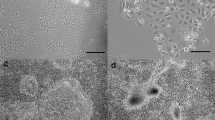
We have established and partially characterized a spontaneously immortalized bovine mammary epithelial cell line, designated HH2a. The cells express the gene encoding for mammary derived growth inhibitor (MDGI) when grown on released collagen gels in the presence of lactogenic hormones. This is the first report of a cell line that expresses MDGI. Immunohistochemical studies showed that HH2a cells contain keratin intermediate filaments and desmosomes. When plated on confluent monolayer of live fibroblasts, HH2a cells extensively contacted with fibroblasts. When embedded in the collagen gels, they rearranged themselves to produce three-dimensional duct-like outgrowths extending into the matrix. The HH2a cell line should be useful in investigations of the roles of cell-cell and cell-extracellular interactions in regulation of breast epithelial cell proliferation, and of the hormonal regulation of MDGI gene expression.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, L. W.; Danielson, K. D.; Hosick, H. Epithelial cell line and subline established from premalignant mouse mammary tissue. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. 15:841–843; 1979.
Ball, R. K.; Friis, R. R.; Schoenenberger, C. A., et al. Prolactin regulation ofβ-casein gene expression and of a cytosolic 120 kDa protein in a cloned mouse mammary epithelial cell line. EMBO J. 7:2089–2095; 1988.
Binas, B.; Spitzer, E.; Zschiesche, W., et al. Hormonal induction of functional differentiation and mammary derived growth inhibitor expression in cultured mouse mammary gland explants. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. 28A:625–634; 1992.
Bohmer, F. D.; Kraft, R.; Otto, A., et al. Identification of a polypeptide growth inhibitor from bovine mammary gland. J. Biol. Chem. 262:15137–15143; 1987.
Bohmer, F. D.; Lehmann, W.; Noll, F., et al. Specific neutralizing antiserum against a polypeptide growth inhibitor for mammary cells purified from bovine mammary gland. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 846:145–154; 1985.
Bohmer, F.; Lehman, W.; Schmidt, H. E.; et al. Purification of a growth inhibitor for ehrlich ascites mammary carcinoma cells from bovine mammary gland. Exp. Cell. Res. 150:466–476; 1984.
Bohmer, F. D.; Sun, Q.; Pepperle, M., et al. Antibodies against mammary derived growth inhibitor (MDGI) react with a fibroblast growth inhibitor and with heart fatty acid binding protein. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 148:1425–1431; 1987.
Brandt, R.; Pepperle, M.; Otto, A., et al. A 13-kilodalton protein purified from milk fat globule membranes is closely related to a mammary-derived growth inhibitor. Biochem. 27:1420–1425; 1988.
Burwen, S. J.; Pitelka, D. Secretory function of lactating mouse mammary epithelial cells culture on collagen gels. Exp. Cell. Res. 126:249–262; 1980.
Campbell, S. M.; Taka, M. M.; Medina, D., et al. A clonal derivative of mammary epithelial cell line COMA-D retains stem cell characteristics of unique morphological and functional heterogeneity. Exp. Cell. Res. 177:109–121; 1988.
Danielson, K. G.; Oborn, C. J.; Durban, E. M., et al. Epithelial mouse mammary cell line exhibiting normal morphogenesis in vivo and functional differentiation in vitro. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 81:3756–3760; 1984.
Degen, J. L.; Neubauer, M. G.; Degen, S. J. F., et al. Regulation of protein synthesis in mitogen-activated bovine lymphocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 258:12153–12162; 1983.
Emerman, J. T.; Pitelka, D. R. Maintenance and induction of morphological differentiation in dissociated mammary epithelia on floating collagen membranes. In Vitro 13:316–328; 1977.
Ghosh, S. K.; Roholt, O. A.; Kim, U. Establishment of two non-metastasizing and one metastasizing rat mammary carcinoma cell lines. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. 19:919–927; 1993.
Hall, H. G.; Farson, D. A.; Bissell, M. J. Lumen formation by epithelial cell lines in response to collagen overlay: a morphogenetic model in culture. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 79:4672–4676; 1982.
Haslam, S. Z. Cell to cell interaction and normal mammary gland function. J. Dairy Sci. 108:1127–1138; 1988.
Howard, D. K.; Schlom, J.; Fisher, P. B. Chemical carcinogen-mouse mammary tumor virus interactions in cell transformation. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. 19:58–65; 1983.
Huynh, T. H.; Robitaille, G.; Turner, J. D. Established of bovine mammary epithelial cell line (MAC-T): an in vitro model for bovine lactation. Exp. Cell. Res. 197:191–199; 1991.
Kurtz, A.; Vogel, F.; Funa, K., et al. Developmental regulation of mammary-derived growth inhibitor expression in bovine mammary tissue. J. Cell. Biol. 110:1779–1789; 1990.
Lee, E. Y. H.; Lee, W.; Keatzel, C. S., et al. Interaction of mouse epithelial cells with collagen substrata: regulation of casein gene expression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 82:1419–1423; 1985.
Li, M. L.; Aggeler, J.; Farson, D. A., et al. Influence of a reconstituted basement membrane and its components in casein gene expression and secretion in mouse mammary epithelial cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 84:136–140; 1987.
Maniatis, T.; Fritsch, E. F.; Shambrook, J. Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor, NY: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; 1982.
Medina, D. Breast cancer. Vol. 2. New York: Plenum; 1978:47–102.
Medina, D.; Oborn, C. J.; Kittrell, F. S., et al. Properties mouse mammary epithelial cell lines characterized by in vivo transplantation and in vitro immunocytochemical methods. JNCI 76:1143–1151; 1986.
Michalopoulos, G.; Pitot, H. C. Primary culture of parenchymal liver cells on collagen membranes. Exp. Cell. Res. 94:70–78; 1975.
Muller, T.; Kurtz, A.; Vogel, F., et al. A mammary-derived growth inhibitor (MDGI) related 70 kDa antigen identified in nuclei of mammary epithelial cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 138:415–423; 1989.
Reichmann, E.; Ball, R.; Groner, B., et al. New mammary epithelial and fibroblastic cell clones in coculture form structures competent to differentiate functionally. J. Cell. Biol. 108:1127–1138; 1989.
Schmid, E.; Franke, W. W.; Grund, C., et al. An epithelial cell line with elongated myoid morphology derived from bovine mammary gland. Exp. Cell. Res. 146:309–328; 1983.
Schmid, E.; Schiller, D. L.; Grund, C., et al. Tissue type-specific expression of intermediate filament proteins in a cultured epithelial cell line from bovine mammary gland. J. Cell. Biol. 96:37–50; 1983.
Sugahara, K.; Caldwell, J. H.; Mason, R. Electrical currents flow out of domes formed by cultured epithelial cells. J. Cell. Biol. 99:1541–1546; 1984.
Van Deurs, B.; Zou, Z. Z.; Briand, P., et al. Epithelial membrane polarity: a stable, differentiated feature of an established human breast carcinoma cell line MCF-7. J. Histochem. 35:461–469; 1987.
Wicha, M. S.; Lowrie, G.; Kohn, E., et al. Extracellular matrix promotes mammary epithelial growth and differentiation in vitro. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 79:3213–3217; 1982.
Yang, J.; Richards, J.; Bowman, P., et al. Sustained growth and three-dimensional organization of primary mammary tumour epithelial cells embedded in collagen gels. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 76:3401–3405; 1979.
Yang, J.; Richards, J.; Guzman, R., et al. Sustained growth in primary culture of normal mammary epithelial cells embedded in collagen gels. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 77:2088–2092; 1980.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huynh, H., Pollak, M. HH2A, an immortalized bovine mammary epithelial cell line, expresses the gene encoding mammary derived growth inhibitor (MDGI). In Vitro Cell Dev Biol - Animal 31, 25–29 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02631334
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02631334